
Ferdinandea
Background Information
The articles in this Schools selection have been arranged by curriculum topic thanks to SOS Children volunteers. A quick link for child sponsorship is http://www.sponsor-a-child.org.uk/
| Ferdinandea | |
|---|---|
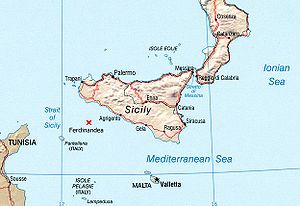 Approximate location of Ferdinandea |
|
| Summit depth | Roughly 6 m (20 ft) |
| Height | 63 m (207 ft) (maximum) |
| Summit area | Campi Flegrei del Mar di Sicilia (Phlegraean Fields of the Sea of Sicily) |
| Location | |
| Location | Between Sicily and Tunisia |
| Coordinates | 37°10′N, 12°43′E |
| Country | |
| Geology | |
| Type | Submarine volcano |
| Last eruption | 1831 |
| History | |
| Discovery date | First eruption 10 B.C. |
| Discovered by | Ancient Romans |
Ferdinandea ( Sicilian: Ìsula Firdinandèa) is a submerged volcanic island which forms part of the underwater volcano Empedocles, 30 km (19 mi) south of Sicily, and which is one of a number of submarine volcanoes known as the Campi Flegrei del Mar di Sicilia. Currently a seamount, eruptions have raised it above sea level several times before erosion has caused it to submerge again. When it last rose above sea level after erupting in 1831, a four-way dispute over its sovereignty began, which was still unresolved when it disappeared beneath the waves again in early 1832. During its brief life, the French geologist Constant Prévost was on hand, accompanied by an artist, to witness it in July 1831; he named it Île Julia, for its July appearance, and reported in the Bulletin de la Société Géologique de France. Some observers at the time wondered if a chain of mountains would spring up, linking Sicily to Tunisia and thus upsetting the geopolitics of the region. More recently, it has showed signs of volcanic activity in 2000 and 2002, forecasting a possible appearance; however, as of 2006 it remains 6 m (20 ft) under sea level.
Early history
Ferdinandea lies in a volcanic area known as the Campi Flegrei del Mar di Sicilia (Phlegraean Fields of the Sea of Sicily), in between Sicily and Tunisia in the Mediterranean Sea. Many submarine volcanoes ( seamounts) exist in the region, as well as some volcanic islands such as Pantelleria. Volcanic activity at Ferdinandea was first reported during the First Punic War, and the island has appeared and disappeared four or five times. Several eruptions have been reported since the 17th century.
1831 eruption
Ferdinandea's most recent appearance as an island was in July 1831. The first sign of an eruption was a period of high seismic activity spanning from June 28 to July 10 reported by the nearby town of Sciacca. On July 4 an odour of sulfur spread through the town reportedly in such quantities that it blackened silver. On July 13, a column of smoke was clearly seen from St. Domenico. The residents believed it to be a ferry on fire. On the same day, the brig Gustavo passed through the area, confirming a bubbling in the sea that the captain thought was a sea monster. Another ship reported dead fish floating in the water. By July 17, a fully grown islet had formed.
The eruptions of 1831 resulted in the island increasing in size to about 4 km (2.5 mi). However, it was composed of loose tephra, easily eroded by wave action, and when the eruptive episode ended it rapidly subsided, disappearing beneath the waves in January 1832, before the issue of its sovereignty could be resolved. Fresh eruptions in 1863 caused the island to reappear briefly before again sinking below sea level. At its maximum (in July and August 1831), it was 4,800 m (15,700 ft) in circumference and 63 m (207 ft) in height. It sported two small lakes, the larger of which was 20 metres (66 ft) in circumference and 2 m (6 ft 7 in) in depth.
Dispute
Ferdinandea was subject to a four-way dispute over its sovereignty, originally claimed for the United Kingdom and given the name Graham Island. The King of the Two Sicilies, Ferdinand II, after whom the island was named Ferdinandea, sent ships to the nascent island to claim it for the Bourbon crown. The French Navy also made a landing, and called the island Julia. Spain also declared its territorial ambitions. Each wanted the island for its useful position in the Mediterranean trade route (to England and France) and its close position to Spain and Italy.
Initial conflict
In August 1831 the volcano had risen to above sea level, although still only a couple of rocks, but the British Navy thought it was very suitable as a base to control the traffic in the Mediterranean, as it was closer to the European continent than the island of Malta. The small volcanic point was an important strategic point in the Mediterranean to the world's largest sea force of the time, being closer to Spain and Italy than Malta, the next closest. The British fleet landed, named it Graham Island, after Sir James Graham, the First Lord of the Admiralty, and planted their flag, the Union Jack.
But the King of Sicily also realized its strategic significance, and dispatched the corvette Etna to claim the new land and dub it Ferdinandea in honour of King Ferdinand II. Last on the scene was Constant Prévost, a co-founder of the French Geological Society, who compared the eruption to a bottle of champagne being uncorked. He named the island Julia, because it was born in July. Diplomatic wrangling broke out.
Extended conflict
For five months conflict raged in newspapers and elsewhere as the different nations fought over a roughly 60 m (200 ft) high piece of basalt. Tourists traveled to the island to see its two small lakes. Sailors watched it when passing by, and nobles of the House of Bourbon reportedly planned to set up a holiday resort on its beaches. None of these ideas came to light, however, as the island soon sank back beneath the waters. By December 17, 1831, officials reported no trace of it. As dynamically as the seamount appeared, it disappeared, defusing the conflict with it.
Recent activity
After 1863 the volcano lay dormant for many decades, its summit just 8 m (26 ft) below sea level. Following the 1986 US bombing of Libya, American warplanes mistook the shoal for a Libyan submarine and dropped depth charges on it.
In 2000, renewed seismic activity around Ferdinandea led volcanologists to speculate that a new eruptive episode could be imminent, and the seamount might once again become an island. To forestall a renewal of the sovereignty disputes, Italian divers planted a flag on the top of the volcano in advance of its expected resurfacing. To bolster their case, Sicilians, who call it Ferdinandea, summoned the descendant of the Bourbon King of Naples. In a ceremony filmed by a flotilla of camera crews, Prince Carlo di Bourbon lowered a plaque into the waves and told cheering locals: "It will always be Sicilian." C. Lobbied by fishermen and sailors, Ignazio Cucchiara, the mayor of Sciacca, invited Prince Carlo to attend the ceremony with his wife, Countess Camilla Cruciani. To accommodate television crews the plaque was lowered well before reaching the shoal, which is a danger to shipping. Choppy waters forced divers to postpone the operation a week, until November 13, 2000. The diving crew planted Sicily's flag, which features a Medusa's head surrounded by three naked legs – a sign traditionally interpreted as "keep away."
The marble plaque, weighing 150 kg (330 lb), was inscribed “This piece of land, once Ferdinandea, belonged and shall always belong to the Sicilian people." The Prince told cheering locals: “It will always be Sicilian.” But within six months it had been fractured into 12 pieces, mostly likely by fishing gear but possibly by vandalism. Professor Enzo Boschi, from the Institute of Geophysics and Volcanology in Rome, told BBC News Online, in November 2002:
We have observed minor seismic activity, gas emissions but this is quite normal.
He put the time of resurfacing at a couple of weeks or months. However, in an interview with Time magazine, Boris Behncke, a German researcher at the University of Catania's department of geological sciences in Sicily, said:
Geologically speaking, it's a possibility, But geology has a very long time scale ... We really should not be too worried.
Despite showing signs in both 2000 and 2002, the seismicity did not lead to volcanic eruptions and as of 2006 Ferdinandea's summit remains about 6 metres (20 ft) below sea level. Should it reappear, Federico Eichberg, an international relations expert based in Rome, believes it would do so within Italian territorial waters — and in all probability would be formally claimed by Italy. Eichberg does not expect that a renewed international rumpus would arise, noting:
“If it's just a little island, we're not going to have a big fight over it.”
Additionally, the island would not have the same strategic importance today that it had in the summer of 1831. A diplomatic disagreement would be highly improbable, and the island would likely belong to Italy. A spokeswoman for Britain's Foreign and Commonwealth Office, however, kept all options open. The British government “would look at this if and when any island were to emerge,” she said, adding: “We don't want to make waves now.
Significance
Scientific study
The sudden geologic phenomenon was observed and studied by numerous scientists. Among the Germans were Hoffmann, Schultz, and Philippi. Among the English were Edward Davy and Warington Wilkinson Smyth. Among the French was Constant Prévost. Among the Italians there was Scinà Domenico (1765-1837) who published his observations in the "Effeméridi Sicilians" (1832- Vol. 2), and Carlo Gemmellaro (1787–1866), teacher of geology and mineralogy at Catania University, who published "Actions of the Gioenia Academy of Catania" (1831- Vol.8).
In 2006, further study revealed Ferdinandea to be just one part of the larger volcanic cone Empedocles.
Marine significance
Ferdinandea is still referenced on marine charts, as its top is only 6 metres short of breaking the surface, much higher than the draft of most seafaring vessels. It is also a small shoal on which near-surface maritime creatures dwell.
Coinage
In Sicily in 2000 there was produced an unofficial minting of a penny, featuring the island of Ferdinandea on one side and, unusually, a bust of Elizabeth II on the other. (Italy, including Sicily, was using the italian lira by this time and the coin did not circulate.) The designer of the coin is David Mannucci. The idea to make this coin occurred to Mannucci after he "found out the existence of the ghost island" from a newspaper article. Besides the copper piece, varieties exist in silver, copper "with protective enamel", and in silver "with protective enamel". While this Italian-made coin fittingly bears the Italian name for the island, the conflicted piece also features a bust of “Elizabeth II D.G.R.” and bears a British denomination.
In popular culture
During its emergence it was visited by Sir Walter Scott, and it provided inspiration for James Fenimore Cooper's The Crater, or Vulcan's Peak, Alexandre Dumas, père's The Speronara and Jules Verne's Captain Antifer and The Survivors of the Chancellor. It also provided the inspiration for the isle of Leshp in Terry Pratchett's Jingo.






