Chapter 9
Production
By Boundless

The production function relates the maximum amount of output that can be obtained from a given number of inputs.
The law of diminishing returns states that adding more of one factor of production will at some point yield lower per-unit returns.

In the basic production function, inputs are typically capital and labor and output is whatever good the firm produces.
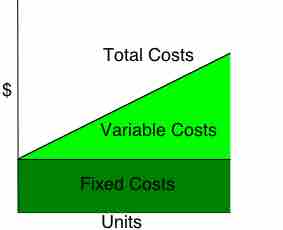
Variable costs change according to the quantity of goods produced; fixed costs are independent of the quantity of goods being produced.
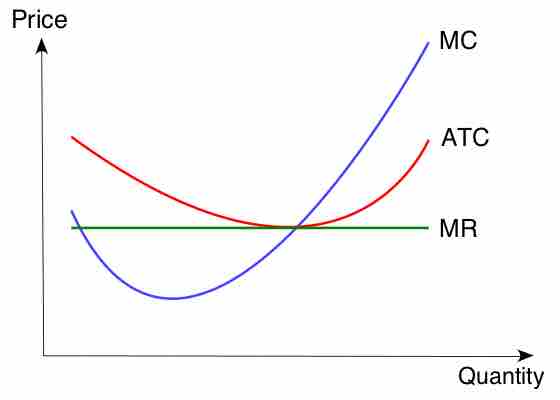
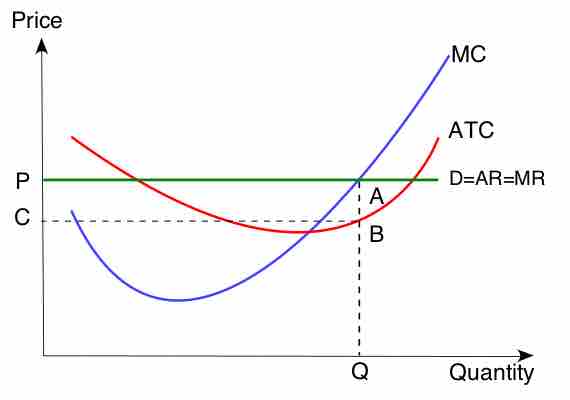
Marginal cost is the change in total cost when another unit is produced; average cost is the total cost divided by the number of goods produced.
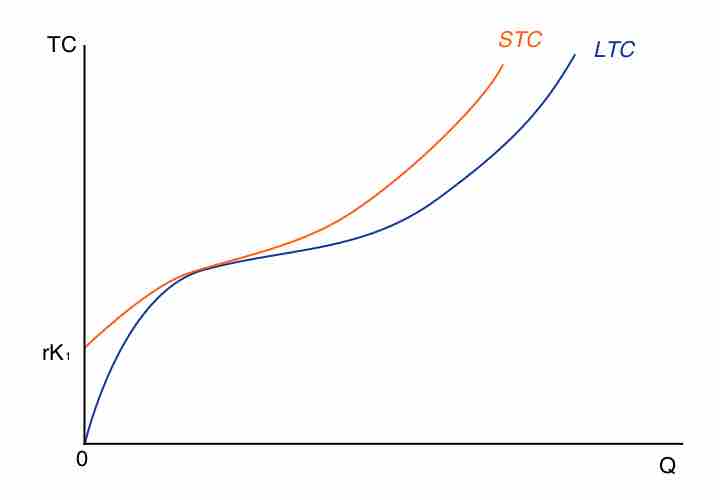
Long run costs have no fixed factors of production, while short run costs have fixed factors and variables that impact production.
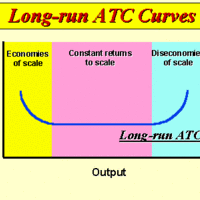
Increasing, constant, and diminishing returns to scale describe how quickly output rises as inputs increase.
The economic cost is based on the cost of the alternative chosen and the benefit that the best alternative would have provided if chosen.
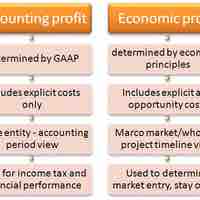
Economic profit consists of revenue minus implicit (opportunity) and explicit (monetary) costs; accounting profit consists of revenue minus explicit costs.
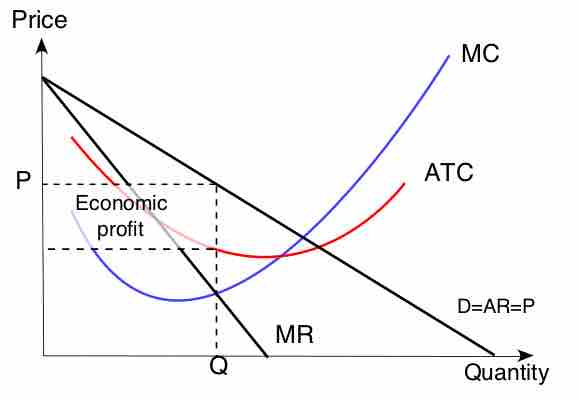
Whether economic profit exists or not depends how competitive the market is, and the time horizon that is being considered.