Gross domestic product (GDP) is defined as the sum of all goods and services that are produced within a nation's borders over a specific time interval, typically one calendar year.
Components of GDP
GDP (Y) is a sum of Consumption (C), Investment (I), Government Spending (G) and Net Exports (X – M):
()
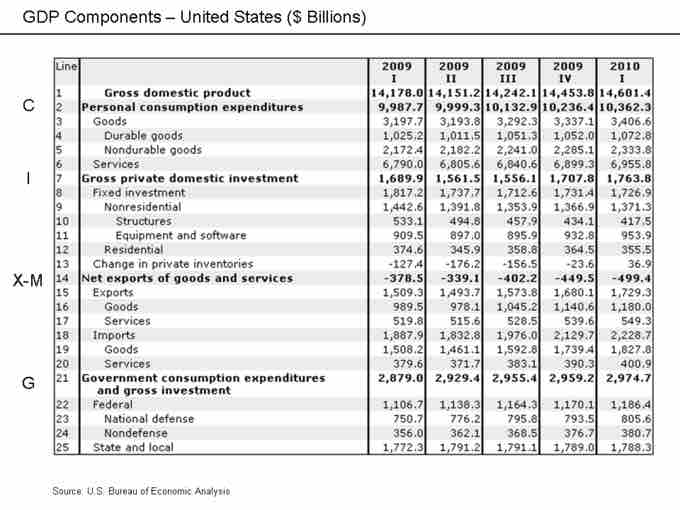
Expenditure accounts
Components of the expenditure approach to calculating GDP as presented in the National Income Accounts (U.S. Bureau of Economic Analysis).
Defining the components
Consumption
Consumption (C) is normally the largest GDP component in the economy, consisting of private (household final consumption expenditure) in the economy. These personal expenditures fall under one of the following categories: durable goods, non-durable goods, and services. Examples include food, rent, jewelry, gasoline, and medical expenses but does not include the purchase of new housing. Also, it is important to note that goods such as hand-knit sweaters are not counted as part of GDP if they are gifted and not sold. Only expenditure based consumption is counted.
Investment
Investment (I) includes, for instance, business investment in equipment, but does not include exchanges of existing assets. Examples include construction of a new mine, purchase of software, or purchase of machinery and equipment for a factory. Spending by households (not government) on new houses is also included in Investment. In contrast to common usage, 'Investment' in GDP does not mean purchases of financial products. Buying financial products is classified as 'saving', as opposed to investment. This avoids double-counting: if one buys shares in a company, and the company uses the money received to buy plant, equipment, etc., the amount will be counted toward GDP when the company spends the money on those things. To count it when one gives it to the company would be to count two times an amount that only corresponds to one group of products. Note that buying bonds or stocks is a swapping of deeds, a transfer of claims on future production, not directly an expenditure on products.
Government Spending
Government spending (G) is the sum of government expenditures on final goods and services. It includes salaries of public servants, purchase of weapons for the military, and any investment expenditure by a government. It does not include any transfer payments, such as social security or unemployment benefits.
Net Exports
Exports (X) represents gross exports. GDP captures the amount a country produces, including goods and services produced for other nations' consumption, therefore exports are added.
Imports (M) represents gross imports. Imports are subtracted since imported goods will be included in the terms G, I, or C, and must be deducted to avoid counting foreign supply as domestic.
Sometimes, net exports is simply written as NX, but is the same thing as X-M.
Note that C, G, and I are expenditures on final goods and services; expenditures on intermediate goods and services do not count.