Water Potential
Plants are phenomenal hydraulic engineers. Using only the basic laws of physics and the simple manipulation of potential energy, plants can move water to the top of a 116-meter-tall tree. Plants can also use hydraulics to generate enough force to split rocks and buckle sidewalks . Water potential is critical for moving water to leaves so that photosynthesis can take place.

Water potential in plants
With heights nearing 116 meters, (a) coastal redwoods (Sequoia sempervirens) are the tallest trees in the world. Plant roots can easily generate enough force to (b) buckle and break concrete sidewalks.
Water potential is a measure of the potential energy in water, or the difference in potential energy between a given water sample and pure water (at atmospheric pressure and ambient temperature). Water potential is denoted by the Greek letter ψ (psi) and is expressed in units of pressure (pressure is a form of energy) called megapascals (MPa). The potential of pure water (Ψwpure H2O) is designated a value of zero (even though pure water contains plenty of potential energy, that energy is ignored). Water potential values for the water in a plant root, stem, or leaf are, therefore, expressed in relation to Ψwpure H2O.
The water potential in plant solutions is influenced by solute concentration, pressure, gravity, and factors called matrix effects. Water potential can be broken down into its individual components using the following equation:
Ψsystem = Ψtotal = Ψs + Ψp + Ψg + Ψm
where
- Ψs = solute potential
- Ψp, = pressure potential
- Ψg, = gravity potential
- Ψm = matric potential
"System" can refer to the water potential of the soil water (Ψsoil), root water (Ψroot), stem water (Ψstem), leaf water (Ψleaf), or the water in the atmosphere (Ψatmosphere), whichever aqueous system is under consideration. As the individual components change, they raise or lower the total water potential of a system. When this happens, water moves to equilibrate, moving from the system or compartment with a higher water potential to the system or compartment with a lower water potential. This brings the difference in water potential between the two systems (Δ) back to zero (Δ = 0). Therefore, for water to move through the plant from the soil to the air (a process called transpiration), the conditions must exist as such:
Ψsoil > Ψroot > Ψstem > Ψleaf > Ψatmosphere.
Water only moves in response to Δ, not in response to the individual components. However, because the individual components influence the total Ψsystem, a plant can control water movement by manipulating the individual components (especially Ψs).
Solute Potential
Solute potential (Ψs), also called osmotic potential, is negative in a plant cell and zero in distilled water. Typical values for cell cytoplasm are –0.5 to –1.0 MPa. Solutes reduce water potential (resulting in a negative Ψw) by consuming some of the potential energy available in the water. Solute molecules can dissolve in water because water molecules can bind to them via hydrogen bonds; a hydrophobic molecule like oil, which cannot bind to water, cannot go into solution. The energy in the hydrogen bonds between solute molecules and water is no longer available to do work in the system because it is tied up in the bond. In other words, the amount of available potential energy is reduced when solutes are added to an aqueous system. Thus, Ψs decreases with increasing solute concentration. Because Ψs is one of the four components of Ψsystem or Ψtotal, a decrease in Ψs will cause a decrease in Ψtotal. The internal water potential of a plant cell is more negative than pure water because of the cytoplasm's high solute content . Because of this difference in water potential, water will move from the soil into a plant's root cells via the process of osmosis. This is why solute potential is sometimes called osmotic potential.
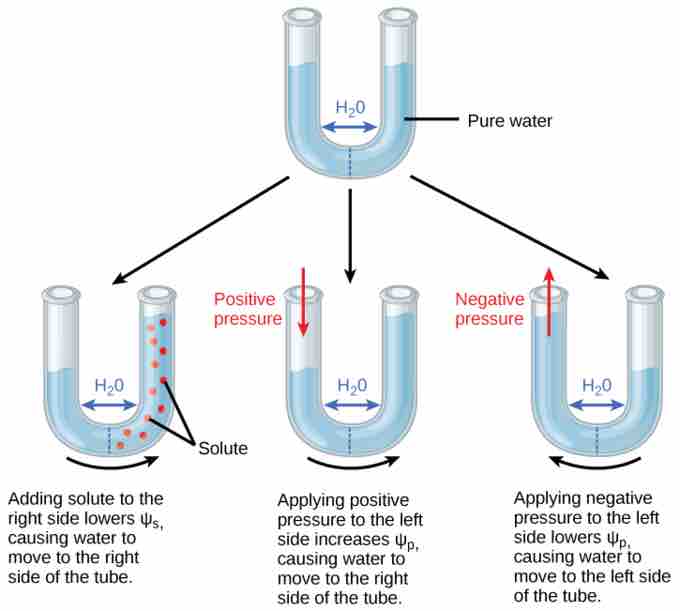
Solute potential
In this example with a semipermeable membrane between two aqueous systems, water will move from a region of higher to lower water potential until equilibrium is reached. Solutes (Ψs), pressure (Ψp), and gravity (Ψg) influence total water potential for each side of the tube (Ψtotal right or left) and, therefore, the difference between Ψtotal on each side (Δ). (Ψm , the potential due to interaction of water with solid substrates, is ignored in this example because glass is not especially hydrophilic). Water moves in response to the difference in water potential between two systems (the left and right sides of the tube).
Plant cells can metabolically manipulate Ψs (and by extension, Ψtotal) by adding or removing solute molecules. Therefore, plants have control over Ψtotal via their ability to exert metabolic control over Ψs.