Accounts receivable are reported as a line item on the balance sheet. Supplementary reports, such as the accounts receivable aging report, provide further detail.
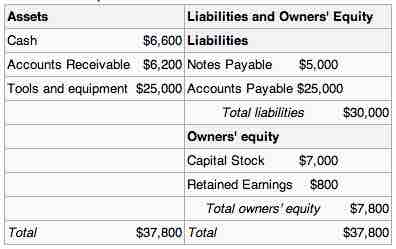
Balance sheet
Accounts receivable are a line item in a balance sheet.
The aging report, for example, shows how long invoices from each customer have been outstanding. Generally the accounts in an aging report are subdivided into categories based on how overdue the invoices are.
An accounts receivable aging report summarizes receivables based on their age—how long they have been outstanding. The accounts receivable age analysis, also known as the Debtors Book, is divided into categories for current, 30 days, 60 days, 90 days, 120 days, 150 days, 180 days, and overdue that are produced in modern accounting systems. For example, all the unpaid invoices posted in the past month are current, all the unpaid invoices from the prior month are over 30 days, the unpaid invoices from two months ago are over 60 days, etc. The aging report can help a business identify issues soon after they arise and prevent larger problems from occurring later on.