Long-Run Growth
Economic growth is the increase in the market value of the goods and services that an economy produces over time. It is measured as the percentage rate change in the real gross domestic product (GDP) .
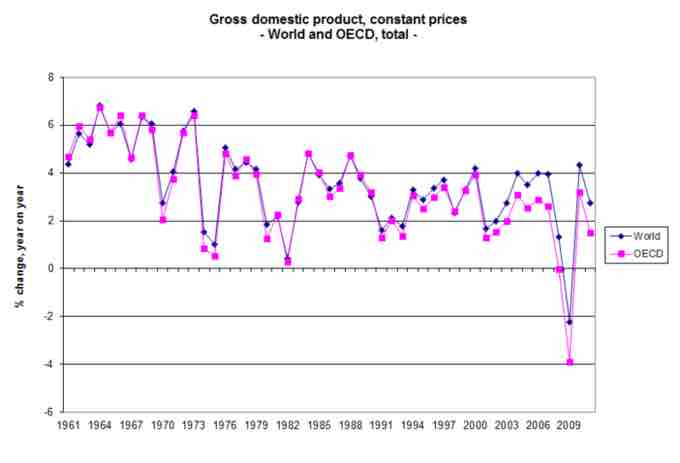
Measuring the GDP
Economic growth is the percentage rate increase in the GDP. Long-run growth is directly impacted by the GDP.
Long-run growth is defined as the sustained rise in the quantity of goods and services that an economy produces. The GDP of a country is closely tied to the growth of the population in addition to prices and supply and demand.
Determinants of Long-Run Growth
There are specific determinants that impact the long-run growth of an economy:
- Growth of productivity: is the ratio of economic outputs to inputs (capital, labor, energy, materials, and services). When the productivity increases the cost of goods is lowered. Lower prices increase the demand for the product or service. An increase in demand can lead to higher revenue.
- Demographic changes: demographic factors influence economic growth by changing the employment to population ratio. Factors include the quantity and quality of available natural resources. Age structure of the population also influences employment and long-run growth.
- Labor force participation: the amount of labor force participation and the size of economic sectors influence economic growth. The labor force participation is the amount of workers available. In countries with high development and industrialization, labor force participation is high because of low birth and death rates.
Inflation and Excessive Growth
When the economic growth matches the growth of money supply, an economy will continue to grow and thrive. In this case, population growth would increase, but the need for goods and services would also increase. As a result, more jobs would be available and the employment rate would also increase.
However, when economic growth is not balanced, the result can include inflation and excessive growth. Inflation occurs when the price of goods and services are rising which causes purchasing power to fall if wages don't also rise . A decrease in the demand for goods and services will lead to a decrease in revenue and employment. A high rate of population growth will cause less capital per worker, lower productivity, and lower GDP growth.
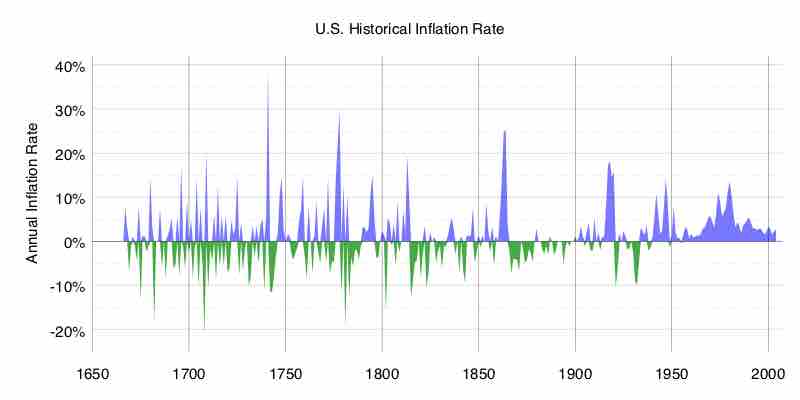
Inflation
Inflation occurs when the price of goods and services are rising which causes purchasing power to fall if wages don't also rise. Inflation is a negative effect of economic growth that is not balanced.
When the GDP growth is only caused by increases in population (not increases in supply, demand, revenue) the growth is excessive. In order for an economy to be successful, it must meet the needs of the population (supply, demand, revenue, and employment). When a population grows too fast the economic system cannot support the changes. Excessive growth leads to an imbalance in supply and demand and higher levels of unemployment. The quality of living decreases when the economy cannot support the population growth.