Freezing point depression is the phenomena that describes why adding a solute to a solvent results in the lowering of the freezing point of the solvent. When a substance starts to freeze, the molecules slow down due to the decreases in temperature, and the intermolecular forces start to take over. The molecules will then arrange themselves in a pattern, and thus turn into a solid. For example, as water is cooled to the freezing point, its molecules become slower and hydrogen bonds begin to "stick" more, eventually creating a solid. If salt is added to the water, the Na+ and Cl- ions attract to the water molecules and interfere with the formation of the large network solid known as ice. In order to achieve a solid, the solution must be cooled to an even lower temperature.
The freezing point depression can also be explained in terms of vapor pressure. Adding solute to a solvent will essentially dilute the solvent molecules, and according to Raoult's law, this leads to a decrease in vapor pressure. Considering the fact that the vapor pressure of the solid and liquid forms must be the same at freezing point, because otherwise the system would not be at equilibrium, the lowering of the vapor pressure leads to the lowering of the temperature at which the vapor pressures of the liquid and frozen forms of the solution will be equal.
Effect of solutes on physical properties
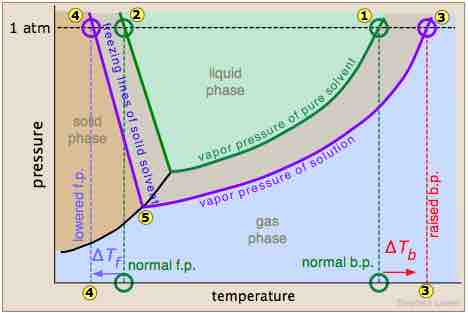
A triple phase diagram which shows the pressure and temperature of the normal boiling and freezing points of a solvent (green lines) and the boiling and freezing points of a solution (purple lines). Notice that at 1 atm of pressure, the freezing point has been lowered (represented by numbers 2 and 4).
The freezing point depression can be calculated by the formula:
In this equation,
Example
What is the freezing point of an aqueous solution when enough NaCl has been added to create a 0.25 m solution? The Kf value for water is 1.858 oC/m.
To solve this, you must remember that NaCl breaks into two ions, Na+ and Cl-, when it dissolves in water. In simplest terms, this means it has an "i" factor of 2.
This might seem like the end of the problem, but it is not. The value of 0.93 oC is the change in the freezing point. The new freezing point of water, which is normally 0 oC, is equal to: 0 - 0.93 = -0.93 oC.