Geography of Burkina Faso
Background Information
SOS believes education gives a better chance in life to children in the developing world too. Click here for more information on SOS Children.
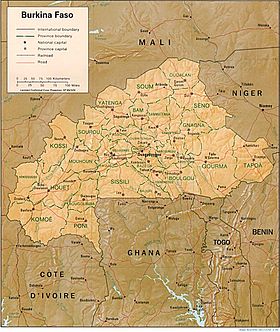
Burkina Faso (formerly Upper Volta) is a landlocked Sahel country that shares borders with six nations. It lies between the Sahara Desert and the Gulf of Guinea, south of the loop of the Niger River. The land is green in the south, with forests and fruit trees, and desert in the north. Most of central Burkina Faso lies on a savanna plateau, 198–305 metres (650–1,001 ft) above sea level, with fields, brush, and scattered trees. Burkina Faso's game preserves—the most important of which are Arly, Nazinga, and W National Park--contain lions, elephants, hippopotamus, monkeys, warthogs, and antelopes. Previously the endangered Painted Hunting Dog, Lycaon pictus occurred in Burkina Faso, but, although last sightings were made in Arli National Park, the species is considered extirpated in Burkina Faso. Tourism is not well developed.
Climate
Tropical; warm, dry winters; hot, wet summers. Annual rainfall varies from about 1,000 mm (39.4 in) in the south to less than 250 mm (9.8 in) in the extreme north and northeast, where hot desert winds accentuate the dryness of the region. Burkina Faso has three distinct seasons: warm and dry (November-March), hot and dry (March-May), and hot and wet (June-October). Rivers are not navigable.
Location: Western Africa, north of Ghana
Geographic coordinates: 13°N 2°W Coordinates: 13°N 2°W
Map references: Africa
Area:
- total: 274,200 km²
- land: 273,800 km²
- water: 400 km²
Area - comparative: slightly larger than Colorado
Land boundaries:
total: 3,193 km
border countries:
Coastline: 0 km (landlocked)
Maritime claims: none (landlocked)
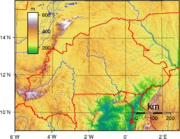
Terrain: mostly flat to dissected, undulating plains; hills in west and southeast
Elevation extremes:
- lowest point: Mouhoun ( Black Volta) River 200 m
- highest point: Tena Kourou 749 m
Natural resources: manganese, limestone, marble; small deposits of gold, phosphates, pumice, salt
Land use:
- arable land: 17.66%
- permanent crops: 0.22%
- other: 82.12% (2005)
Irrigated land: 250 km² (2003 est.)
Total renewable water resources: 17.5 m³ (2001)
Freshwater withdrawal (domestic/industrial/agricultural):
- total: 0.8 km³/yr (13%/1%/86%)
- per capita: 60 m³/yr (2000)
Natural hazards: Recurring droughts and floods
Environment - current issues: recent droughts and desertification severely affecting agricultural activities, population distribution, and the economy; overgrazing; soil degradation; deforestation
Environment - international agreements:
party to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Desertification, Endangered Species, Hazardous Wastes, Marine Life Conservation, Ozone Layer Protection, Wetlands
signed, but not ratified: Law of the Sea, Nuclear Test Ban
Geography - note: landlocked savanna cut by the three principal rivers of the Black, Red and White Voltas