Sales
Net sales are operating revenues earned by a company for selling its products or rendering its services. Also referred to as revenue, they are reported directly on the income statement as Sales or Net sales.
For financial ratios that use income statement sales values, "sales" refers to net sales, not gross sales. Sales are the unique transactions that occur in professional selling or during marketing initiatives.
The term sales in a marketing, advertising or a general business context often refers to a contract in which a buyer has agreed to purchase some products at a set time in the future. "Outstanding orders" refers to sales orders that have not been filled.
A sale is a transfer of property for money or credit. In double-entry bookkeeping, a sale of merchandise is recorded in the general journal as a debit to cash or accounts receivable and a credit to the sales account. A discount from list price might be noted if it applies to the sale (discount expense debit).
Fees for services are recorded separately from sales of merchandise, but the bookkeeping transactions for recording sales of services are similar to those for recording sales of tangible goods.
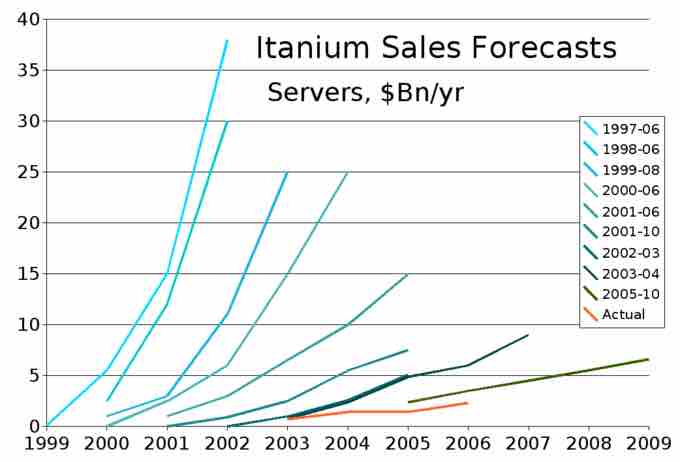
Sales Forecasting
An example of sales forecasting for a company over a decade.
Forecasting: Gross Sales and Net Sales
Net sales = Gross sales - (Customer discounts, returns, allowances)
Gross sales are the sum of all sales during a time period. Net sales are gross sales minus sales returns, sales allowances, and sales discounts. Gross sales do not normally appear on an income statement. The sales figures reported on an income statement are net sales.
- sales returns are refunds to customers for returned merchandise/credit notes
- debit notes
- sales journal entries non-current, current batch-processed transactions, predictive analytics in strategic management/administration/governance research metaframeworks
- sales allowances are reductions in sales price for merchandise with minor defects, the allowance agreed upon after the customer has purchased the merchandise
- sales discounts allowed are reduced payments from the customer based on invoice payment terms such as 2/10, n/30 (2% discount if paid within 10 days, net invoice total due in 30 days)
- interest received for amounts in arrears
- includes/excludes amounts capital goods & services, non-capital goods & services, input valued-added tax, with cost of non-capital goods sold
- input vat - output vat
- sales of portfolio items and capital gains taxes
- Sales Returns and Allowances and Sales Discounts are contra-revenue accounts
Sales Forecasting
In launching a program, managers often start with an idea of the dollar profit they desire and ask what sales levels will be required to reach it. Target volume is the unit sales quantity required to meet an earnings goal. Target revenue is the corresponding figure for dollar sales. Both of these metrics can be viewed as extensions of break-even analysis. Increasingly, marketers are expected to generate volumes that meet the target profits of their firm. This will often require them to revise sales targets as prices and costs change.
- Target volume: the volume of sales necessary to generate the profits specified in a company's plans.
- Target Volume = [Fixed costs + Target Profits] / Contribution per Unit
- The formula for target volume will be familiar to those who have performed break-even analysis. The only change is to add the required profit target to the fixed costs. From another perspective, the break-even volume equation can be viewed as a special case of the general target volume calculation — one in which the profit target is zero, and a company seeks only to cover its fixed costs.
- In target volume calculations, the company broadens this objective to solve for a desired profit.
- Target Revenue = Target Volume * Selling Price per Unit; or
- Target Revenue = 100 * [ { Fixed Costs + Target Profits } / Contribution Margin ]
The purpose of profit-based sales target metrics is to ensure that marketing and sales objectives mesh with profit targets. In target volume and target revenue calculations, managers go beyond break-even analysis (the point at which a company sells enough to cover its fixed costs) to determine the level of unit sales or revenues needed not only to cover a firm's costs but also to attain its profit targets.