Section 3
Monopoly Production and Pricing Decisions and Profit Outcome
Book
Version 3
By Boundless
By Boundless
Boundless Economics
Economics
by Boundless
5 concepts

Market Differences Between Monopoly and Perfect Competition
Monopolies, as opposed to perfectly competitive markets, have high barriers to entry and a single producer that acts as a price maker.
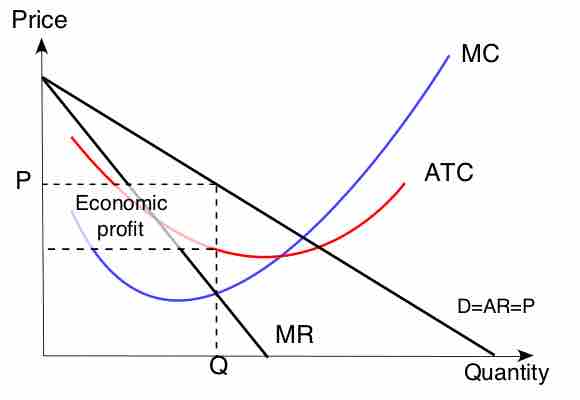
Marginal Revenue and Marginal Cost Relationship for Monopoly Production
For monopolies, marginal cost curves are upward sloping and marginal revenues are downward sloping.
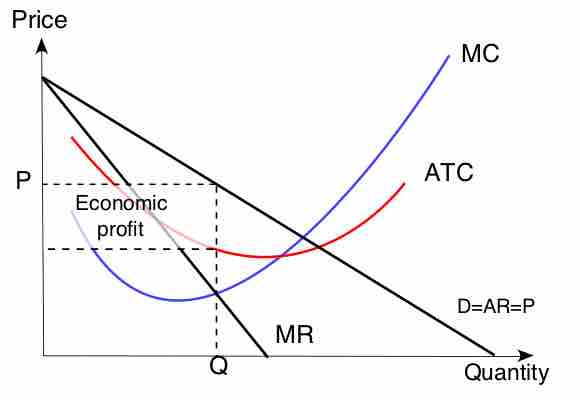
Profit Maximization Function for Monopolies
Monopolies set marginal cost equal to marginal revenue in order to maximize profit.
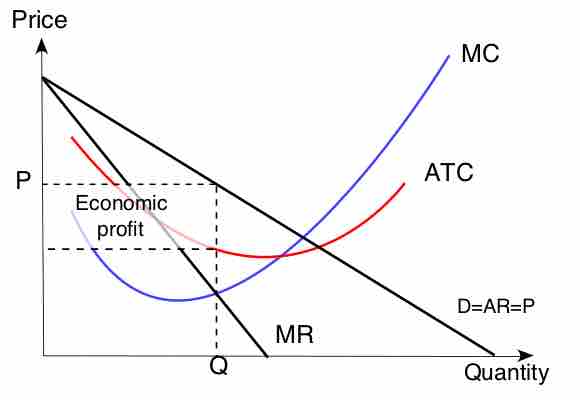
Monopoly Production Decision
To maximize output, monopolies produce the quantity at which marginal supply is equal to marginal cost.
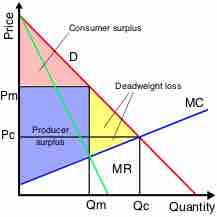
Monopoly Price and Profit
Monopolies can influence a good's price by changing output levels, which allows them to make an economic profit.