Genetic Control of Flowers
Flower development is the process by which angiosperms produce a pattern of gene expression in meristems that leads to the appearance of a flower. A flower (also referred to as a bloom or blossom) is the reproductive structure found in flowering plants . There are three physiological developments that must occur in order for reproduction to take place:
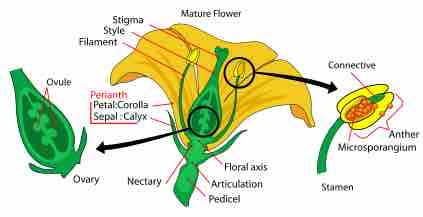
Anatomy of a flower
Mature flowers aid in reproduction for the plant. In order to achieve reproduction, the plant must become sexually mature, the apical meristem must become a floral meristem, and the flower must develop its individual reproductive organs.
- the plant must pass from sexual immaturity into a sexually mature state
- the apical meristem must transform from a vegetative meristem into a floral meristem or inflorescence
- the flowers individual organs must grow (modeled using the ABC model)
Flower Development
A flower develops on a modified shoot or axis from a determinate apical meristem (determinate meaning the axis grows to a set size). The transition to flowering is one of the major phase changes that a plant makes during its life cycle. The transition must take place at a time that is favorable for fertilization and the formation of seeds, hence ensuring maximal reproductive success. In order to flower at an appropriate time, a plant can interpret important endogenous and environmental cues such as changes in levels of plant hormones and seasonable temperature and photoperiod changes. Many perennial and most biennial plants require vernalization to flower.
Genetic Control of Flower Development
When plants recognize an opportunity to flower, signals are transmitted through florigen, which involves a variety of genes, including CONSTANS, FLOWERING LOCUS C and FLOWERING LOCUS T. Florigen is produced in the leaves in reproductively favorable conditions and acts in buds and growing tips to induce a number of different physiological and morphological changes.
From a genetic perspective, two phenotypic changes that control vegetative and floral growth are programmed in the plant. The first genetic change involves the switch from the vegetative to the floral state. If this genetic change is not functioning properly, then flowering will not occur. The second genetic event follows the commitment of the plant to form flowers. The sequential development of plant organs suggests that a genetic mechanism exists in which a series of genes are sequentially turned on and off. This switching is necessary for each whorl to obtain its final unique identity.
ABC Model of Flower Development
In the simple ABC model of floral development, three gene activities (termed A, B, and C-functions) interact to determine the developmental identities of the organ primordia (singular: primordium) within the floral meristem. The ABC model of flower development was first developed to describe the collection of genetic mechanisms that establish floral organ identity in the Rosids and the Asterids; both species have four verticils (sepals, petals, stamens and carpels), which are defined by the differential expression of a number of homeotic genes present in each verticil.
In the first floral whorl only A-genes are expressed, leading to the formation of sepals. In the second whorl both A- and B-genes are expressed, leading to the formation of petals. In the third whorl, B and C genes interact to form stamens and in the center of the flower C-genes alone give rise to carpels. For example, when there is a loss of B-gene function, mutant flowers are produced with sepals in the first whorl as usual, but also in the second whorl instead of the normal petal formation. In the third whorl the lack of B function but presence of C-function mimics the fourth whorl, leading to the formation of carpels also in the third whorl .
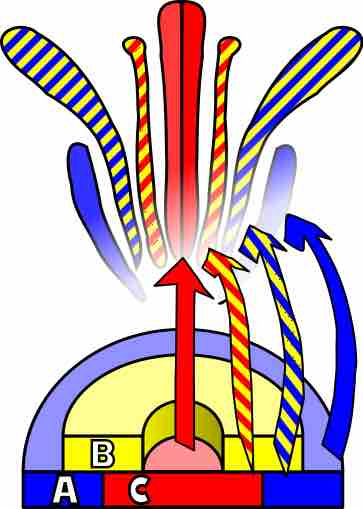
ABC model of flower development
Class A genes (blue) affect sepals and petals, class B genes (yellow) affect petals and stamens, class C genes (red) affect stamens and carpels.
Most genes central in this model belong to the MADS-box genes and are transcription factors that regulate the expression of the genes specific for each floral organ.