As we noted in Chapter 14 "Organic Compounds of Oxygen", the oxidation of aldehydes or primary alcohols forms carboxylic acids:

In the presence of an oxidizing agent, ethanol is oxidized to acetaldehyde, which is then oxidized to acetic acid.
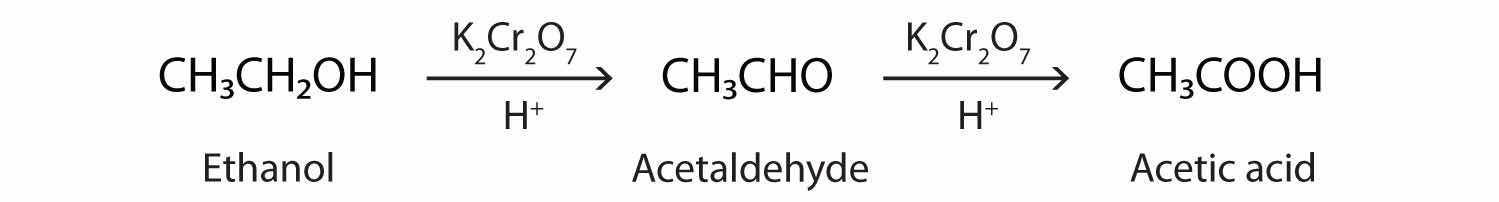
This process also occurs in the liver, where enzymes catalyze the oxidation of ethanol to acetic acid.
Acetic acid can be further oxidized to carbon dioxide and water.
Caproic acid (hexanoic acid) can be prepared in an oxidation reaction from
Give the structures of the aldehyde and the carboxylic acid formed by the oxidation of isobutyl alcohol [(CH3)2CHCH2OH].
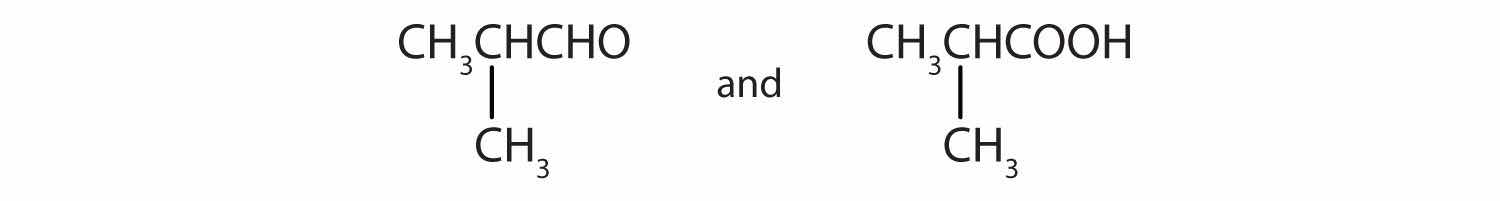
Caprylic acid (octanoic acid) can be prepared in an oxidation reaction from
Give the structures of the aldehyde and the carboxylic acid formed by the oxidation of 1,4-butanediol (HOCH2CH2CH2CH2OH).