The second derivative, or second order derivative, is the derivative of the derivative of a function. The derivative of the function may be denoted by
Furthermore, the third derivative is the derivative of the derivative of the derivative of a function, which can be represented by
If
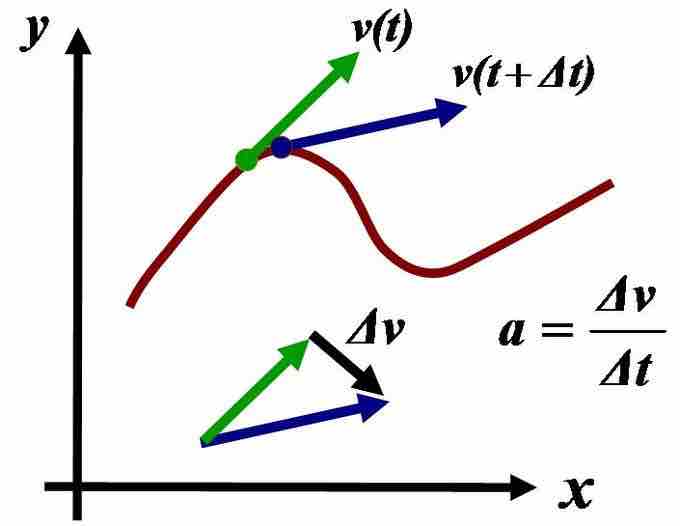
Acceleration
Acceleration is the time-rate of change of velocity, and the second-order rate of change of position.
An example of a function with higher-order derivatives is:
where the higher derivatives are found to be:
-
$f'(x) = 15x^2 + 6x - 1$ -
$f''(x) = 30x + 6$ -
$f'''(x) = 30$