Chapter 15
Product and Pricing Strategies
By Boundless

Cost-based pricing involves calculating the cost of the product, and then adding a percentage mark-up to determine price.
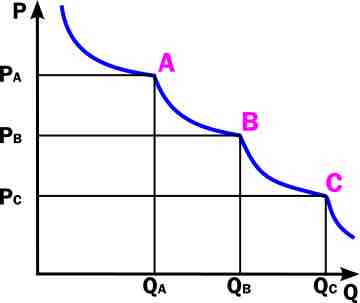
Demand-based pricing uses consumer demand (and therefore perceived value) to set a price of a good or service.
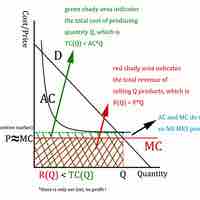
Competitive-based pricing occurs when a company sets a price for its good based on what competitors are selling a similar product for.
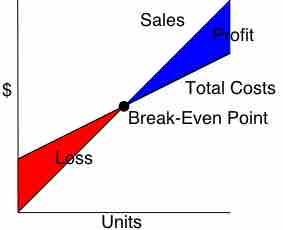
The break-even point (BEP) is the point where expenses and revenue intersect.
Firms utilize strategies such as price and promotional reduction to minimize cost, maximize revenue, and thereby optimize profits.

Return on investment (ROI) is one way of considering profits in relation to capital invested.
Market share is an indicator of how well a firm is doing against its competitors and can often be influenced through pricing.

Firms can engage in premium pricing by keeping the price of their good artificially higher than the benchmark price.
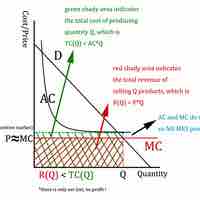
Status quo pricing is the practice of maintaining current price levels that other firms are charging.

Penetration and skimming are two strategies employed in pricing new products.

Differential pricing exists when sales of identical goods or services are transacted at different prices from the same provider.

Psychological pricing or price ending is a marketing practice based on the theory that certain prices have a psychological impact.

Product lining is the marketing strategy of offering several related products for sale as individual units.

Promotional pricing means temporarily reducing the price of an established product in order to increase interest in customers.

Price is both the money someone charges for a good or service and what the consumer is willing to give up to receive a good or service.
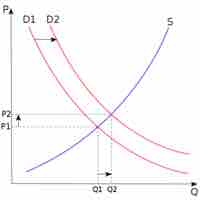
The supply and demand model states that the price of a good will be the level where the quantity demanded equals the quantity supplied.
Innovation is the creation of better, more effective products, processes, services, or technologies.
New product ideas can generate from existing frustrations using a certain product, or a desire to do something better or more simply.

Product development is idea generation, screening, business analysis, technical development, manufacturing, testing, and commercialization.

Idea screening attempts to eliminate unsound product concepts prior to devoting resources to them.
The focus of the business analysis is primarily on profits, but other considerations such as social responsibilities may also be involved.

The objective of testing is to test all the variabilites in the marketing plan, including elements of the product.

Once a product is ready to take to market, commercialization involves key decisions about distribution, promotion, and pricing.
Organizations assess the current market for new product opportunities and, when potentially profitable, develop new product prototypes to test feasibility of production.

Service products are offered by a wide variety of industries such as barbers, travel agencies, and consulting firms.

Consumer products can be classified as convenience, shopping, or specialty goods.

Business products are goods or services that are sold to other businesses rather than to end-consumers.

Products can be classified based on consumer versus industrial goods and goods versus services.
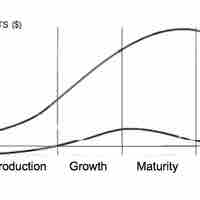
Evidence suggests that every product goes through a lifecycle with different phases of sales and profits.

A brand refers to a name, term, symbol, or any other type of feature that defines or identifies a seller's product or service.

Similar goods and services are classified in brand categories.

Good branding gives a company several advantages including establishing a positive reputation and building an image attractive to consumers.

Developing a brand successfully requires a company to analyze the characteristics and values a customer base desires.
Through effective brand management, organizations can build a loyal following of engaged consumers.

Packaging refers to the physical appearance of a product when a consumer sees it, and labels are an informative component of packaging.