Reserve requirements have long been a part of the United States banking history. Depository institutions maintain a fraction of certain liabilities in reserve in specified assets. The Federal Reserve can adjust reserve requirements by changing required reserve ratios, the liabilities to which the ratios apply, or both. Changes in reserve requirements can have profound effects on the money stock and on the cost to banks of extending credit and are also costly to administer; therefore, reserve requirements are not adjusted frequently. Nonetheless, reserve requirements play a useful role in the conduct of open market operations by helping to ensure a predictable demand for Federal Reserve balances and thus enhancing the Federal Reserve's control over the federal funds rate.
Requiring depository institutions to hold a certain fraction of their deposits in reserve, either as cash in their vaults or as non-interest-bearing balances at the Federal Reserve, does impose a cost on the private sector. The cost is equal to the amount of forgone interest on these funds—or at least on the portion of these funds that depository institutions hold only because of legal requirements and not to meet their customers' needs.
Changes in reserve requirements can affect the money stock, by altering the volume of deposits that can be supported by a given level of reserves, and bank funding costs. Unless it is accompanied by an increase in the supply of Federal Reserve balances, an increase in reserve requirements (through an increase in the required reserve ratio, for example) reduces excess reserves, induces a contraction in bank credit and deposit levels, and raises interest rates. It also pushes up bank funding costs by increasing the amount of non-interest-bearing assets that must be held in reserve. Conversely, a decrease in reserve requirements, unless accompanied by a reduction in Federal Reserve balances, initially leaves depository institutions with excess reserves, which can encourage an expansion of bank credit and deposit levels and reduce interest rates.
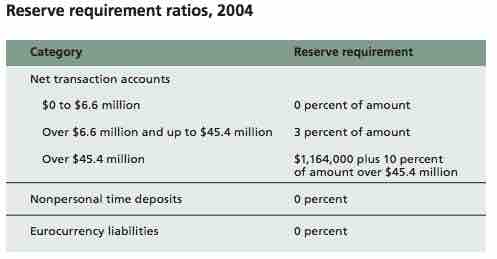
Reserve Requirement
Reserve Requirement Ratios, 2004