Behavioral economics is the study of the effects of social, cognitive, and emotional factors on the economic decisions of individuals and institutions. It also studies the consequences for market prices, returns, and resource allocation. Behavioral economics focuses on the bounds of rationality of economic agents.
Characteristics
Behavioral economics has specific characteristics based on what is studied. Areas of focus include:
- Behavioral finance: the intent is to explain why market participants make systematic errors. Errors impact prices and returns which the create market inefficiencies. It also looks at how other participants take advantage of market inefficiencies.
- Financial models: some financial models used in money management incorporate behavioral financial parameters. Examples of areas studied include overreaction and irrational purchasing habits.
- Behavioral game theory: analyzes interactive strategic decisions and behavior using the methods of game theory, experimental economics, and experimental psychology. Studies interactive learning, social preferences, altruism, framing, and fairness.
There are many aspects in behavioral economics, and three of the most prevalent are:
- Heuristics: people make decisions based on approximate rules and not strict logic.
- Framing: using a collection of anecdotes and stereotypes that make up the mental and emotional filters that individuals rely on the understand and respond to events.
- Market inefficiencies: include the study non-rational decision making and incorrect pricing.
Behavioral economics focuses on the study of how and why individuals and institutions make economic decisions .
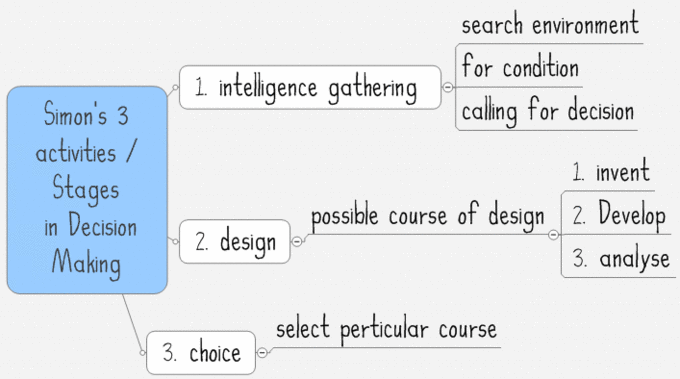
Decision making
This graph shows the three stages of rational decision making that was devised by Herbert Simon, a notable economist and scientist.
History
Behavioral economics was born out of the combination of economics and psychology. By 1979, economists used cognitive psychology to explain economic decision making, which included an editing stage and an evaluation stage. The editing stage simplified risky situations using heuristics of choice. The evaluation stage evaluated risky alternatives through the study of dependence, loss aversion, non-linear probability weighting, and sensitivity to gains and losses. Throughout its history, behavioral economics has studied the economic choices of individuals and institutions by analyzing psychology against economic research. The study of behavioral economics shows both the strengths and weaknesses in decision making tendencies and how the decisions impact economic choices.