Colligative Properties and Boiling Point Elevation
There is one category of properties that can only be applied to solutions; these are known as colligative properties. Properties can be considered colligative only if they are dependent on the amount of solute present in the solution, disregarding the identity of the solute itself.
The boiling point of a solvent will increase when a solute is dissolved in it. This is referred to as boiling point elevation. The elevation of the boiling point is directly dependent on the amount of solute present in the solution, but it is not based on the identity of the solute, so it is considered a colligative property.
The Relationship Between Boiling Point Elevation and Vapor Pressure
Boiling point elevation can be explained in terms of vapor pressure. Vapor pressure is defined as the pressure exerted by a vapor in thermodynamic equilibrium with its condensed phases at a given temperature. In layman's terms, it is simply a measure of the tendency of the solution molecules to escape by entering the gas phase. A liquid boils when its vapor pressure is equal to the air pressure.
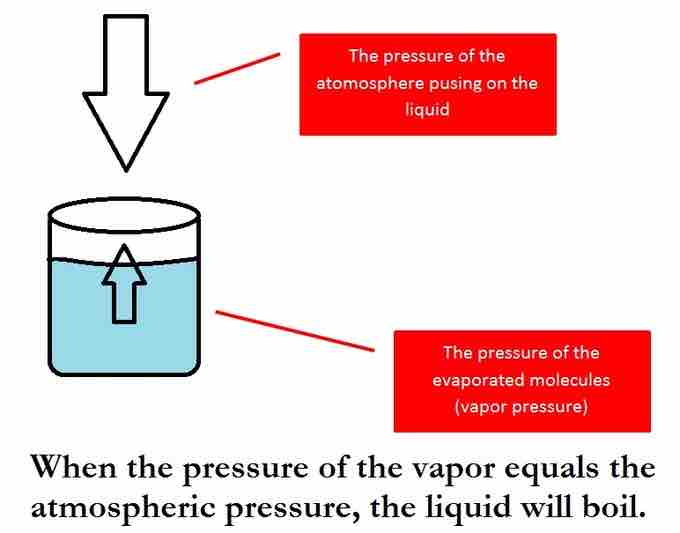
Boiling point
The boiling point of a pure liquid. When the vapor pressure of the liquid matches the atmospheric pressure, the liquid will boil.
Boiling Point Elevation
A solvent's vapor pressure will lower when a solute is added. This happens because of the displacement of solvent molecules by the solute. This means that some of the of solvent molecules at the surface of the liquid are replaced by the solute; it can occur in both electrolytic and non-electrolytic solutions. The lower number of solvent molecules at the surface means that fewer will evaporate, and thus the vapor pressure is lowered. For the vapor pressure to equal the atmospheric pressure, a higher temperature is required, and a higher boiling point is observed.
Calculating Boiling Point Elevation
The extent of the boiling point elevation can be calculated. It is directly proportional to the molal concentration of the solution. The amount the boiling point is elevated is determined using the equation:
In this equation,
Example
Calculate the boiling point of an aqueous solution where enough NaCl is added to make a 0.37 molal solution. The Kb for water is 0.512
Water normally boils at 100 oC, so the new boiling point of the solution would be 100.38 oC.