Chapter 18
Introduction to Macroeconomics
By Boundless
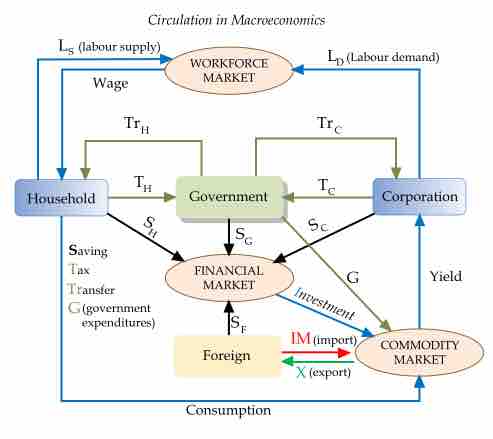
Macroeconomics is a branch of economics that focuses on the behavior and decision-making of an economy as a whole.
Money can either be consumed, invested, or saved (deferred consumption or investment).

A financial market or system is a market in which people and entities can trade financial securities, commodities, and other fungible items.
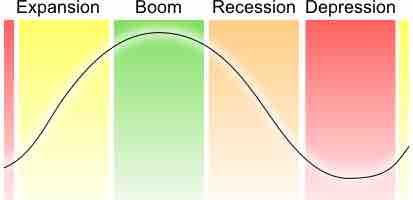
The term business cycle refers to economy-wide fluctuations in production, trade, and general economic activity.

A recession is a business cycle contraction; a general slowdown in economic activity.
When the economy is not at a steady state, the government and monetary authorities have policy mechanisms to move the economy back to consistent growth.
Long run growth is the increase in the market value of the goods and services produced by an economy over time.