Mendelian Crosses
Mendel performed crosses, which involved mating two true-breeding individuals that have different traits . In the pea, which is a naturally self-pollinating plant, this is done by manually transferring pollen from the anther of a mature pea plant of one variety to the stigma of a separate mature pea plant of the second variety. In plants, pollen carries the male gametes (sperm) to the stigma, a sticky organ that traps pollen and allows the sperm to move down the pistil to the female gametes (ova) below. To prevent the pea plant that was receiving pollen from self-fertilizing and confounding his results, Mendel painstakingly removed all of the anthers from the plant's flowers before they had a chance to mature.
Mendelian Crosses
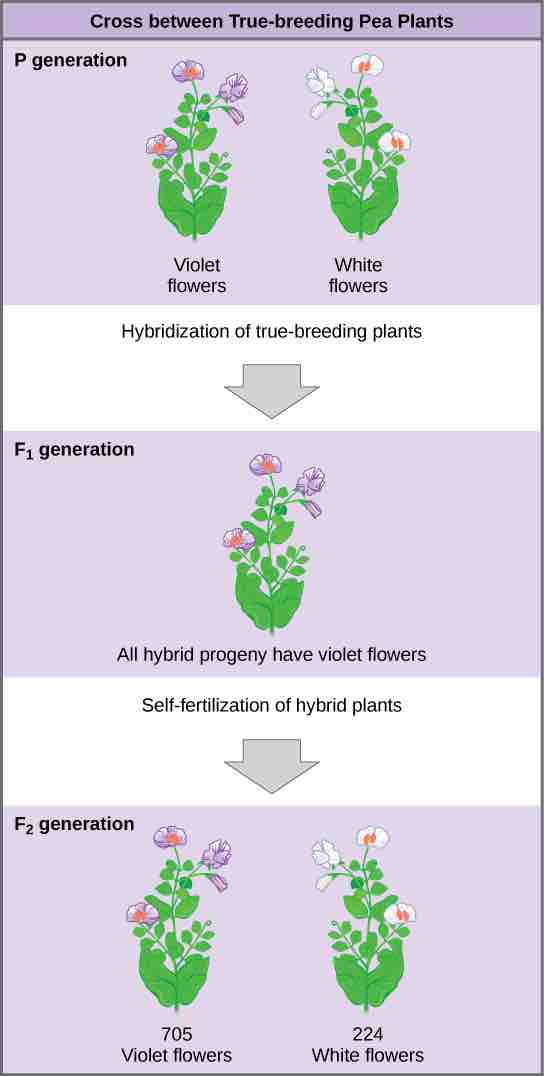
In one of his experiments on inheritance patterns, Mendel crossed plants that were true-breeding for violet flower color with plants true-breeding for white flower color (the P generation). The resulting hybrids in the F1 generation all had violet flowers. In the F2 generation, approximately three-quarters of the plants had violet flowers, while one-quarter had white flowers.
Plants used in first-generation crosses were called P0, or parental generation one, plants. Mendel collected the seeds belonging to the P0 plants that resulted from each cross and grew them the following season. These offspring were called the F1, or the first filial (filial = offspring, daughter or son), generation. Once Mendel examined the characteristics in the F1 generation of plants, he allowed them to self-fertilize naturally. He then collected and grew the seeds from the F1 plants to produce the F2, or second filial, generation. Mendel's experiments extended beyond the F2 generation to the F3 and F4 generations, and so on, but it was the ratio of characteristics in the P0−F1−F2 generations that were the most intriguing and became the basis for Mendel's postulates.