Concept
Version 9
Created by Boundless
Reactions of Aromatic Compounds
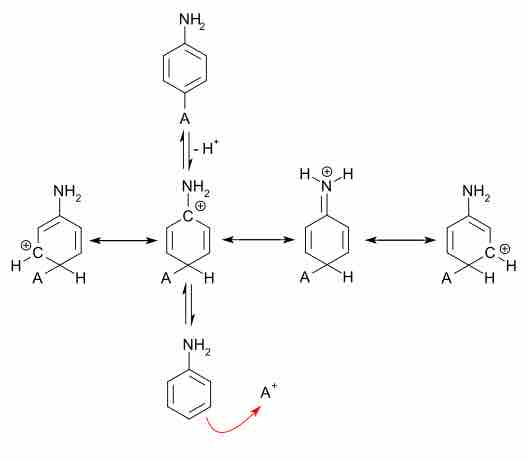
Electrophilic aromatic substitution (EAS)
This reaction mechanism takes place from bottom to top. EAS occurs ortho or para to electron donating groups, such as amines, due to the stabilization of the intermediate positive charge. The four structures drawn in the middle of the diagram are all resonance structures. Due to the electrons provided by the NH2 group, this intermediate is stabilized, and the para-substitution is favored. As an exercise, draw out the stabilization of the positive charge when ortho substitution occurs.
Source
Boundless vets and curates high-quality, openly licensed content from around the Internet. This particular resource used the following sources:
"File:EAS substitution Para director.svg - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia."
http://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=File:EAS_substitution_Para_director.svg&page=1
Wikipedia
CC BY-SA.