Howland Island
Background Information
SOS believes education gives a better chance in life to children in the developing world too. Sponsoring children helps children in the developing world to learn too.
Howland Island (pron.: / ˈ h aʊ l ə n d /) is an uninhabited coral island located just north of the equator in the central Pacific Ocean, about 1,700 nautical miles (3,100 km) southwest of Honolulu. The island lies almost halfway between Hawaii and Australia and is an unincorporated, unorganized territory of the United States. Geographically, it is part of the Phoenix Islands. For statistical purposes, Howland is grouped as one of the United States Minor Outlying Islands.
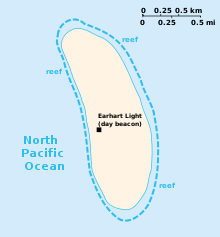
Howland is located at 0°48′24″N 176°36′59″W Coordinates: 0°48′24″N 176°36′59″W. It covers 450 acres (1.8 km2), with 4 miles (6.4 km) of coastline. The island has an elongated shape on a north-south axis. There is no lagoon.
Howland Island National Wildlife Refuge consists of the 455 acres (1.84 km2) island and the surrounding 32,074 acres (129.80 km2) of submerged land. The island is managed by the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service as an insular area under the U.S. Department of the Interior and is part of the Pacific Remote Islands Marine National Monument.
The atoll has no economic activity. It is perhaps best known as the island Amelia Earhart was searching for but never reached when her airplane disappeared on July 2, 1937. Airstrips constructed to accommodate her planned stopover were never used, subsequently damaged, not maintained and gradually disappeared. There are no harbors or docks. The fringing reefs may pose a maritime hazard. There is a boat landing area along the middle of the sandy beach on the west coast, as well as a crumbling day beacon. The island is visited every two years by the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service.
Flora and fauna
The climate is equatorial, with little rainfall and intense sunshine. Temperatures are moderated somewhat by a constant wind from the east. The terrain is low-lying and sandy: a coral island surrounded by a narrow fringing reef with a slightly raised central area. The highest point is about six meters above sea level.
There are no natural fresh water resources. The landscape features scattered grasses along with prostrate vines and low-growing pisonia trees and shrubs. A 1942 eyewitness description spoke of "a low grove of dead and decaying kou trees" on a very shallow hill at the island's centre. In 2000, a visitor accompanying a scientific expedition reported seeing "a flat bulldozed plain of coral sand, without a single tree" and some traces of building ruins. Howland is primarily a nesting, roosting and foraging habitat for seabirds, shorebirds and marine wildlife.
The U.S. claims an Exclusive Economic Zone of 200 nautical miles (370 km) and a territorial sea of 12 nautical miles (22 km) around the island.
Since Howland Island is uninhabited, no time zone is specified. It lies within a nautical time zone which is 12 hours behind UTC.

History
Prehistoric settlement
Sparse remnants of trails and other artifacts indicate a sporadic early Polynesian presence. A canoe, a blue bead, pieces of bamboo, and other relics of early settlers have been found. The island's prehistoric settlement may have begun about 1000 BC when eastern Melanesians traveled north and may have extended down to Rawaki, Kanton, Manra and Orona of the Phoenix Islands, 500 to 700 km southeast. K.P. Emery, an ethnologist for Honolulu's Bernice P. Bishop Museum, indicated that settlers on Manra Island were apparently of two distinct groups, one Polynesian and the other Micronesian, hence the same might have been true on Howland Island, though no proof of this has been forthcoming.
The difficult life on these isolated islands along with unreliable fresh water supplies may have led to the dereliction or extinction of the settlements, much the same as other islands in the area (such as Kiritimati and Pitcairn) were abandoned.
Sightings by whalers
Captain George B. Worth of the Nantucket whaler Oeno sighted Howland around 1822 and called it "Worth Island". Daniel MacKenzie of the American whaler Minerva Smith was unaware of Worth's sighting when he charted the island in 1828 and named it after his ship's owners on 1 December 1828. Howland Island was at last named after a lookout who sighted it from the whaleship Isabella of New Bedford on September 9, 1842.
U.S. possession and guano mining
Howland Island was uninhabited when the United States took possession of it in 1857 under the Guano Islands Act of 1856. The island was a known navigation hazard for many decades and several ships were wrecked there. Its guano deposits were mined by American companies until October 1878. John T. Arundel and Company, a British firm using laborers from the Cook Islands and Niue, occupied the island from 1886 to 1891.
In the late 19th Century there were British claims on the island, as well as attempts at setting up mining. To clarify American sovereignty, Executive Order 7368 was issued on May 13, 1936.
Itascatown (1935–1942)
In 1935, a brief attempt at colonization was made, part of a larger project administered by the Department of Commerce to establish a permanent U.S. presence on the equatorial Line Islands. It began with a rotating group of four alumni and students from the Kamehameha School for Boys, a private school in Honolulu. Although the recruits had signed on as part of a scientific expedition and expected to spend their three-month assignment collecting botanical and biological samples, once out to sea they were told, "Your names will go down in history" and that the islands would become "famous air bases in a route that will connect Australia with California".
The settlement was named Itascatown after the USCGC Itasca that brought the colonists to Howland and made regular cruises between the other Line Islands during that era. Itascatown was a line of a half-dozen small wood-framed structures and tents near the beach on the island's western side. The fledgling colonists were given large stocks of canned food, water, and other supplies including a gasoline powered refrigerator, radio equipment, complete medical kits and (characteristic of that era) vast quantities of cigarettes. Fishing provided much-needed variety for their diet. Most of the colonists' endeavors involved making hourly weather observations and gradually developing a rudimentary infrastructure on the island, including the clearing of a landing strip for airplanes. During this period the island was on Hawaii time, which was then 10.5 hours behind UTC. Similar colonization projects were started on nearby Baker Island, Jarvis Island and two other islands.
Kamakaiwi Field
Ground for a rudimentary aircraft landing area was cleared during the mid-1930s, in anticipation that the island might eventually become a stopover for commercial trans-Pacific air routes and also to further U.S. territorial claims in the region against rival claims from Great Britain. Howland Island was designated as a scheduled refueling stop for American pilot Amelia Earhart and navigator Fred Noonan on their round-the-world flight in 1937. Works Progress Administration (WPA) funds were used by the Bureau of Air Commerce to construct three graded, unpaved runways meant to accommodate Earhart's modern twin-engined Lockheed Model 10 Electra.
The facility was named Kamakaiwi Field after James Kamakaiwi, a young Hawaiian who arrived with the first group of four colonists. He was selected as the group's leader and he spent more than three years on Howland, far longer than the average recruit. It has also been referred to as WPA Howland Airport (the WPA contributed about 20% of the $12,000 cost). Earhart and Noonan took off from Lae, New Guinea, and their radio transmissions were picked up on the island when their aircraft reached the vicinity but they were never seen again.
Japanese attacks during World War II

A Japanese air attack on December 8, 1941 by 14 twin-engined Mitsubishi G3M "Nell" bombers killed two of the Kamehameha School colonists: Richard "Dicky" Kanani Whaley, and Joseph Kealoha Keliʻhananui. The raid came one day after the Japanese attack on Pearl Harbour and damaged the three airstrips of Kamakaiwi Field. Two days later a Japanese submarine shelled what was left of the colony's few buildings into ruins. A single bomber returned twice during the following weeks and dropped more bombs on the rubble of tiny Itascatown. The two survivors were finally evacuated by a U.S. Navy destroyer on January 31, 1942. Howland was occupied by a battalion of the United States Marine Corps in September 1943 and known as Howland Naval Air Station until May 1944.
All attempts at habitation were abandoned after 1944. Colonization projects on the other four islands were also disrupted by the war and ended at this time.
On July 10, 1944, a U.S. Navy Martin PBM-3-D Mariner flying boat (BuNo 48199), piloted by William Hines, had an engine fire and made a forced landing in the ocean offshore of Howland. Hines beached the aircraft and although it burned, the crew escaped unharmed, was rescued by the USCGC Balsam (the same ship that later took Unit 92 to Gardner Island), transferred to a sub chaser and taken to Canton Island.
Kamakaiwi Field suffered additional damage during World War II and it all but disappeared. Howland Island was colonized in 1935 as a future aviation facility and it is known mainly because of its association with the last flight of Earhart and Noonan. However, no aircraft is known to have ever landed there, although anchorages nearby could be used by float planes and flying boats during World War II.
National Wildlife Refuge
On June 27, 1974, Secretary of the Interior Rogers Morton created Howland Island National Wildlife Refuge which was expanded in 2009 to add submerged lands within 12 nautical miles (22 km) of the island. The refuge now includes 648 acres (2.62 km2) of land and 410,351 acres (1,660.63 km2) of water. Along with six other islands, the island was administered by the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service as part of the Pacific Remote Islands National Wildlife Refuge Complex. In January 2009, that entity was upgraded to the Pacific Remote Islands Marine National Monument by President George W. Bush.
The island habitat has suffered from the presence from multiple invasive exotic species. Black rats were introduced in 1854 and eradicated in 1938 by feral cats introduced the year before. The cats proved to be destructive to bird species and they were eliminated by 1985. Pacific crabgrass continues to compete with local plants.
Public entry to the island is onlyby special use permit from the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service and it is generally restricted to scientists and educators. Representatives from the agency visit the island on average once every two years, often coordinating transportation with amateur radio operators or the U.S. Coast Guard to defray the high cost of logistical support.
Earhart Light
"Colonists", sent to the island to establish possession claims by the United States, built the Earhart Light ( 0°48′20.48″N 176°37′8.55″W), named after Amelia Earhart, as a day beacon or navigational landmark. It is shaped somewhat like a short lighthouse. It was constructed of white sandstone with painted black bands and a black top meant to be seen several miles out to sea during daylight hours. It is located near the boat landing at the middle of the west coast by the former site of Itascatown. The beacon was partially destroyed during early World War II by the Japanese attacks, but it was rebuilt in the early 1960s by men from the U.S. Coast Guard ship Blackhaw. By 2000, the beacon was reported to be crumbling and it had not been repainted in decades.
Ann Dearing Holtgren Pellegreno overflew the island in 1967, and Linda Finch did so in 1997, during memorial circumnavigation flights to commemorate Earhart's 1937 world flight. No landings were attempted but both Pellegreno and Finch flew low enough to drop a wreath on the island.
Principality of Howland
Howland Island is now claimed by H.R.H Prince Jean-Nekbar de la Vibray. Prince Jean-Nekbar de la Vibray still waiting to be officially recognized as the head of state of the Principality of Howland.