Hierarchical Structure of the Atom
There are four hierarchical levels that describe the position and energy of the electrons an atom has. Here they are listed along with some of the possible values (or letters) they can have:
- Principal energy levels (1, 2, 3, etc.)
- Sublevels (s, p, d, f)
- Orbitals
- Electrons
Principal energy levels are made out of sublevels, which are in turn made out of orbitals, in which electrons are found.
Atomic Orbitals
An atomic orbital is defined as the probability of finding an electron in an area around an atom's nucleus. Generally, orbital shapes are drawn to describe the region in space in which electrons are likely to be found. This is referred to as "electron density."

Atomic orbitals
The shapes of the first five atomic orbitals are shown in order: 1s, 2s, and the three 2p orbitals. Both blue and orange-shaded regions represent regions in space where electrons can be found 'belonging' to these orbitals.
Sigma Bonds
Covalent bonding occurs when two atomic orbitals come together in close proximity and their electron densities overlap. The strongest type of covalent bonds are sigma bonds, which are formed by the direct overlap of orbitals from each of the two bonded atoms. Regardless of the atomic orbital type, sigma bonds can occur as long as the orbitals directly overlap between the nuclei of the atoms.
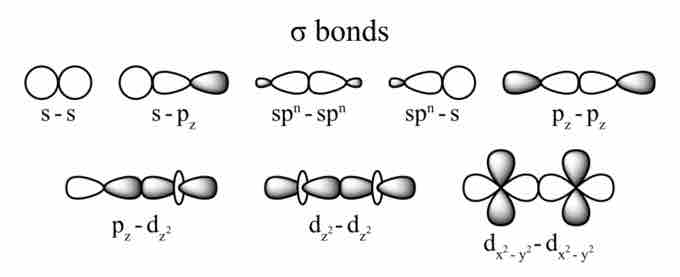
Orbital overlaps and sigma bonds
These are all possible overlaps between different types of atomic orbitals that result in the formation of a sigma bond between two atoms. Notice that the area of overlap always occurs between the nuclei of the two bonded atoms.
Single covalent bonds occur when one pair of electrons is shared between atoms as part of a molecule or compound. A single covalent bond can be represented by a single line between the two atoms. For instance, the diatomic hydrogen molecule, H2, can be written as H—H to indicate the single covalent bond between the two hydrogen atoms.
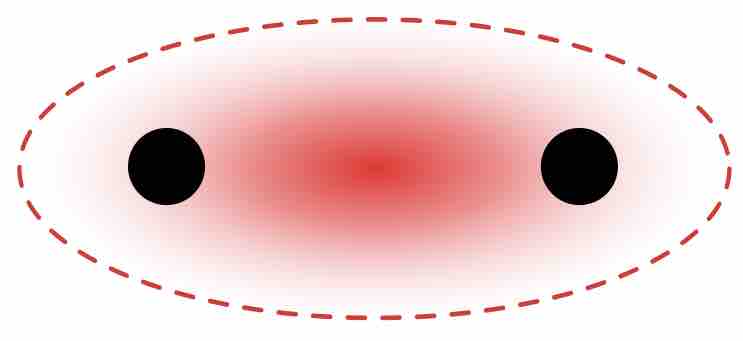
Sigma bond in the hydrogen molecule
Higher intensity of the red color indicates a greater probability of the bonding electrons being localized between the nuclei.