Please be sure you are familiar with the topics discussed in Essential Skills 2 (Section 3.7 "Essential Skills 2") before proceeding to the Application Problems. Problems marked with a ♦ involve multiple concepts.
Hydrogen sulfide is a noxious and toxic gas produced from decaying organic matter that contains sulfur. A lethal concentration in rats corresponds to an inhaled dose of 715 molecules per million molecules of air. How many molecules does this correspond to per mole of air? How many moles of hydrogen sulfide does this correspond to per mole of air?
Bromine, sometimes produced from brines (salt lakes) and ocean water, can be used for bleaching fibers and silks. How many moles of bromine atoms are found in 8.0 g of molecular bromine (Br2)?
Paris yellow is a lead compound that is used as a pigment; it contains 16.09% chromium, 19.80% oxygen, and 64.11% lead. What is the empirical formula of Paris yellow?
A particular chromium compound used for dyeing and waterproofing fabrics has the elemental composition 18.36% chromium, 13.81% potassium, 45.19% oxygen, and 22.64% sulfur. What is the empirical formula of this compound?
Compounds with aluminum and silicon are commonly found in the clay fractions of soils derived from volcanic ash. One of these compounds is vermiculite, which is formed in reactions caused by exposure to weather. Vermiculite has the following formula: Ca0.7[Si6.6Al1.4]Al4O20(OH)4. (The content of calcium, silicon, and aluminum are not shown as integers because the relative amounts of these elements vary from sample to sample.) What is the mass percent of each element in this sample of vermiculite?
♦ Pheromones are chemical signals secreted by a member of one species to evoke a response in another member of the same species. One honeybee pheromone is an organic compound known as an alarm pheromone, which smells like bananas. It induces an aggressive attack by other honeybees, causing swarms of angry bees to attack the same aggressor. The composition of this alarm pheromone is 64.58% carbon, 10.84% hydrogen, and 24.58% oxygen by mass, and its molecular mass is 130.2 amu.
Amoxicillin is a prescription drug used to treat a wide variety of bacterial infections, including infections of the middle ear and the upper and lower respiratory tracts. It destroys the cell walls of bacteria, which causes them to die. The elemental composition of amoxicillin is 52.59% carbon, 5.24% hydrogen, 11.50% nitrogen, 21.89% oxygen, and 8.77% sulfur by mass. What is its empirical formula?
Monosodium glutamate (MSG; molar mass = 169 g/mol), is used as a flavor enhancer in food preparation. It is known to cause headaches and chest pains in some individuals, the so-called Chinese food syndrome. Its composition was found to be 35.51% carbon, 4.77% hydrogen, 8.28% nitrogen, and 13.59% sodium by mass. If the “missing” mass is oxygen, what is the empirical formula of MSG?
Ritalin is a mild central nervous system stimulant that is prescribed to treat attention deficit disorders and narcolepsy (an uncontrollable desire to sleep). Its chemical name is methylphenidate hydrochloride, and its empirical formula is C14H20ClNO2. If you sent a sample of this compound to a commercial laboratory for elemental analysis, what results would you expect for the mass percentages of carbon, hydrogen, and nitrogen?
Fructose, a sugar found in fruit, contains only carbon, oxygen, and hydrogen. It is used in ice cream to prevent a sandy texture. Complete combustion of 32.4 mg of fructose in oxygen produced 47.6 mg of CO2 and 19.4 mg of H2O. What is the empirical formula of fructose?
Coniine, the primary toxin in hemlock, contains only carbon, nitrogen, and hydrogen. When ingested, it causes paralysis and eventual death. Complete combustion of 28.7 mg of coniine produced 79.4 mg of CO2 and 34.4 mg of H2O. What is the empirical formula of the coniine?
Copper and tin alloys (bronzes) with a high arsenic content were presumably used by Bronze Age metallurgists because bronze produced from arsenic-rich ores had superior casting and working properties. The compositions of some representative bronzes of this type are as follows:
| Origin | % Composition | |
|---|---|---|
| Cu | As | |
| Dead Sea | 87.0 | 12.0 |
| Central America | 90.7 | 3.8 |
If ancient metallurgists had used the mineral As2S3 as their source of arsenic, how much As2S3 would have been required to process 100 g of cuprite (Cu2O) bronzes with these compositions?
♦ The phrase mad as a hatter refers to mental disorders caused by exposure to mercury(II) nitrate in the felt hat manufacturing trade during the 18th and 19th centuries. An even greater danger to humans, however, arises from alkyl derivatives of mercury.
Magnesium carbonate, aluminum hydroxide, and sodium bicarbonate are commonly used as antacids. Give the empirical formulas and determine the molar masses of these compounds. Based on their formulas, suggest another compound that might be an effective antacid.
♦ Nickel(II) acetate, lead(II) phosphate, zinc nitrate, and beryllium oxide have all been reported to induce cancers in experimental animals.
♦ Methane, the major component of natural gas, is found in the atmospheres of Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune.
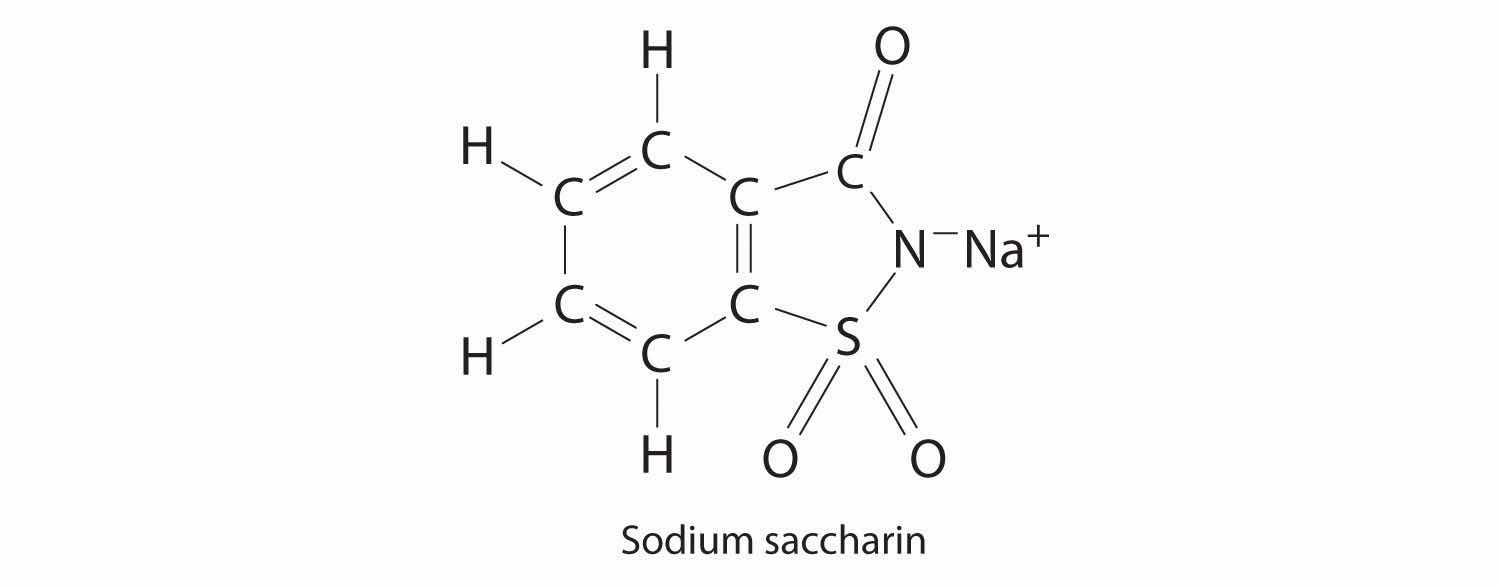
Sodium saccharin, which is approximately 500 times sweeter than sucrose, is frequently used as a sugar substitute. What are the percentages of carbon, oxygen, and sulfur in this artificial sweetener?
Lactic acid, found in sour milk, dill pickles, and sauerkraut, has the functional groups of both an alcohol and a carboxylic acid. The empirical formula for this compound is CH2O, and its molar mass is 90 g/mol. If this compound were sent to a laboratory for elemental analysis, what results would you expect for carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen content?
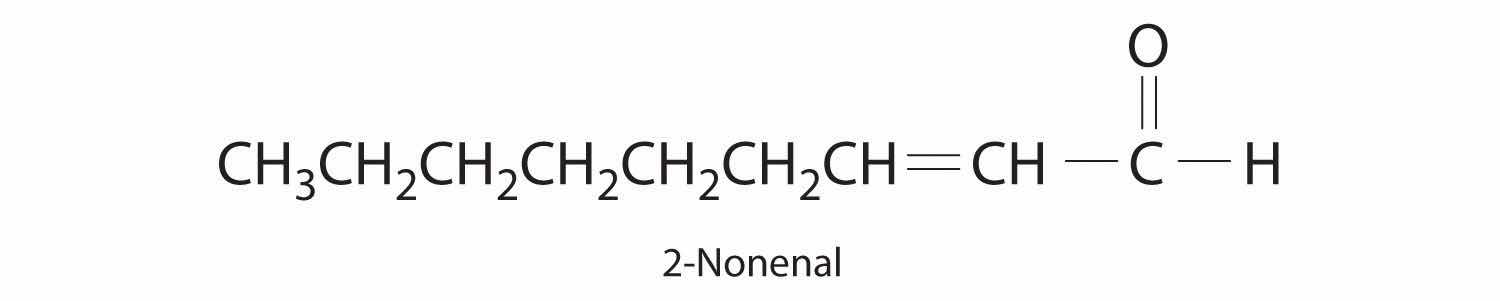
The compound 2-nonenal is a cockroach repellant that is found in cucumbers, watermelon, and carrots. Determine its molecular mass.
You have obtained a 720 mg sample of what you believe to be pure fructose, although it is possible that the sample has been contaminated with formaldehyde. Fructose and formaldehyde both have the empirical formula CH2O. Could you use the results from combustion analysis to determine whether your sample is pure?
♦ The booster rockets in the space shuttles used a mixture of aluminum metal and ammonium perchlorate for fuel. Upon ignition, this mixture can react according to the chemical equation
Al(s) + NH4ClO4(s) → Al2O3(s) + AlCl3(g) + NO(g) + H2O(g)Balance the equation and construct a table showing how to interpret this information in terms of the following:
♦ One of the byproducts of the manufacturing of soap is glycerol. In 1847, it was discovered that the reaction of glycerol with nitric acid produced nitroglycerin according to the following unbalanced chemical equation:
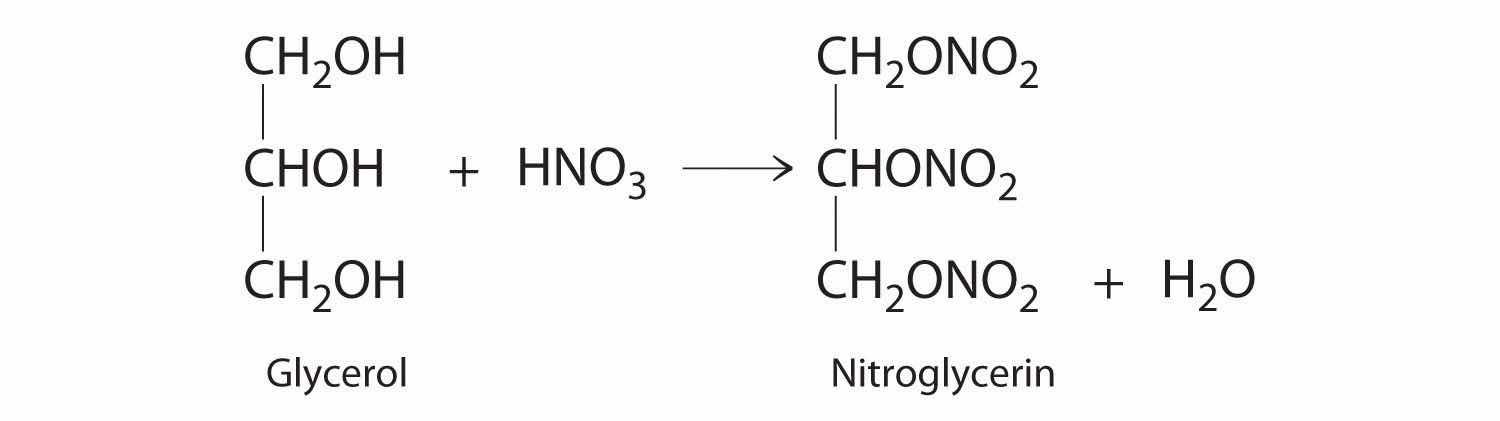
Nitroglycerine is both an explosive liquid and a blood vessel dilator that is used to treat a heart condition known as angina.
♦ A significant weathering reaction in geochemistry is hydration–dehydration. An example is the transformation of hematite (Fe2O3) to ferrihydrite (Fe10O15·9H2O) as the relative humidity of the soil approaches 100%:
Fe2O3(s) + H2O(l) → Fe10O15·9H2O(s)This reaction occurs during advanced stages of the weathering process.
♦ Hydrazine (N2H4) is used not only as a rocket fuel but also in industry to remove toxic chromates from waste water according to the following chemical equation:
4CrO42−(aq) + 3N2H4(l) + 4H2O(l) → 4Cr(OH)3(s) + 3N2(g) + 8OH−(aq)Identify the species that is oxidized and the species that is reduced. What mass of water is needed for the complete reaction of 15.0 kg of hydrazine? Write a general equation for the mass of chromium(III) hydroxide [Cr(OH)3] produced from x grams of hydrazine.
♦ Corrosion is a term for the deterioration of metals through chemical reaction with their environment. A particularly difficult problem for the archaeological chemist is the formation of CuCl, an unstable compound that is formed by the corrosion of copper and its alloys. Although copper and bronze objects can survive burial for centuries without significant deterioration, exposure to air can cause cuprous chloride to react with atmospheric oxygen to form Cu2O and cupric chloride. The cupric chloride then reacts with the free metal to produce cuprous chloride. Continued reaction of oxygen and water with cuprous chloride causes “bronze disease,” which consists of spots of a pale green, powdery deposit of [CuCl2·3Cu(OH)2·H2O] on the surface of the object that continues to grow. Using this series of reactions described, complete and balance the following equations, which together result in bronze disease:
Equation 1: ___ + O2 → ___ + ___
Equation 2: ___ + Cu → ___
Equation 3: ___ + O2 + H2O →
♦ Iron submerged in seawater will react with dissolved oxygen, but when an iron object, such as a ship, sinks into the seabed where there is little or no free oxygen, the iron remains fresh until it is brought to the surface. Even in the seabed, however, iron can react with salt water according to the following unbalanced chemical equation:
Fe(s) + NaCl(aq) + H2O(l) → FeCl2(s) + NaOH(aq) + H2(g)The ferrous chloride and water then form hydrated ferrous chloride according to the following equation:
FeCl2(s) + 2H2O(l) → FeCl2·2H2O(s)When the submerged iron object is removed from the seabed, the ferrous chloride dihydrate reacts with atmospheric moisture to form a solution that seeps outward, producing a characteristic “sweat” that may continue to emerge for many years. Oxygen from the air oxidizes the solution to ferric resulting in the formation of what is commonly referred to as rust (ferric oxide):
FeCl2(aq) + O2(g) → FeCl3(aq) + Fe2O3(s)The rust layer will continue to grow until arrested.
♦ The glass industry uses lead oxide in the production of fine crystal glass, such as crystal goblets. Lead oxide can be formed by the following reaction:
PbS(s) + O2(g) → PbO(s) + SO2(g)Balance the equation and determine what has been oxidized and what has been reduced. How many grams of sulfur dioxide would be produced from 4.0 × 103 g of lead sulfide? Discuss some potential environmental hazards that stem from this reaction.
♦ The Deacon process is one way to recover Cl2 on-site in industrial plants where the chlorination of hydrocarbons produces HCl. The reaction uses oxygen to oxidize HCl to chlorine, as shown.
HCl(g) + O2(g) → Cl2(g) + H2O(g)The reaction is frequently carried out in the presence of NO as a catalyst.
In 1834, Eilhardt Mitscherlich of the University of Berlin synthesized benzene (C6H6) by heating benzoic acid (C6H5COOH) with calcium oxide according to this balanced chemical equation:
(Heating is indicated by the symbol Δ.) How much benzene would you expect from the reaction of 16.9 g of benzoic acid and 18.4 g of calcium oxide? Which is the limiting reactant? How many grams of benzene would you expect to obtain from this reaction, assuming a 73% yield?
Aspirin (C9H8O4) is synthesized by the reaction of salicylic acid (C7H6O3) with acetic anhydride (C4H6O3) according to the following equation:
C7H6O3(s) + C4H6O3(l) → C9H8O4(s) + H2O(l)Balance the equation and find the limiting reactant given 10.0 g of acetic anhydride and 8.0 g of salicylic acid. How many grams of aspirin would you expect from this reaction, assuming an 83% yield?
♦ Hydrofluoric acid etches glass because it dissolves silicon dioxide, as represented in the following chemical equation:
SiO2(s) + HF(aq) → SiF62−(aq) + H+(aq) + H2O(l)♦ Lead sulfide and hydrogen peroxide react to form lead sulfate and water. This reaction is used to clean oil paintings that have blackened due to the reaction of the lead-based paints with atmospheric hydrogen sulfide.
♦ It has been suggested that diacetylene (C4H2, HC≡C–C≡CH) may be the ozone of the outer planets. As the largest hydrocarbon yet identified in planetary atmospheres, diacetylene shields planetary surfaces from ultraviolet radiation and is itself reactive when exposed to light. One reaction of diacetylene is an important route for the formation of higher hydrocarbons, as shown in the following chemical equations:
C4H2(g) + C4H2(g) → C8H3(g) + H(g) C8H3(g) + C4H2(g) → C10H3(g) + C2H2(g)Consider the second reaction.
♦ Glucose (C6H12O6) can be converted to ethanol and carbon dioxide using certain enzymes. As alcohol concentrations are increased, however, catalytic activity is inhibited, and alcohol production ceases.
Early spacecraft developed by the National Aeronautics and Space Administration for its manned missions used capsules that had a pure oxygen atmosphere. This practice was stopped when a spark from an electrical short in the wiring inside the capsule of the Apollo 1 spacecraft ignited its contents. The resulting explosion and fire killed the three astronauts on board within minutes. What chemical steps could have been taken to prevent this disaster?
4.31 × 1020 molecules, 7.15 × 10−4
PbCrO4
To two decimal places, the percentages are: H: 0.54%; O: 51.39%; Al: 19.50%; Si: 24.81%; Ca: 3.75%
C16H19O5N3S
C, 40.98%; O, 23.39%; S, 15.63%
140.22 amu
3Al(s) + 3NH4ClO4(s) → Al2O3(s) + AlCl3(g) + 3NO(g) + 6H2O(g)
| 3Al | 3NH4ClO4 | Al2O3 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| a. | 3 atoms | 30 atoms, 6 ions | 5 atoms |
| b. | 3 mol | 3 mol | 1 mol |
| c. | 81 g | 352 g | 102 g |
| d. | 6 × 1023 | 6 × 1023 | 2 × 1023 |
| AlCl3 | 3NO | 6H2O | |
|---|---|---|---|
| a. | 4 atoms, 1 molecule | 6 atoms, 3 molecules | 18 atoms, 6 molecules |
| b. | 1 mol | 3 mol | 6 mol |
| c. | 133 g | 90 g | 108 g |
| d. | 2 × 1023 | 6 × 1023 | 1.2 × 1022 |
Equation 1: 8CuCl + O2 → 2Cu2O + 4CuCl2
Equation 2: CuCl2 + Cu → 2CuCl Equation 3: 12CuCl + 3O2 + 8H2O → 2[CuCl2 3Cu(OH)2 H2O] + 4CuCl22PbS(s) + 3O2(g) → 2PbO(s) + 2SO2(g) Sulfur in PbS has been oxidized, and oxygen has been reduced. 1.1 × 103 g SO2 is produced. Lead is a toxic metal. Sulfur dioxide reacts with water to make acid rain.
10.8 g benzene; limiting reactant is benzoic acid; 7.9 g of benzene
The disaster occurred because organic compounds are highly flammable in a pure oxygen atmosphere. Using a mixture of 20% O2 and an inert gas such as N2 or He would have prevented the disaster.