Pro Forma Financial Statements
In business, pro forma financial statements are prepared in advance of a planned transaction, such as a merger, an acquisition, a new capital investment, or a change in capital structure such as incurrence of new debt or issuance of equity. The pro forma models the anticipated results of the transaction, with particular emphasis on the projected cash flows, net revenues and (for taxable entities) taxes. Consequently, pro forma statements summarize the projected future status of a company, based on the current financial statements. For example, when a transaction with a material effect on a company's financial condition is contemplated, the Finance Department will prepare, for management and Board review, a business plan containing pro forma financial statements demonstrating the expected effect of the proposed transaction on the company's financial viability.
Pro Forma Balance Sheet
If applicable to the business, summary values for the following items should be included in the pro forma balance sheet :
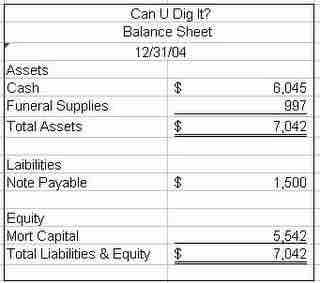
Balance Sheet
Simple balance sheet including basic items
- Assets
- Current assets
- Cash and cash equivalents
- Accounts receivable
- Inventories
- Prepaid expenses for future services that will be used within a year
- Non-current assets (Fixed assets)
- Property, plant and equipment
- Investment property, such as real estate held for investment purposes
- Intangible assets
- Financial assets (excluding investments accounted for using the equity method, accounts receivables, and cash and cash equivalents)
- Investments accounted for using the equity method
- Biological assets, which are living plants or animals. Bearer biological assets are plants or animals which bear agricultural produce for harvest, such as apple trees grown to produce apples and sheep raised to produce wool.
- Liabilities
- Accounts payable
- Provisions for warranties or court decisions
- Financial liabilities (excluding provisions and accounts payable), such as promissory notes and corporate bonds
- Liabilities and assets for current tax
- Deferred tax liabilities and deferred tax assets
- Unearned revenue for services paid for by customers, but not yet provided
- Equity
- The net assets shown by the balance sheet equals the third part of the balance sheet, which is known as the shareholders' equity. It comprises:
- Issued capital and reserves attributable to equity holders of the parent company (controlling interest)
- Non-controlling interest in equity
- Formally, shareholders' equity is part of the company's liabilities: they are funds "owing" to shareholders (after payment of all other liabilities). Usually, however, "liabilities" is used in the more restrictive sense of liabilities excluding shareholders' equity. The balance of assets and liabilities (including shareholders' equity) is not a coincidence. Records of the values of each account in the balance sheet are maintained using a system of accounting known as double-entry bookkeeping. In this sense, shareholders' equity by construction must equal assets minus liabilities, and are a residual.
- Regarding the items in equity section, the following disclosures are required:
- Numbers of shares authorized, issued and fully paid, and issued but not fully paid
- Par value of shares
- Reconciliation of shares outstanding at the beginning and the end of the period
- Description of rights, preferences, and restrictions of shares
- Treasury shares, including shares held by subsidiaries and associates
- Shares reserved for issuance under options and contracts
- A description of the nature and purpose of each reserve within owners' equity
Lenders and investors will require such statements to structure or confirm compliance with debt covenants such as debt service reserve coverage and debt to equity ratios. Similarly, when a new corporation is envisioned, its founders will prepare pro forma financial statements for the information of prospective investors. Pro forma figures should be clearly labeled as such and the reason for any deviation from reported past figures clearly explained.