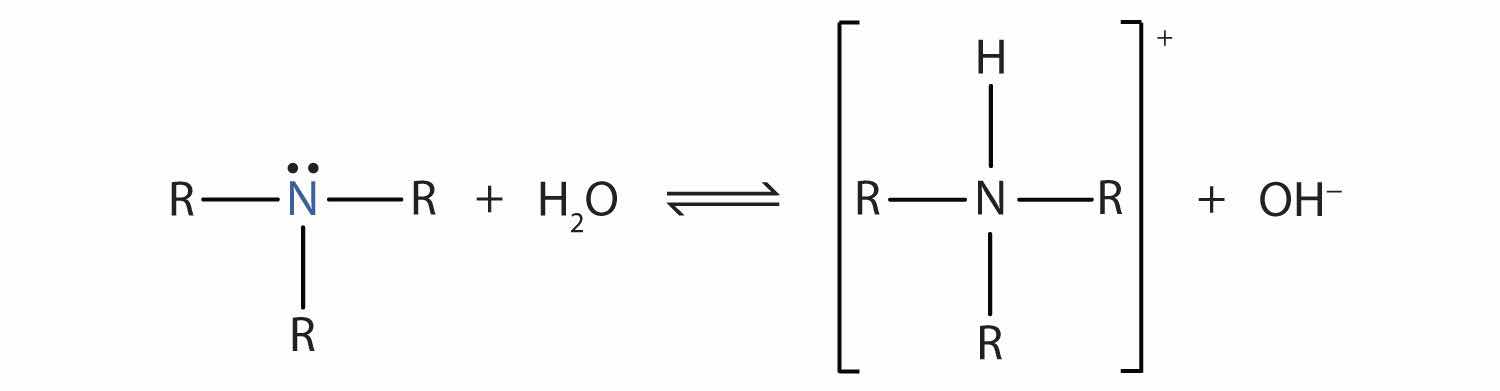
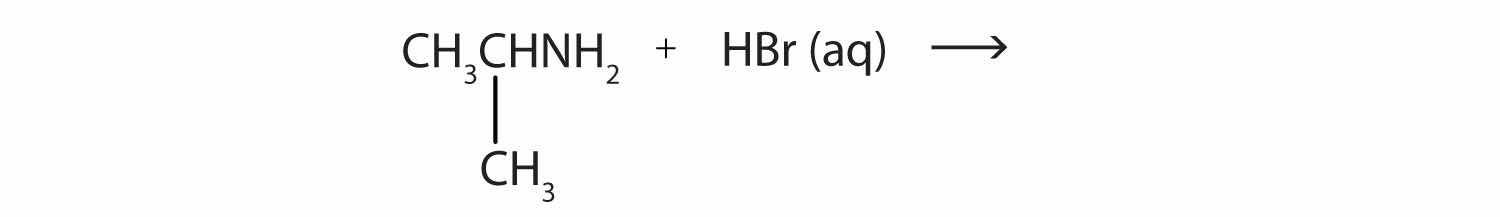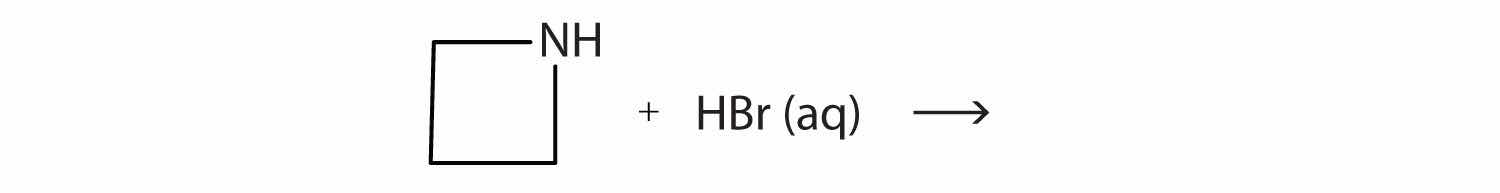Recall that ammonia (NH3) acts as a base because the nitrogen atom has a lone pair of electrons that can accept a proton. Amines also have a lone electron pair on their nitrogen atoms and can accept a proton from water to form substituted ammonium (NH4+) ions and hydroxide (OH−) ions:
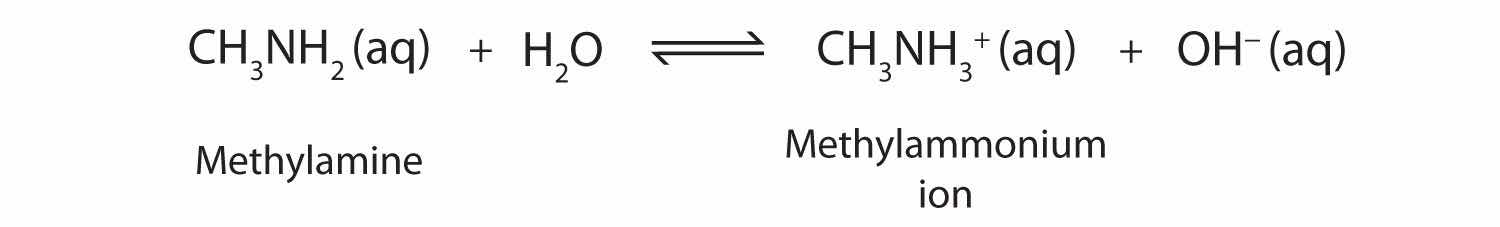
As a specific example, methylamine reacts with water to form the methylammonium ion and the OH− ion.
Nearly all amines, including those that are not very soluble in water, will react with strong acids to form salts soluble in water.
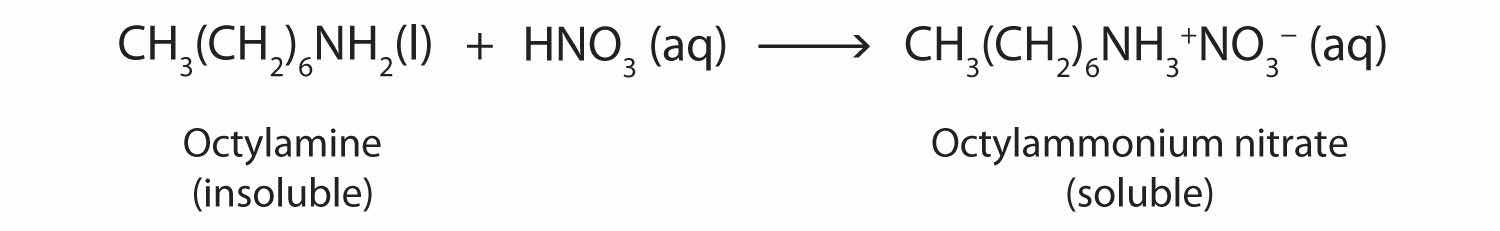
Amine salts are named like other salts: the name of the cation is followed by the name of the anion.
What are the formulas of the acid and base that react to form [CH3NH2CH2CH3]+CH3COO−?
Solution
The cation has two groups—methyl and ethyl—attached to the nitrogen atom. It comes from ethylmethylamine (CH3NHCH2CH3). The anion is the acetate ion. It comes from acetic acid (CH3COOH).
What are the formulas of the acid and base that react to form (CH3CH2CH2)3NH+I−?
Salts of aniline are properly named as anilinium compounds, but an older system, still in use for naming drugs, identifies the salt of aniline and hydrochloric acid as “aniline hydrochloride.” These compounds are ionic—they are salts—and the properties of the compounds (solubility, for example) are those characteristic of salts. Many drugs that are amines are converted to hydrochloride salts to increase their solubility in aqueous solution.
Looking back at the various cyclic hydrocarbons introduced in Chapter 12 "Organic Chemistry: Alkanes and Halogenated Hydrocarbons" and Chapter 13 "Unsaturated and Aromatic Hydrocarbons", we see that all the atoms in the rings of these compounds are carbon atoms. In other cyclic compounds, called heterocyclic compoundsA cyclic compound in which one or more atoms in the ring is an element other than a carbon atom. (Greek heteros, meaning “other”), nitrogen, oxygen, sulfur, or some other atom is incorporated in the ring. Many heterocyclic compounds are important in medicine and biochemistry. Some compose part of the structure of the nucleic acids, which in turn compose the genetic material of cells and direct protein synthesis. (For more information about nucleic acids, see Chapter 19 "Nucleic Acids".)
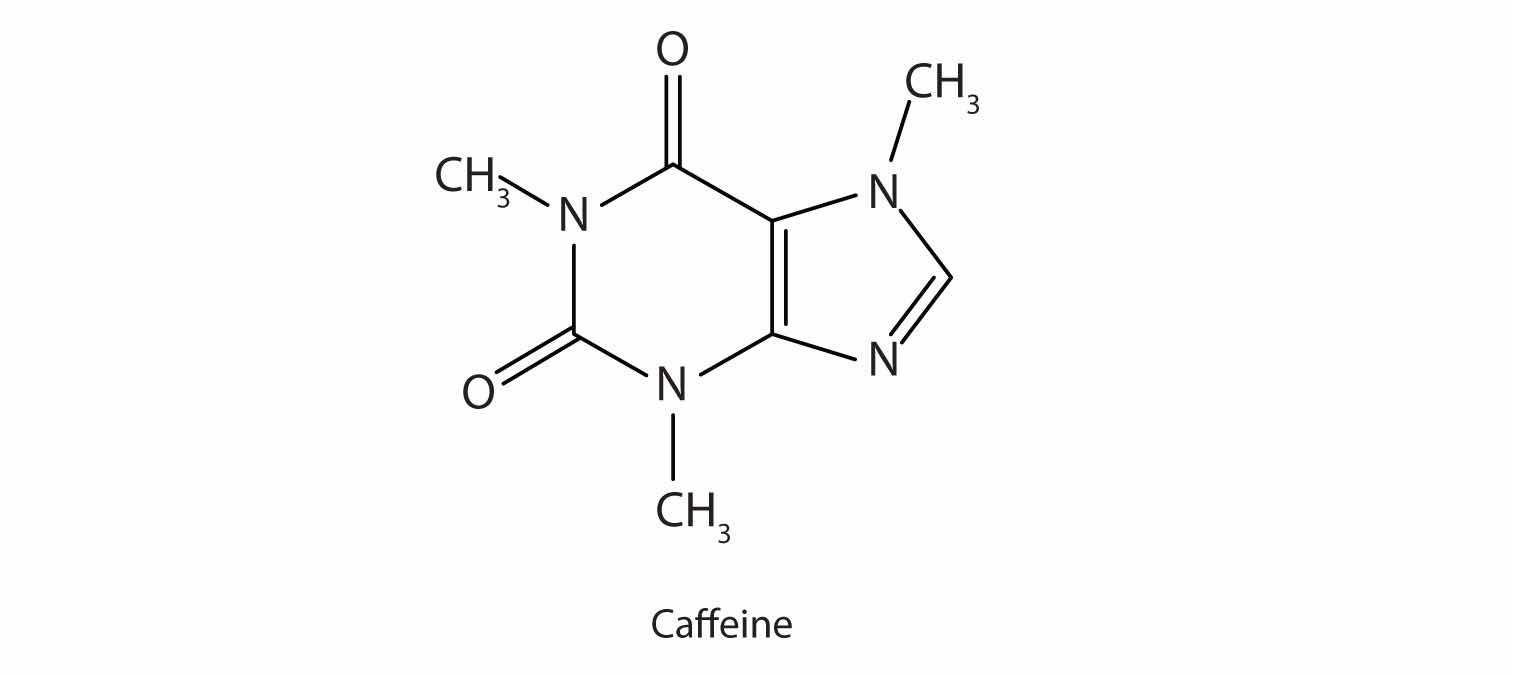
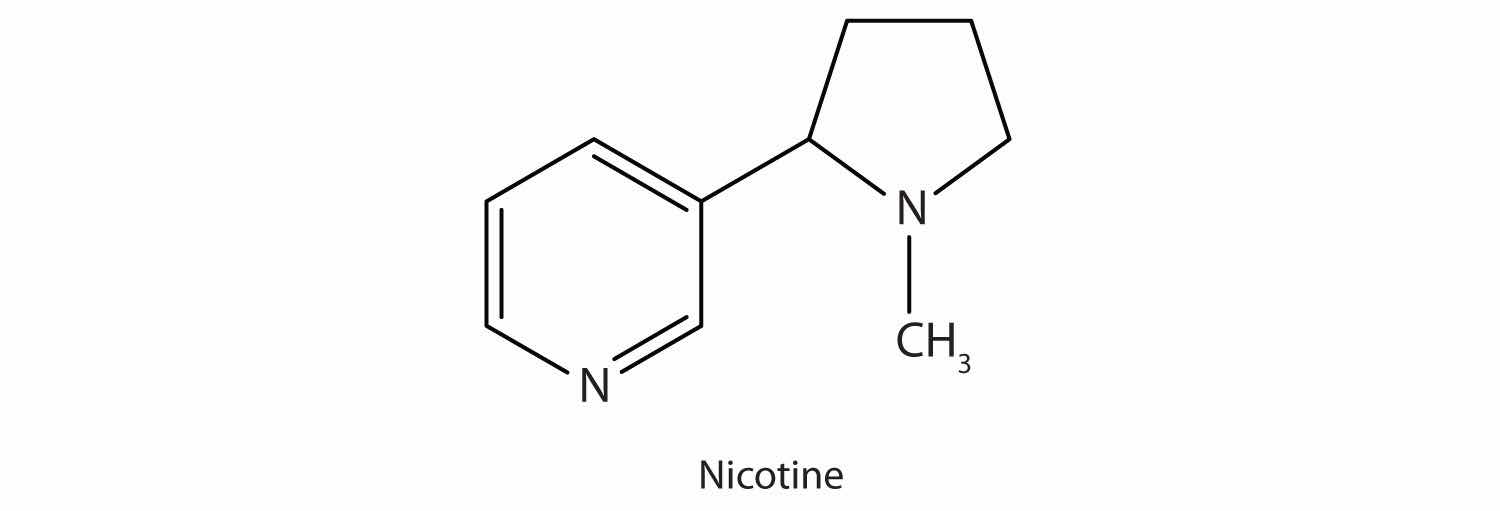
Many heterocyclic amines occur naturally in plants. Like other amines, these compounds are basic. Such a compound is an alkaloidA nitrogen-containing organic compound obtained from plants that has physiological properties., a name that means “like alkalis.” Many alkaloids are physiologically active, including the familiar drugs caffeine, nicotine, and cocaine.
Caffeine is a stimulant found in coffee, tea, and some soft drinks. Its mechanism of action is not well understood, but it is thought to block the activity of adenosine, a heterocyclic base that acts as a neurotransmitter, a substance that carries messages across a tiny gap (synapse) from one nerve cell (neuron) to another cell. The effective dose of caffeine is about 200 mg, corresponding to about two cups of strong coffee or tea.
Nicotine acts as a stimulant by a different mechanism; it probably mimics the action of the neurotransmitter acetylcholine. People ingest this drug by smoking or chewing tobacco. Its stimulant effect seems transient, as this initial response is followed by depression. Nicotine is highly toxic to animals. It is especially deadly when injected; the lethal dose for a human is estimated to be about 50 mg. Nicotine has also been used in agriculture as a contact insecticide.
Cocaine acts as a stimulant by preventing nerve cells from taking up dopamine, another neurotransmitter, from the synapse. High levels of dopamine are therefore available to stimulate the pleasure centers of the brain. The enhancement of dopamine action is thought to be responsible for cocaine’s “high” and its addictive properties. After the binge, dopamine is depleted in less than an hour. This leaves the user in a pleasureless state and (often) craving more cocaine.
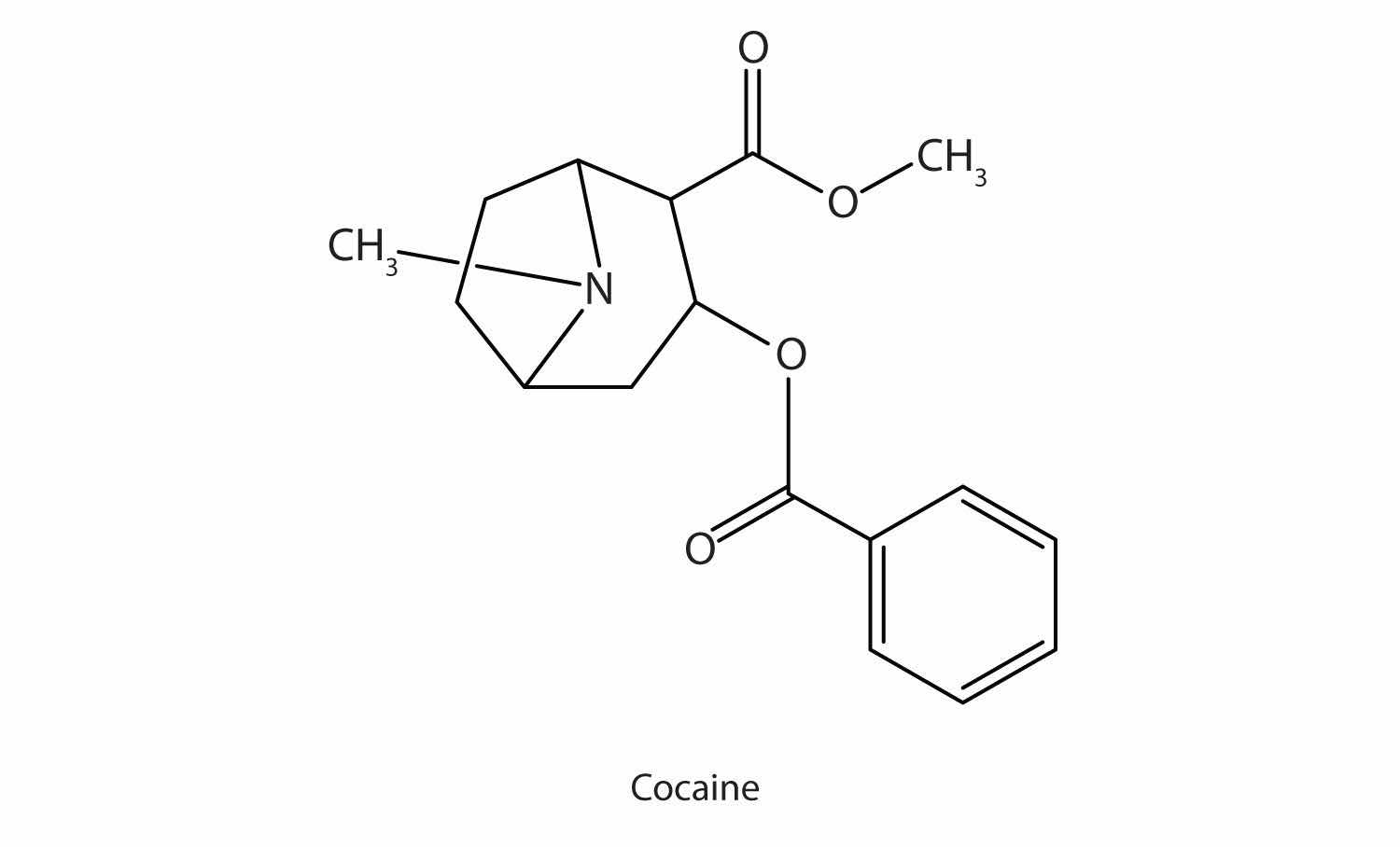
Cocaine is used as the salt cocaine hydrochloride and in the form of broken lumps of the free (unneutralized) base, which is called crack cocaine.
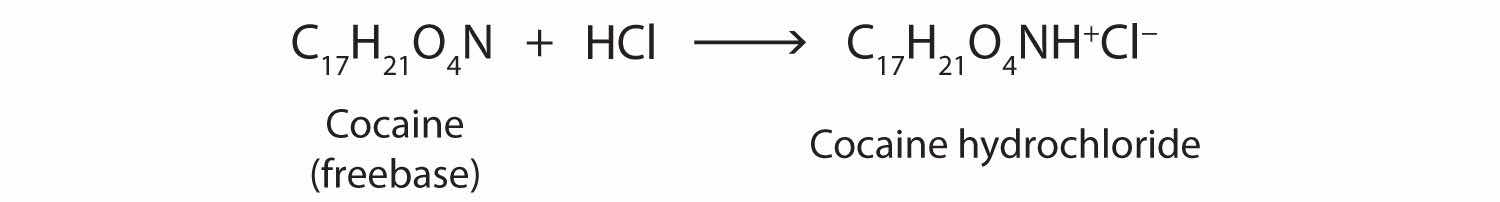
Because it is soluble in water, cocaine hydrochloride is readily absorbed through the watery mucous membranes of the nose when it is snorted. Crack cocaine is more volatile than cocaine hydrochloride. It vaporizes at the temperature of a burning cigarette. When smoked, cocaine reaches the brain in 15 s.
Explain the basicity of amines.
Contrast the physical properties of amines with those of alcohols and alkanes.
What is a heterocyclic compound?
Amines have a lone pair of electrons on the nitrogen atom and can thus act as proton acceptors (bases).
The solubilities of amines are similar to those of alcohols; the boiling points of primary and secondary amines are similar to those of alcohols; the boiling points of tertiary amines, which cannot engage in hydrogen bonding because they do not have a hydrogen atom on the nitrogen atom, are comparable to those of alkanes.
Heterocyclic compounds are ring compounds with atoms other than carbon atoms in the ring.
What salt is formed in each reaction? Write its condensed structural formula.
What salt is formed in each reaction? Draw its structure.