Section 4
Long-Run Growth
By Boundless
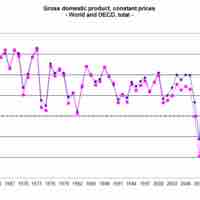
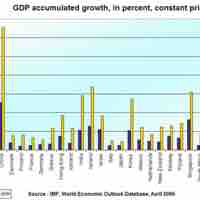
Long-run growth is defined as the sustained rise in the quantity of goods and services that an economy produces.
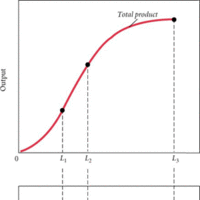
The aggregate production function examines how the productivity depends on the quantities of physical capital per worker and human capital per worker.

In economics and long-run growth, worker productivity is influenced directly by fixed capital, human capital, physical capital, and technology.
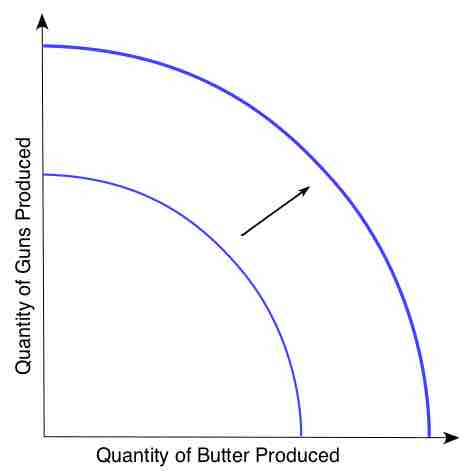
In economics, technological change is a term used to describe the change in a set of feasible production possibilities.
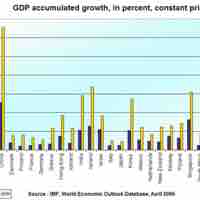
Government activity and policies have a direct impact on long-run growth. It can invest, and operate through monetary and fiscal policy.
Economic growth has the potential to make all people richer, but may have downsides such as increased inequality and environmental impacts.