Chapter 25
Seedless Plants
By Boundless

A diverse array of seedless plants still populate and thrive in the world today, particularly in moist environments.

The geologic periods of the Paleozoic are marked by changes in the plant life that inhabited the earth.
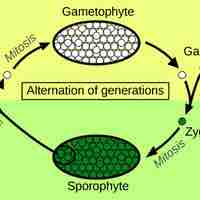
Plants adapted to the dehydrating land environment through the development of new physical structures and reproductive mechanisms.
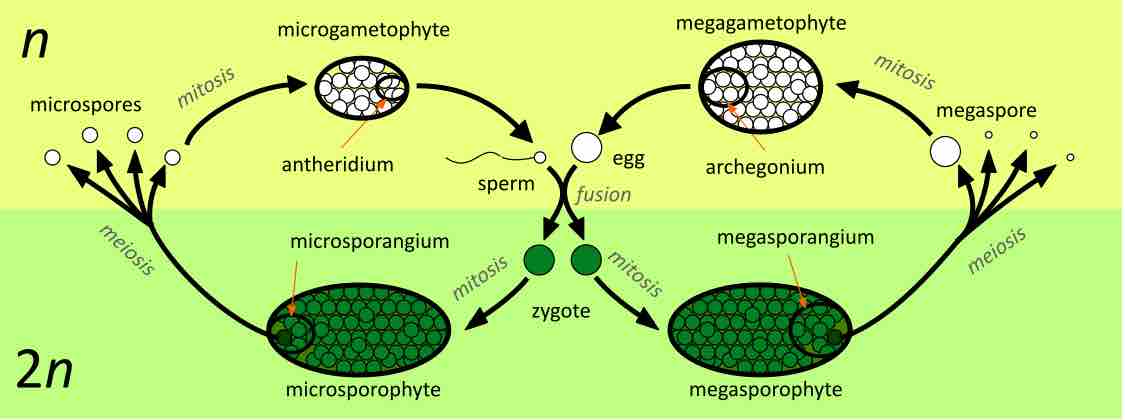
Sporophytes (2n) undergo meiosis to produce spores that develop into gametophytes (1n) which undergo mitosis.
Plants developed a series of organs and structures to facilitate life on dry land independent from a constant source of water.
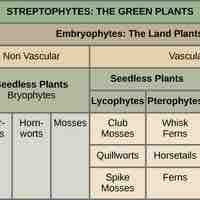
Land plants, or embryophytes, are classified by the presence or absence of vascular tissue and how they reproduce (with or without seeds).
Land plants and closely-related green algae (charophytes) are classified as Streptophytes; the remaining green algae are chlorophytes.

Algae in the order Charales live in fresh water and are often considered the closest-living relatives of embryophytes.
Bryophytes (liverworts, mosses, and hornworts) are non-vascular plants that appeared on earth over 450 million years ago.
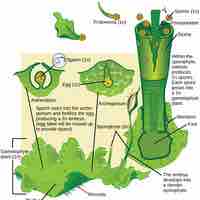
Liverworts and hornworts are both bryophytes, but aspects of their structures and development are different.
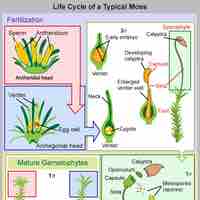
Mosses are bryophytes that live in many environments and are characterized by their short flat leaves, root-like rhizoids, and peristomes.
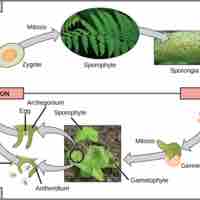
Seedless vascular plants, which reproduce and spread through spores, are plants that contain vascular tissue, but do not flower or seed.
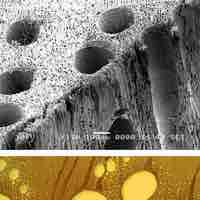
Xylem and phloem form the vascular system of plants to transport water and other substances throughout the plant.
Roots support plants by anchoring them to soil, absorbing water and minerals, and storing products of photosynthesis.

Ferns, club mosses, horsetails, and whisk ferns are seedless vascular plants that reproduce with spores and are found in moist environments.
Seedless vascular plants provide many benefits to life in ecosystems, including food and shelter and, to humans, fuel and medicine.
- Characteristics of Fungi
- Ecology of Fungi
- Classifications of Fungi
- Fungal Parasites and Pathogens
- Importance of Fungi in Human Life