Saffron
Background to the schools Wikipedia
SOS Children, which runs nearly 200 sos schools in the developing world, organised this selection. Do you want to know about sponsoring? See www.sponsorachild.org.uk
| Saffron crocus | |
|---|---|
 |
|
| C. sativus blossom with crimson stigmas. | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| (unranked): | Angiosperms |
| (unranked): | Monocots |
| Order: | Asparagales |
| Family: | Iridaceae |
| Subfamily: | Crocoideae |
| Genus: | Crocus |
| Species: | C. sativus |
| Binomial name | |
| Crocus sativus L. |
|
Saffron (pronounced / ˈ s æ f r ə n / or / ˈ s æ f r ɒ n /) is a spice derived from the flower of Crocus sativus, commonly known as the saffron crocus. Crocus is a genus in the family Iridaceae. Each saffron crocus grows to 20–30 cm (8–12 in) and bears up to four flowers, each with three vivid crimson stigmas, which are each the distal end of a carpel. Together with the styles, or stalks that connect the stigmas to their host plant, the dried stigmas are used mainly in various cuisines as a seasoning and colouring agent. Saffron, long among the world's most costly spices by weight, is native to Greece or Southwest Asia and was first cultivated in Greece. As a genetically monomorphic clone, it was slowly propagated throughout much of Eurasia and was later brought to parts of North Africa, North America, and Oceania.
The saffron crocus, unknown in the wild, likely descends from Crocus cartwrightianus, which originated in Crete; C. thomasii and C. pallasii are other possible precursors. The saffron crocus is a triploid that is "self-incompatible" and male sterile; it undergoes aberrant meiosis and is hence incapable of independent sexual reproduction—all propagation is by vegetative multiplication via manual "divide-and-set" of a starter clone or by interspecific hybridisation. If C. sativus is a mutant form of C. cartwrightianus, then it may have emerged via plant breeding, which would have selected for elongated stigmas, in late Bronze-Age Crete.
Saffron's bitter taste and iodoform- or hay-like fragrance result from the chemicals picrocrocin and safranal. It also contains a carotenoid dye, crocin, which imparts a rich golden-yellow hue to dishes and textiles. Its recorded history is attested in a 7th-century BC Assyrian botanical treatise compiled under Ashurbanipal, and it has been traded and used for over four millennia. Iran now accounts for approximately 90 percent of the world production of saffron. Because each flower's stigmas need to be collected by hand and there are only a few per flower, saffron is the most expensive spice in the world.
Etymology
The ultimate origin of the English word saffron is, like that of the cultivated saffron clone itself, of somewhat uncertain origin. It immediately stems from the Latin word safranum via the 12th-century Old French term safran. Safranum derives from the Persian intercessor زعفران, or za'ferân. Old Persian is the first language in which the use of saffron in cooking is recorded, with references dating back thousands of years.
Species
Description
The domesticated saffron crocus, Crocus sativus, is an autumn- flowering perennial plant unknown in the wild. Its progenitors are possibly the eastern Mediterranean autumn-flowering Crocus cartwrightianus, which is also known as "wild saffron" and originated in Greece. The saffron crocus likely resulted when C. cartwrightianus was subjected to extensive artificial selection by growers seeking longer stigmas. C. thomasii and C. pallasii are other possible sources.
It is a sterile triploid form, which means that three homologous sets of chromosomes compose each specimen's genetic complement; C. sativus bears eight chromosomal bodies per set, making for 24 in total. Being sterile, the purple flowers of Crocus sativus fail to produce viable seeds; reproduction hinges on human assistance: corms, underground bulb-like starch-storing organs, must be dug up, broken apart, and replanted. A corm survives for one season, producing via this vegetative division up to ten "cormlets" that can grow into new plants in the next season. The compact corms are small brown globules that can measure as large as 5 centimetres (2.0 in) in diameter, have a flat base, and are shrouded in a dense mat of parallel fibres; this coat is referred to as the "corm tunic". Corms also bear vertical fibres, thin and net-like, that grow up to 5 cm above the plant's neck.
The plant grows to a height of 20–30 cm (8–12 in), and sprouts 5–11 white and non-photosynthetic leafs known as cataphylls. They are membrane-like structures that cover and protect the crocus's 5–11 true leaves as they bud and develop. The latter are thin, straight, and blade-like green foliage leaves, which are 1–3 mm in diameter, either expand after the flowers have opened ("hysteranthous") or do so simultaneously with their blooming ("synanthous"). C. sativus cataphylls are suspected by some to manifest prior to blooming when the plant is irrigated relatively early in the growing season. Its floral axes, or flower-bearing structures, bear bracteoles, or specialised leaves that sprout from the flower stems; the latter are known as pedicels. After aestivating in spring, the plant sends up its true leaves, each up to 40 cm (16 in) in length. In autumn, purple buds appear. Only in October, after most other flowering plants have released their seeds, do its brilliantly hued flowers develop; they range from a light pastel shade of lilac to a darker and more striated mauve. The flowers possess a sweet, honey-like fragrance. Upon flowering, plants average less than 30 cm (12 in) in height. A three-pronged style emerges from each flower. Each prong terminates with a vivid crimson stigma 25–30 mm (0.98–1.2 in) in length.
Cultivation
Crocus sativus thrives in the Mediterranean maquis, an ecotype superficially resembling the North American chaparral, and similar climates where hot and dry summer breezes sweep semi-arid lands. It can nonetheless survive cold winters, tolerating frosts as low as −10 °C (14 °F) and short periods of snow cover. Irrigation is required if grown outside of moist environments such as Kashmir, where annual rainfall averages1,000–1,500 mm (39–59 in); saffron-growing regions in Greece (500 mm or 20 in annually) and Spain (400 mm or 16 in) are far drier than the main cultivating Iranian regions. What makes this possible is the timing of the local wet seasons; generous spring rains and drier summers are optimal. Rain immediately preceding flowering boosts saffron yields; rainy or cold weather during flowering promotes disease and reduces yields. Persistently damp and hot conditions harm the crops, and rabbits, rats, and birds cause damage by digging up corms. Nematodes, leaf rusts, and corm rot pose other threats. Yet Bacillus subtilis inoculation may provide some benefit to growers by speeding corm growth and increasing stigma biomass yield.
The plants fare poorly in shady conditions; they grow best in full sunlight. Fields that slope towards the sunlight are optimal (i.e., south-sloping in the Northern Hemisphere). Planting is mostly done in June in the Northern Hemisphere, where corms are lodged 7–15 cm (2.8–5.9 in) deep; its roots, stems, and leaves can develop between October and February. Planting depth and corm spacing, in concert with climate, are critical factors in determining yields. Mother corms planted deeper yield higher-quality saffron, though form fewer flower buds and daughter corms. Italian growers optimise thread yield by planting 15 cm (5.9 in) deep and in rows 2–3 cm (0.79–1.2 in) apart; depths of 8–10 cm (3.1–3.9 in) optimise flower and corm production. Greek, Moroccan, and Spanish growers employ distinct depths and spacings that suit their locales.
C. sativus prefers friable, loose, low-density, well-watered, and well-drained clay- calcareous soils with high organic content. Traditional raised beds promote good drainage. Soil organic content was historically boosted via application of some 20–30 tonnes of manure per hectare. Afterwards, and with no further manure application, corms were planted. After a period of dormancy through the summer, the corms send up their narrow leaves and begin to bud in early autumn. Only in mid-autumn do they flower. Harvests are by necessity a speedy affair: after blossoming at dawn, flowers quickly wilt as the day passes. All plants bloom within a window of one or two weeks. Roughly 150 flowers together yield but 1 g (0.035 oz) of dry saffron threads; to produce 12 g (0.42 oz) of dried saffron (or 72 g (2.5 oz) moist and freshly harvested), 1 kg (2.2 lb) of flowers are needed; 1 lb (0.45 kg) yields 0.2 oz (5.7 g) of dried saffron. One freshly picked flower yields an average 30 mg (0.0011 oz) of fresh saffron or 7 mg (0.00025 oz) dried.
Spice
Chemistry
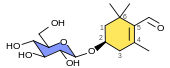
Saffron contains more than 150 volatile and aroma-yielding compounds. It also has many nonvolatile active components, many of which are carotenoids, including zeaxanthin, lycopene, and various α- and β- carotenes. However, saffron's golden yellow-orange colour is primarily the result of α-crocin. This crocin is trans- crocetin di-(β-D- gentiobiosyl) ester; it bears the systematic (IUPAC) name 8,8-diapo-8,8-carotenoic acid. This means that the crocin underlying saffron's aroma is a digentiobiose ester of the carotenoid crocetin. Crocins themselves are a series of hydrophilic carotenoids that are either monoglycosyl or diglycosyl polyene esters of crocetin. Crocetin is a conjugated polyene dicarboxylic acid that is hydrophobic, and thus oil-soluble. When crocetin is esterified with two water-soluble gentiobioses, which are sugars, a product results that is itself water-soluble. The resultant α-crocin is a carotenoid pigment that may comprise more than 10% of dry saffron's mass. The two esterified gentiobioses make α-crocin ideal for colouring water-based and non-fatty foods such as rice dishes.
The bitter glucoside picrocrocin is responsible for saffron's flavour. Picrocrocin (chemical formula: C16H26O7; systematic name: 4-(β-D-glucopyranosyloxy)-2,6,6- trimethylcyclohex-1-ene-1-carboxaldehyde) is a union of an aldehyde sub-element known as safranal (systematic name: 2,6,6-trimethylcyclohexa-1,3-diene-1-carboxaldehyde) and a carbohydrate. It has insecticidal and pesticidal properties, and may comprise up to 4% of dry saffron. Picrocrocin is a truncated version of the carotenoid zeaxanthin that is produced via oxidative cleavage, and is the glycoside of the terpene aldehyde safranal. The reddish-coloured zeaxanthin is, incidentally, one of the carotenoids naturally present within the retina of the human eye.
When saffron is dried after its harvest, the heat, combined with enzymatic action, splits picrocrocin to yield D–glucose and a free safranal molecule. Safranal, a volatile oil, gives saffron much of its distinctive aroma. Safranal is less bitter than picrocrocin and may comprise up to 70% of dry saffron's volatile fraction in some samples. A second element underlying saffron's aroma is 2-hydroxy-4,4,6-trimethyl-2,5-cyclohexadien-1-one, the scent of which has been described as "saffron, dried hay like". Chemists found this to be the most powerful contributor to saffron's fragrance despite its being present in a lesser quantity than safranal. Dry saffron is highly sensitive to fluctuating pH levels, and rapidly breaks down chemically in the presence of light and oxidizing agents. It must therefore be stored away in air-tight containers in order to minimise contact with atmospheric oxygen. Saffron is somewhat more resistant to heat.
Grades
Saffron is graded via laboratory measurement of crocin (colour), picrocrocin (taste), and safranal (fragrance) content. Determination of non-stigma content ("floral waste content") and other extraneous matter such as inorganic material (" ash") are also key. Grading standards are set by the International Organization for Standardization, a federation of national standards bodies. ISO 3632 deals exclusively with saffron and establishes four empirical colour intensity grades: IV (poorest), III, II, and I (finest quality). Samples are assigned grades by gauging the spice's crocin content, revealed by measurements of crocin-specific spectroscopic absorbance. Graders measure absorbances of 440-nm light by dry saffron samples. Higher absorbances imply greater crocin concentration, and thus a greater colourative intensity. These data are measured through spectrophotometry reports at certified testing laboratories worldwide. These colour grades proceed from grades with absorbances lower than 80 (for all category IV saffron) up to 190 or greater (for category I). The world's finest samples (the selected most red-maroon tips of stigmas picked from the finest flowers) receive absorbance scores in excess of 250. Market prices for saffron types follow directly from these ISO scores. However, many growers, traders, and consumers reject such lab test numbers. They prefer a more holistic method of sampling batches of thread for taste, aroma, pliability, and other traits in a fashion similar to that practised by practised wine tasters.
Despite such attempts at quality control and standardisation, an extensive history of saffron adulteration—particularly among the cheapest grades—continues into modern times. Adulteration was first documented in Europe's Middle Ages, when those found selling adulterated saffron were executed under the Safranschou code. Typical methods include mixing in extraneous substances like beets, pomegranate fibres, red-dyed silk fibres, or the saffron crocus's tasteless and odourless yellow stamens. Other methods included dousing saffron fibres with viscid substances like honey or vegetable oil. However, powdered saffron is more prone to adulteration, with turmeric, paprika, and other powders used as diluting fillers. Adulteration can also consist of selling mislabelled mixes of different saffron grades. Thus, in India, high-grade Kashmiri saffron is often sold and mixed with cheaper Iranian imports; these mixes are then marketed as pure Kashmiri saffron, a development that has cost Kashmiri growers much of their income.
Varieties
The various saffron crocus cultivars give rise to thread types that are often regionally distributed and characteristically distinct. Varieties from Spain, including the tradenames "Spanish Superior" and "Creme", are generally mellower in colour, flavour, and aroma; they are graded by government-imposed standards. Italian varieties are slightly more potent than Spanish; the most intense varieties tend to be Iranian. Various "boutique" crops are available from New Zealand, France, Switzerland, England, the United States, and other countries, some of them organically grown. In the U.S., Pennsylvania Dutch saffron—known for its "earthy" notes—is marketed in small quantities.
Consumers may regard certain cultivars as "premium" quality. The "Aquila" saffron, or zafferano dell'Aquila, is defined by high safranal and crocin content, distinctive thread shape, unusually pungent aroma, and intense colour; it is grown exclusively on eight hectares in the Navelli Valley of Italy's Abruzzo region, near L'Aquila. It was first introduced to Italy by a Dominican monk from Inquisition-era Spain. But the biggest saffron cultivation in Italy is in San Gavino Monreale, Sardinia, where it is grown on 40 hectares, representing 60% of Italian production; it too has unusually high crocin, picrocrocin, and safranal content. Another is the "Mongra" or "Lacha" saffron of Kashmir (Crocus sativus 'Cashmirianus'), which is among the most difficult for consumers to obtain. Repeated droughts, blights, and crop failures in the Indian-controlled areas of Kashmir combine with an Indian export ban to contribute to its prohibitive overseas prices. Kashmiri saffron is recognisable by its dark maroon-purple hue; it is among the world's darkest, which hints at strong flavour, aroma, and colourative effect.
History
The documented history of saffron cultivation spans more than three millennia. The wild precursor of domesticated saffron crocus was Crocus cartwrightianus. Human cultivators bred wild specimens by selecting for unusually long stigmas; thus, a sterile mutant form of C. cartwrightianus, C. sativus, likely emerged in late Bronze Age Crete.
Eastern
Saffron was detailed in a 7th-century BC Assyrian botanical reference compiled under Ashurbanipal. Documentation of saffron's use over the span of 4,000 years in the treatment of some 90 illnesses has been uncovered. Saffron-based pigments have indeed been found in 50,000 year-old depictions of prehistoric places in northwest Iran. The Sumerians later used wild-growing saffron in their remedies and magical potions. Saffron was an article of long-distance trade before the Minoan palace culture's 2nd millennium BC peak. Ancient Persians cultivated Persian saffron (Crocus sativus 'Hausknechtii') in Derbena, Isfahan, and Khorasan by the 10th century BC. At such sites, saffron threads were woven into textiles, ritually offered to divinities, and used in dyes, perfumes, medicines, and body washes. Saffron threads would thus be scattered across beds and mixed into hot teas as a curative for bouts of melancholy. Non-Persians also feared the Persians' usage of saffron as a drugging agent and aphrodisiac. During his Asian campaigns, Alexander the Great used Persian saffron in his infusions, rice, and baths as a curative for battle wounds. Alexander's troops imitated the practice from the Persians and brought saffron-bathing to Greece.
Conflicting theories explain saffron's arrival in South Asia. Kashmiri and Chinese accounts date its arrival anywhere between 900–2500 years ago. Historians studying ancient Persian records date the arrival to sometime prior to 500 BC, attributing it to a Persian transplantation of saffron corms to stock new gardens and parks. Phoenicians then marketed Kashmiri saffron as a dye and a treatment for melancholy. Its use in foods and dyes subsequently spread throughout South Asia. Buddhist monks wear saffron-coloured robes; however, the robes are not dyed with costly saffron but turmeric, a less expensive dye, or jackfruit. Monks' robes are dyed the same colour to show equality with each other, and turmeric or ochre were the cheapest, most readily available dyes. Gamboge is now used to dye the robes.
Some historians believe that saffron came to China with Mongol invaders from Persia. Yet saffron is mentioned in ancient Chinese medical texts, including the forty-volume pharmacopoeia titled Shennong Bencaojing (神農本草經: "Shennong's Great Herbal", also known as Pen Ts'ao or Pun Tsao), a tome dating from 200–300 BC. Traditionally credited to the fabled Yan ("Fire") Emperor (炎帝) Shennong, it discusses 252 phytochemical-based medical treatments for various disorders. Nevertheless, around the 3rd century AD, the Chinese were referring to saffron as having a Kashmiri provenance. According to Chinese herbalist Wan Zhen, "[t]he habitat of saffron is in Kashmir, where people grow it principally to offer it to the Buddha." Wan also reflected on how it was used in his time: "The flower withers after a few days, and then the saffron is obtained. It is valued for its uniform yellow colour. It can be used to aromatise wine."
Wider Near East and Western
The Minoans portrayed saffron in their palace frescoes by 1500–1600 BC; they hint at its possible use as a therapeutic drug. Ancient Greek legends told of sea voyages to Cilicia, where adventurers sought what they thought to be the world's most valued threads. Another legend tells of Crocus and Smilax, whereby Crocus is bewitched and transformed into the first saffron crocus. Ancient perfumers in Egypt, physicians in Gaza, townspeople in Rhodes, and the Greek hetaerae courtesans used saffron in their scented waters, perfumes and potpourris, mascaras and ointments, divine offerings, and medical treatments.
In late Hellenistic Egypt, Cleopatra used saffron in her baths so that lovemaking would be more pleasurable. Egyptian healers used saffron as a treatment for all varieties of gastrointestinal ailments. Saffron was also used as a fabric dye in such Levantine cities as Sidon and Tyre. Aulus Cornelius Celsus prescribes saffron in medicines for wounds, cough, colic, and scabies, and in the mithridatium. Such was the Romans' love of saffron that Roman colonists took it with them when they settled in southern Gaul, where it was extensively cultivated until Rome's fall. Competing theories state that saffron only returned to France with 8th-century AD Moors or with the Avignon papacy in the 14th century AD.
European saffron cultivation plummeted after the Roman Empire went into eclipse. As with France, the spread of Islamic civilization may have helped reintroduce the crop to Spain and Italy. The 14th-century Black Death caused demand for saffron-based medicaments to peak, and large quantities of threads had to be imported via Venetian and Genoan ships from southern and Mediterranean lands such as Rhodes; the theft of one such shipment by noblemen sparked the fourteen-week long "Saffron War". The conflict and resulting fear of rampant saffron piracy spurred corm cultivation in Basel; it thereby grew prosperous. The crop then spread to Nuremberg, where endemic and insalubrious adulteration brought on the Safranschou code—whereby culprits were variously fined, imprisoned, and executed. The corms soon spread throughout England, especially Norfolk and Suffolk. The Essex town of Saffron Walden, named for its new speciality crop, emerged as England's prime saffron growing and trading centre. However, an influx of more exotic spices—chocolate, coffee, tea, and vanilla—from newly contacted Eastern and overseas countries caused European cultivation and usage of saffron to decline. Only in southern France, Italy, and Spain did the clone significantly endure.
Europeans introduced saffron to the Americas when immigrant members of the Schwenkfelder Church left Europe with a trunk containing its corms; church members had widely grown it in Europe. By 1730, the Pennsylvania Dutch were cultivating saffron throughout eastern Pennsylvania. Spanish colonies in the Caribbean bought large amounts of this new American saffron, and high demand ensured that saffron's list price on the Philadelphia commodities exchange was set equal to that of gold. The trade with the Caribbean later collapsed in the aftermath of the War of 1812, when many saffron-bearing merchant vessels were destroyed. Yet the Pennsylvania Dutch continued to grow lesser amounts of saffron for local trade and use in their cakes, noodles, and chicken or trout dishes. American saffron cultivation survived into modern times mainly in Lancaster County, Pennsylvania.
Trade and use
| Nutritional value per 100 g (3.5 oz) | |
|---|---|
| Energy | 1,298 kJ (310 kcal) |
| Carbohydrates | 65.37 g |
| - Dietary fibre | 3.9 g |
| Fat | 5.85 g |
| - saturated | 1.586 g |
| - monounsaturated | 0.429 g |
| - polyunsaturated | 2.067 g |
| Protein | 11.43 g |
| Water | 11.90 g |
| Vitamin A | 530 IU |
| Thiamine (vit. B1) | 0.115 mg (10%) |
| Riboflavin (vit. B2) | 0.267 mg (22%) |
| Niacin (vit. B3) | 1.460 mg (10%) |
| Vitamin C | 80.8 mg (97%) |
| Calcium | 111 mg (11%) |
| Iron | 11.10 mg (85%) |
| Magnesium | 264 mg (74%) |
| Phosphorus | 252 mg (36%) |
| Potassium | 1724 mg (37%) |
| Sodium | 148 mg (10%) |
| Zinc | 1.09 mg (11%) |
| Selenium | 5.6 μg |
| Folate | 93 μg |
| Vitamin B6 | 1.010 mg |
| Ash | 5.45 g |
| Edible thread portion only. Percentages are relative to US recommendations for adults. Source: USDA Nutrient Database |
|
Trade

Almost all saffron grows in a belt bounded by the Mediterranean in the west and the rugged region encompassing Iran and Kashmir in the east. The other continents, except Antarctica, produce smaller amounts. Some 300 t (300,000 kg) of dried whole threads and powder are gleaned yearly, of which 50 t (50,000 kg) is top-grade "coupe" saffron. Iran answers for around 90–93% of global production and exports much of it. A few of Iran's drier eastern and southeastern provinces, including Fars, Kerman, and those in the Khorasan region, glean the bulk of modern global production. In 2005, the second-ranked Greece produced 5.7 t (5,700.0 kg), while Morocco and Kashmir, tied for third rank, each produced 2.3 t (2,300.0 kg).
In recent years, Afghan cultivation has risen; in restive Kashmir it has declined. Azerbaijan, Morocco, and Italy are, in decreasing order, lesser producers. Prohibitively high labour costs and abundant Iranian imports mean that only select locales continue the tedious harvest in Austria, England, Germany, and Switzerland—among them the Swiss village of Mund, whose annual output is a few kilograms.Tasmania, China, Egypt, France, Israel, Mexico, New Zealand, Turkey (mainly around the town of Safranbolu), California, and Central Africa are microscale cultivators.
To glean 1 lb (450 g) of dry saffron requires the harvest of 50,000–75,000 flowers; a kilogram requires 110,000–170,000 flowers. Forty hours of labour are needed to pick 150,000 flowers. Stigmas are dried quickly upon extraction and (preferably) sealed in airtight containers. Saffron prices at wholesale and retail rates range from US$500 to US$5,000 per pound, or US$1,100–11,000/kg, equivalent to £2,500/€3,500 per pound or £5,500/€7,500 per kilogram. The price in Canada recently rose to CAD 18,000 per kilogram. In Western countries, the average retail price in 1974 was $1,000/£500/€700 per pound, or US$2,200/£1,100/€1,550 per kilogram. In February, 2013, a retail bottle containing .06 ounces could be purchased for $16.26 or the equivalent of $4,336 per pound or as little as about $2,000/pound in larger quantities. A pound contains between 70,000 and 200,000 threads. Vivid crimson coloring, slight moistness, elasticity, and lack of broken-off thread debris are all traits of fresh saffron. Saffron is the most expensive spice in the world.
Use
Saffron's aroma is often described by connoisseurs as reminiscent of metallic honey with grassy or hay-like notes, while its taste has also been noted as hay-like and sweet. Saffron also contributes a luminous yellow-orange colouring to foods. Saffron is widely used in Indian, Persian, European, Arab, and Turkish cuisines. Confectioneries and liquors also often include saffron. Common saffron substitutes include safflower (Carthamus tinctorius, which is often sold as "Portuguese saffron" or "açafrão"), annatto, and turmeric (Curcuma longa). Saffron has also been used as a fabric dye, particularly in China and India, and in perfumery. It is used for religious purposes in India, and is widely used in cooking in many cuisines, ranging from the Milanese risotto of Italy to the bouillabaisse of France to the biryani with various meat accompaniments in South Asia.
Saffron has a long medicinal history as part of traditional healing; several modern research studies have hinted that the spice has possible anticarcinogenic (cancer-suppressing), anti-mutagenic (mutation-preventing), immunomodulating, and antioxidant-like properties. Saffron stigmas, and even petals, may be helpful for depression. Early studies show that saffron may protect the eyes from the direct effects of bright light and retinal stress apart from slowing down macular degeneration and retinitis pigmentosa. (Most saffron-related research refers to the stigmas, but this is often not made explicit in research papers.) Other controlled research studies have indicated that saffron may have many potential medicinal properties.