Ukulele
Did you know...
SOS Children offer a complete download of this selection for schools for use on schools intranets. SOS Children is the world's largest charity giving orphaned and abandoned children the chance of family life.
 Martin 3K Professional Ukulele |
|
| String instrument | |
|---|---|
| Classification | String instrument ( plucked, nylon stringed instrument usually played with the bare thumb and/or fingertips, or a felt pick) |
| Hornbostel–Sachs classification | 321.322 (Composite chordophone) |
| Developed | 19th century |
| Related instruments | |
|
|
The ukulele (pron.: / ˌ juː k ə ˈ l eɪ l iː /, yoo-ka-LAY-lee, from Hawaiian: ʻukulele [ˈʔukuˈlɛlɛ], OO-KOO-le-le) sometimes abbreviated to uke, is a member of the guitar family of instruments; it generally employs four nylon or gut strings or four courses of strings.
The ukulele originated in the 19th century as a Hawaiian interpretation of the machete, a small guitar-like instrument related to the cavaquinho, braguinha and the rajao, taken to Hawaii by Portuguese immigrants. It gained great popularity elsewhere in the United States during the early 20th century, and from there spread internationally.
The tone and volume of the instrument varies with size and construction. Ukuleles commonly come in four sizes: soprano, concert, tenor, and baritone.
History
Hawaii
Ukuleles are commonly associated with music from Hawaii where the name roughly translates as "jumping flea," perhaps because of the movement of the player's fingers. Legend attributes it to the nickname of the Englishman Edward William Purvis, one of King Kalākaua's officers, because of his small size, fidgety manner, and playing expertise. According to Queen Liliʻuokalani, the last Hawaiian monarch, the name means “the gift that came here,” from the Hawaiian words uku (gift or reward) and lele (to come).
Developed in the 1880s, the ukulele is based on two small guitar-like instruments of Portuguese origin, the cavaquinho and the rajao, introduced to the Hawaiian Islands by Portuguese immigrants from Madeira and Cape Verde. Three immigrants in particular, Madeiran cabinet makers Manuel Nunes, José do Espírito Santo, and Augusto Dias, are generally credited as the first ukulele makers. Two weeks after they disembarked from the SS Ravenscrag in late August 1879, the Hawaiian Gazette reported that "Madeira Islanders recently arrived here, have been delighting the people with nightly street concerts."
One of the most important factors in establishing the ukulele in Hawaiian music and culture was the ardent support and promotion of the instrument by King Kalākaua. A patron of the arts, he incorporated it into performances at royal gatherings.
Canada
In the 1960s, educator J. Chalmers Doane dramatically changed school music programs across Canada, using the ukulele as an inexpensive and practical teaching instrument to foster musical literacy in the classroom. 50,000 schoolchildren and adults learned ukulele through the Doane program at its peak.
Japan
The ukulele came to Japan in 1929 after Hawaiian-born Yukihiko Haida returned to the country upon his father's death and introduced the instrument. Haida and his brother Katsuhiko formed the Moana Glee Club, enjoying rapid success in an environment of growing enthusiasm for Western popular music, particularly Hawaiian and jazz. During World War II, authorities banned most Western music, but fans and players kept it alive in secret, and it resumed popularity after the war. In 1959, Haida founded the Nihon Ukulele Association. Today, Japan is considered a second home for Hawaiian musicians and ukulele virtuosos.
United Kingdom
The singer and comedian George Formby was perhaps the UK's most famous ukulele player, though he often played a banjolele, a hybrid instrument consisting of an extended ukulele neck with a banjo resonator body. Demand surged in the new century because of its relative simplicity and portability.
United States
Pre–World War II
The ukulele was popularized for a stateside audience during the Panama Pacific International Exposition, held from spring to fall of 1915 in San Francisco. The Hawaiian Pavilion featured a guitar and ukulele ensemble, George E. K. Awai and his Royal Hawaiian Quartet, along with ukulele maker and player Jonah Kumalae. The popularity of the ensemble with visitors launched a fad for Hawaiian-themed songs among Tin Pan Alley songwriters. The ensemble also introduced both the lap steel guitar and the ukulele into U.S. mainland popular music, where it was taken up by vaudeville performers such as Roy Smeck and Cliff "Ukulele Ike" Edwards. On April 15, 1923 at the Rivoli Theatre in New York City, Smeck appeared, playing the ukulele, in Stringed Harmony, a short film made in the DeForest Phonofilm sound-on-film process. On August 6, 1926, Smeck appeared playing the ukulele in a short film His Pastimes, made in the Vitaphone sound-on-disc process, shown with the feature film Don Juan starring John Barrymore.
The ukulele soon became an icon of the Jazz Age. Highly portable and relatively inexpensive, it also proved popular with amateur players throughout the 1920s, as is evidenced by the introduction of uke chord tablature into the published sheet music for popular songs of the time, a role that would eventually be supplanted by the guitar in the early years of rock and roll. A number of mainland-based instrument manufacturers, among them Regal, Harmony, and Martin, added ukulele, banjolele, and tiple lines to their production to take advantage of the demand.
The ukulele also made inroads into early country music or Old-time music. It was played by Jimmie Rodgers and Ernest V. Stoneman, as well as by early string bands, including Cowan Powers and his Family Band, Da Costa Woltz's Southern Broadcasters, Walter Smith and Friends, The Blankenship Family, The Hillbillies, and The Hilltop Singers.
Post–World War II
From the late 1940s to the late 1960s, plastics manufacturer Mario Maccaferri turned out about 9 million inexpensive ukuleles. The ukulele continued to be popular, appearing on many jazz songs throughout the 1950s, 1960s, and 1970s. Much of the instrument's popularity was cultivated via The Arthur Godfrey Show on television. Singer-musician Tiny Tim became closely associated with the instrument after playing it on his 1968 hit " Tiptoe Through the Tulips."
Post-1990 Revival
After the 1960s, the ukulele declined in popularity until the late 1990s, when interest in the instrument reappeared. During the 1990s, new manufacturers began producing ukuleles and a new generation of musicians took up the instrument.
Hawaiian musician Israel Kamakawiwo'ole helped re-popularise the instrument, in particular with his 2003 medley of " Over the Rainbow" and " What a Wonderful World," used in films, television programs, and commercials. The song reached #12 on Billboard's Hot Digital Tracks chart the week of January 31, 2004 (for the survey week ending January 18, 2004).
Types
Construction
Ukuleles are generally made of wood, though variants have been composed partially or entirely of plastic or other materials. Cheaper ukuleles are generally made from ply or laminate woods, in some cases with a soundboard of an acoustically superior wood such as spruce. Such instruments typically cost from $50 to $100. More expensive ukuleles are made of solid hardwoods such as mahogany ( Swietenia spp.) Some of the most expensive ukuleles, which may cost thousands of dollars, are made from koa ( Acacia koa), a Hawaiian wood.
Typically ukuleles have a figure-eight body shape similar to that of a small acoustic guitar. They are also often seen in non-standard shapes, such as cutaway shape and an oval, usually called a "pineapple" ukulele, invented by the Kamaka Ukulele company, or a boat-paddle shape, and occasionally a square shape, often made out of an old wooden cigar box.
These instruments may have just four strings; or some strings may be paired in courses, giving the instrument a total of six or eight strings.
Instruments with six or eight strings in four courses are often called taropatches, or taropatch ukuleles. They were once common in a concert size, but now the tenor size is more common for six-string taropatch ukuleles. The six string, four course version, has two single and two double courses, and is sometimes called a Lili'u, though this name also applies to the eight-string version.
Sizes
Four sizes of ukuleles are common: soprano, concert, tenor, and baritone. The less common sopranino has a nut to bridge of under 13 inches. The bass ukulele anchors the other end of the size spectrum.
The soprano, often called "standard" in Hawaii, is the smallest and was the original size. The concert size was developed in the 1920s as an enhanced soprano, slightly larger and louder with a deeper tone. Shortly thereafter, the tenor was created, having more volume and deeper bass tone. The baritone was created in the 1940s.
| Type | Scale length | Total length | Tuning |
|---|---|---|---|
| soprano or standard | 13" (33 cm) | 21" (53 cm) | A4-D4-F#4-B4 or G4-C4-E4-A4 |
| concert | 15" (38 cm) | 23" (58 cm) | G4-C4-E4-A4, A4-D4-F#4-B4, or G3-C4-E4-A4 |
| tenor | 17" (43 cm) | 26" (66 cm) | G3-C4-E4-A4, G4-C4-E4-A4, A4-D4-F#4-B4, or D4-G3-B3-E4 |
| baritone | 19" (48 cm) | 30" (76 cm) | D3-G3-B3-E4 |
Tuning
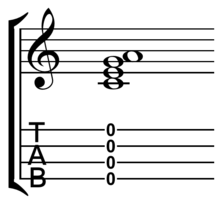
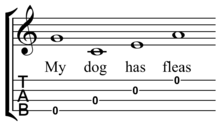
The most common tuning is C6-tuning: G4 C4 E4 A4. The G string is tuned an octave higher than might be expected. This is known as reentrant tuning. Some prefer "Low G" tuning on the tenor, with the G in sequence an octave lower. The baritone is usually tuned to D3 G3 B3 E4, which is the same as the highest four strings of the standard 6-string guitar. (A simple melody is so widely used as an aid in tuning that the ukulele has been referred to as the "My Dog Has Fleas" instrument.)
Another common tuning is D-tuning, A4 D4 F#4 B4, one step higher than the G4 C4 E4 A4 tuning. D tuning is said by some to bring out a sweeter tone in some ukuleles, generally smaller ones. This tuning was commonly used during the Hawaiian music boom of the early 20th century, and is often seen in sheet music from this period. D tuning with a low 4th, A3 D4 F#4 B4 is sometimes called "Canadian tuning" after its use in the Canadian school system, mostly on concert or tenor ukuleles, and extensive use by James Hill and Chalmers Doane.
Hawaiian ukuleles may also be tuned to open tunings, similar to the Hawaiian slack key style.
Related instruments
Ukulele varieties include hybrid instruments such as the guitalele (also called guitarlele), banjo ukulele (also called banjolele), harp ukulele, and lap steel ukulele. There is an electrically amplified version, the electric ukulele. The resonator ukulele produces sound by one or more spun aluminium cones ( resonators) instead of the wooden soundboard, giving it a distinct and louder tone. The Tahitian ukulele, another variant, is usually carved from a single piece of wood, and does not have a hollow soundbox.
Close cousins of the ukulele include the Portuguese forerunners, the cavaquinho (also commonly known as machete or braguinha) and the slightly larger rajao. Other stringed variants include, the Venezuelan cuatro, the Colombian tiple, the timple of the Canary Islands, the Spanish vihuela, the Mexican requinto jarocho, and the Andean charango traditionally made of an armadillo shell. In Indonesia, a similar Portuguese-inspired instrument is the kroncong.