
Craton
About this schools Wikipedia selection
SOS Children made this Wikipedia selection alongside other schools resources. All children available for child sponsorship from SOS Children are looked after in a family home by the charity. Read more...
|
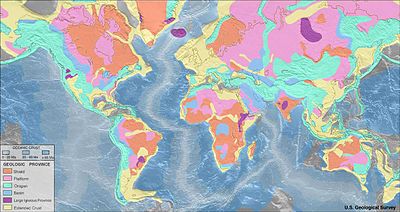
Shield
Platform
Orogen
Basin
Large igneous province
Extended crust
|
Oceanic crust: 0–20 Ma
20–65 Ma
>65 Ma
|
A craton (Greek: kratos / κράτος "strength") is an old and stable part of the continental lithosphere. Having often survived cycles of merging and rifting of continents, cratons are generally found in the interiors of tectonic plates. They are characteristically composed of ancient crystalline basement rock, which may be covered by younger sedimentary rock. They have a thick crust and deep lithospheric roots that extend up to a few hundred kilometers into the Earth's mantle.
The term craton is used to distinguish the stable portion of the continental crust from regions that are more geologically active and unstable. Cratons can be described as shields, in which the basement rock crops out at the surface, and platforms, in which the basement is overlain by sediments and sedimentary rock.
The word craton was first proposed by the German geologist L. Kober in 1921 as "Kratogen", referring to stable continental platforms, and "orogen" as a term for mountain or orogenic belts. Later authors shortened the former term to kraton and then to craton.
Examples of cratons are the Slave craton in Canada, the Wyoming craton in USA, and the Kaapvaal craton in South Africa.
Provinces
Cratons are subdivided geographically into geologic provinces. A geologic province is a spatial entity with common geologic attributes. A province may include a single dominant structural element such as a structural basin or a fold belt, or a number of contiguous related elements. Adjoining provinces may be similar in structure but be considered separate due to differing histories. There are several meanings of geologic provinces, as used in specific contexts.
Structure
Cratons have thick lithospheric roots. Mantle tomography shows that cratons are underlain by anomalously cold mantle corresponding to lithosphere more than twice the approximately 60 mile (100 km) thickness of mature oceanic or noncratonic continental lithosphere. Thus at that depth, it could be argued that some cratons might even be anchored in the asthenosphere. Mantle roots must be chemically distinct because cratons have a neutral or positive buoyancy, and a low intrinsic density that is required to offset any density increases due to geothermal contraction. Rock samples of mantle roots contain peridotites, and have been delivered to the surface as inclusions in subvolcanic pipes called kimberlites. These inclusions have densities consistent with craton composition and are composed of mantle material residual from high degrees of partial melt. Peridotites are important for understanding the deep composition and origin of cratons because peridotite nodules are pieces of mantle rock modified by partial melting. Harzburgite peridotites represent the crystalline residues after extraction of melts of compositions like basalt and komatiite. Alpine peridotites are slabs of uppermost mantle, many from oceanic lithosphere, also residues after extraction of partial melt, but they were subsequently emplaced together with oceanic crust along thrust faults up into the Alpine mountain belts. An associated class of inclusions called eclogites, consists of rocks corresponding compositionally to oceanic crust (basalt), but that metamorphosed under deep mantle conditions. Isotopic studies reveal that many eclogite inclusions are samples of ancient oceanic crust subducted billions of years ago to depths exceeding 90 mi (150 km) into the deep kimberlite diamond areas. They remained fixed there within the drifting tectonic plates until carried to the surface by deep-rooted magmatic eruptions. If peridotite and eclogite inclusions are of the same temporal origin, then peridotite must have also originated from sea-floor spreading ridges billions of years ago, or from mantle affected by subduction of oceanic crust then. During the early years of Earth's existence, when the planet was much hotter, greater degrees of melting at oceanic spreading ridges generated oceanic lithosphere with thick crust, much thicker than 12 miles (20 km), and a highly depleted mantle. Such a lithosphere would not sink deeply or subduct because of its buoyancy, and because of the removal of denser melt that in turn lowered the density of the residual mantle. Accordingly, cratonic mantle roots are probably composed of buoyantly subducted slabs of a highly depleted oceanic lithosphere. These deep mantle roots increase the stability, anchoring and survivability of cratons and makes them much less susceptible to tectonic thickening by collisions, or destruction by sediment subduction.
Formation
The process by which cratons are formed from early rock is called cratonization. The first large cratonic landmasses formed during the Archean eon. During the Early Archean, Earth's heat flow was nearly three times higher than it is today because of the greater concentration of radioactive isotopes and the residual heat from the Earth's accretion. There was considerably greater tectonic and volcanic activity; the mantle was much more fluid and the crust much thinner. This resulted in rapid formation of oceanic crust at ridges and hot spots, and rapid recycling of oceanic crust at subduction zones. Earth's surface was probably broken up into many small plates with volcanic islands and arcs in great abundance. Small protocontinents (cratons) formed as crustal rock was melted and remelted by hot spots and recycled in subduction zones.
There were no large continents in the Early Archean, and small protocontinents were probably the norm in the Mesoarchean because they were prevented from coalescing into larger units by the high rate of geologic activity. These felsic protocontinents (cratons) probably formed at hot spots from a variety of sources: mafic magma melting more felsic rocks, partial melting of mafic rock, and from the metamorphic alteration of felsic sedimentary rocks. Although the first continents formed during the Archean, rock of this age makes up only 7% of the world's current cratons; even allowing for erosion and destruction of past formations, evidence suggests that only 5-40% of the present continental crust formed during the Archean. (Stanley, 1999).
One evolutionary perspective of how the cratonization process "might" have first begun in the Archean is given by Hamilton (1999):
Very thick sections of mostly submarine mafic, and subordinate ultramafic, volcanic rocks, and mostly younger subaerial and submarine felsic volcanic rocks and sediments were oppressed into complex synforms between rising young domiform felsic batholiths mobilized by hydrous partial melting in the lower crust. Upper-crust granite-and- greenstone terrains underwent moderate regional shortening, decoupled from the lower crust, during compositional inversion accompanying doming, but cratonization soon followed. Tonalitic basement is preserved beneath some greenstone sections but supracrustal rocks commonly give way downward to correlative or younger plutonic rocks... Mantle plumes probably did not yet exist, and developing continents were concentrated in cool regions. Hot-region upper mantle was partly molten, and voluminous magmas, mostly ultramafic, erupted through many ephemeral submarine vents and rifts focussed at the thinnest crust.... Surviving Archean crust is from regions of cooler, and more depleted, mantle, wherein greater stability permitted uncommonly thick volcanic accumulations from which voluminous partial-melt, low-density felsic rocks could be generated.
