Redwood National and State Parks
Did you know...
This selection is made for schools by a children's charity read more. Sponsor a child to make a real difference.
| Redwood National and State Parks | |
|---|---|
|
IUCN category II ( national park)
|
|
 Fog in the forest. |
|
| Location of Redwood National and State Parks | |
| Location | Humboldt County & Del Norte County, California, USA |
| Nearest city | Crescent City |
| Coordinates | 41°18′N 124°00′W Coordinates: 41°18′N 124°00′W |
| Area | 112,618 acres (45,575 ha) |
| Established | January 1, 1968 |
| Visitors | 380,167 (in 2011) |
| Governing body | Co-managed by National Park Service and California Department of Parks and Recreation |
| Official name: Redwood National Park | |
| Type: | Natural |
| Criteria: | vii, ix |
| Designated: | 1980 (4th session) |
| Reference No. | 134 |
| State Party: | |
| Region: | Europe and North America |
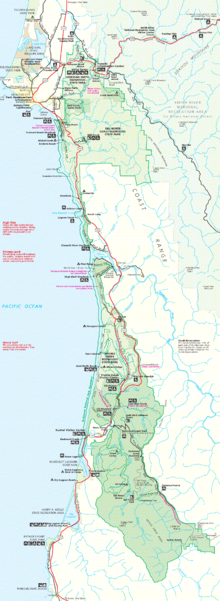
The Redwood National and State Parks (RNSP) are located in the United States, along the coast of northern California. Comprising Redwood National Park (established 1968) and California's Del Norte Coast, Jedediah Smith, and Prairie Creek Redwoods State Parks (dating from the 1920s), the combined RNSP contain 133,000 acres (540 km2). Located entirely within Del Norte and Humboldt Counties, the four parks, together, protect 45% of all remaining coast redwood (Sequoia sempervirens) old-growth forests, totaling at least 38,982 acres (157.75 km2). These trees are the tallest and one of the most massive tree species on Earth. In addition to the redwood forests, the parks preserve other indigenous flora, fauna, grassland prairie, cultural resources, portions of rivers and other streams, and 37 miles (60 km) of pristine coastline.
In 1850, old-growth redwood forest covered more than 2,000,000 acres (8,100 km2) of the California coast. The northern portion of that area, originally inhabited by Native Americans, attracted many lumbermen and others turned gold miners when a minor gold rush brought them to the region. Failing in efforts to strike it rich in gold, these men turned toward harvesting the giant trees for booming development in San Francisco and other places on the West Coast. After many decades of unobstructed clear-cut logging, serious efforts toward conservation began. By the 1920s the work of the Save-the-Redwoods League, founded in 1918 to preserve remaining old-growth redwoods, resulted in the establishment of Prairie Creek, Del Norte Coast, and Jedediah Smith Redwoods State Parks among others. Redwood National Park was created in 1968, by which time nearly 90% of the original redwood trees had been logged. The National Park Service (NPS) and the California Department of Parks and Recreation (CDPR) administratively combined Redwood National Park with the three abutting Redwood State Parks in 1994 for the purpose of cooperative forest management and stabilization of forests and watersheds as a single unit.
The ecosystem of the RNSP preserves a number of threatened animal species such as the Brown Pelican, Tidewater Goby, Bald Eagle, Chinook Salmon, Northern Spotted Owl, and Steller's Sea Lion. In recognition of the rare ecosystem and cultural history found in the parks, the United Nations designated them a World Heritage Site on September 5, 1980 and an International Biosphere Reserve on June 30, 1983.
History

Though Native Americans live in the park area today, archaeological study shows they arrived in the area as far back as 3,000 years ago. Modern day Native groups such as the Yurok, Tolowa, Karok, Chilula, and Wiyot all have historical ties to the region. An 1852 census determined that the Yurok were the most numerous, with 55 villages and an estimated population of 2,500. They used the abundant redwood, which with its linear grain was easily split into planks, as a building material for boats, houses, and small villages. For buildings, the planks would be erected side by side in a narrow trench, with the upper portions bound with leather strapping and held by notches cut into the supporting roof beams. Redwood boards were used to form a shallow sloping roof.
Previous to Jedediah Smith in 1828, no other explorer of European descent is known to have thoroughly investigated the inland region away from the immediate coast. The discovery of gold along the Trinity River in 1850 led to a minor secondary gold rush in California. This brought miners into the area and many stayed on at the coast after failing to strike it rich. This quickly led to conflicts wherein native peoples were placed under great strain, if not forcibly removed or massacred. By 1895, only one third of the Yurok in one group of villages remained; by 1919, virtually all members of the Chilula tribe had either died or been assimilated into other tribes. The miners logged redwoods for building; when this minor gold rush ended, some of them turned again to logging, cutting down the giant redwood trees. Initially, over 2,000,000 acres (8,100 km2) of the California and southwestern coast of Oregon were old-growth redwood forest, but by 1910, extensive logging led conservationists and concerned citizens to begin seeking ways to preserve the remaining trees, which they saw being logged at an alarming rate. In 1911, U.S. Representative John E. Raker, of California, became the first politician to introduce legislation for the creation of a redwood national park. However, no further action was taken by Congress at this time.
Early conservationists John C. Merriam, Madison Grant, and Henry Fairfield Osborn visited the region in 1917. Disappointed there were still no public lands preserving any of the large trees, these men along with Frederick Russell Burnham and others founded the Save-the-Redwoods League in 1918. This was timely as U.S. Route 101, which would soon provide nearly unfettered access to the trees, was under construction. Using matching funds provided initially by the County of Humboldt and later by the State of California, the Save-the-Redwoods League managed to protect areas of concentrated or multiple redwood groves and a few entire forests in the 1920s. As California created a state park system, beginning in 1927, three of the preserved redwood areas became Prairie Creek Redwoods, Del Norte Coast Redwoods, and Jedediah Smith Redwoods State Parks. A fourth became Humboldt Redwoods State Park, by far the largest of the individual Redwood State Parks, but not in the Redwood National and State Park system. Because of the high demand for lumber during World War II and the construction boom that followed in the 1950s, the creation of a national park was delayed. Efforts by the Save-the-Redwoods League, the Sierra Club, and the National Geographic Society to create a national park began in the early 1960s. After intense lobbying of Congress, the bill creating Redwood National Park was signed by President Lyndon Johnson on October 2, 1968. The Save-the-Redwoods League and other entities purchased over 100,000 acres (400 km2), which were added to existing state parks. In 1978, 48,000 acres (190 km2) were added to Redwood National Park in a major expansion. However, only a fifth of that land was old-growth forest, the rest having been logged. This expansion protected the watershed along Redwood Creek from being adversely affected by logging operations outside the park. The federal and state parks were administratively combined in 1994.
The United Nations designated Redwood National and State Parks a World Heritage Site on September 5, 1980. The evaluation committee noted 50 prehistoric archaeological sites, spanning 4,500 years. It also cited ongoing research in the park by Humboldt State University researchers, among others. The park is part of a much larger region designated the California Coast Ranges International Biosphere Reserve on June 30, 1983. The California Coast Ranges biosphere is overseen by the University of California Natural Reserve System.
Park management
Redwood National Park headquarters is located in Crescent City, California, with a service office located in Arcata and an operations centre located in Orick, California.
Lack of money has precluded major improvements, however, and timber companies have replanted much of the logged area with non-native tree species. Coastline areas, including dunes and coastal prairie, have been invaded by exotic species, partly due to the suppression of forest fires until the 1980s. A fire management plan now allows controlled burning as one method to return the parkland to its original state. Since the redwoods were logged on the basis of accessibility, with inaccessible areas being cut last, large old-growth forest sections were isolated from one another, sometimes by many miles. In these cases it will be decades more before mature forest can return, regardless of the amount of money used to rehabilitate the ecosystem.
The park has transformed a few logging roads into scenic public drives. These do not meet current safety standards, but funding to improve them is not available at present. Park structures such as visitor centers and employee housing also need updating to meet increasing demands. Park employees perform air and water quality surveys, monitor endangered and threatened species, and work closely with the California Coastal National Monument, which is managed by the U.S. Bureau of Land Management. In 2005, the parks were authorized to expand another 25,000 acres (100 km2) to include the Mill Creek watershed.
Recreation
The DeMartin Redwood Youth Hostel, a low-amenities shared lodging facility (near Klamath), has now closed. There are no hotels or motels within the parks boundaries. However, nearby towns such as Klamath, Requa, and Orick provide small hotels and inns, with extensive lodging options available in the regional trading centers of Crescent City on the northern end of the park and Arcata and Eureka located to the south. The park is about 260 miles (420 km) north of San Francisco, and 300 miles (480 km) south of Portland, Oregon; U.S. Route 101 passes through it from north to south. The Smith River National Recreation Area, part of the Six Rivers National Forest, is adjacent to the north end of RNSP.
While the state parks have front country campsites that can be driven to, the federal sections of the park do not, and hiking is the only way to reach back country campsites. These are at Mill Creek campground in Del Norte Coast Redwoods State Park and Jedediah Smith campground in Jedediah Smith Redwoods State Park, which together have 251 campsites; the Elk Prairie campground in Prairie Creek Redwoods State Park which has 75; and the Gold Bluffs Beach campground which has 25 campsites. Other nearby state parks have additional front country camping.
Back country camping is by permit only and is only allowed in designated sites, except on gravel bars along Redwood Creek. Access to the back country is highly regulated to prevent overuse while permitting as many groups as possible to explore the forest. Camping in the back country is therefore limited to five consecutive nights, and 15 nights in any one year. Proper food storage to minimize encounters with bears is strongly enforced, and hikers and backpackers are required to take out any trash they generate.
Almost 200 miles (320 km) of hiking trails exist in the parks, but during the rainy season some temporary footbridges are removed, as they would be destroyed by high streams. Throughout the year, trails are often wet and hikers need to be well prepared for rainy weather and consult information centers for updates on trail conditions.
Horseback riding and mountain biking are popular but are only allowed on certain trails. Kayaking is popular along the seacoast and in the various rivers and streams. Kayakers and canoeists frequently travel the Smith River, which is the longest undammed river remaining in California. Fishing for salmon and steelhead, a highly prized anadromous form of rainbow trout over 16 inches (41 cm), is best in the Smith and Klamath rivers. A California sport fishing license is required to fish any of the rivers and streams. Hunting is not permitted anywhere in the parks, but is allowed in nearby National Forests.
The park has three visitor centers, where guided nature walks and general information are available, along with two additional information points. Each campground offers campfire talks during the summer months as well as guided tours. The parks have many picnic areas, which are all easily accessed by vehicle.
In films
The park has served as a filming location for numerous films. The Endor scenes for Star Wars Episode VI: Return of the Jedi were filmed in the Tall Trees Redwood Grove in the northern part of Humboldt County. Scenes for The Lost World: Jurassic Park as well as the movie Outbreak were filmed at the nearby Prairie Creek Redwoods State Park and at Patrick's Point State Park.
The park was also used to represent Jurassic forests of Colorado in Walking with Dinosaurs in "Time of the Titans" and in the 2007 IMAX film Dinosaurs Alive!, where they were used to represent Triassic forests of New Mexico, which was based on Petrified wood in Petrified Forest National Park in Arizona.