Many random experiments include counting the number of successes in a series of a fixed number of independently repeated trials, which may result in either success or failure. The distribution of the number of successes is a binomial distribution. It is a discrete probability distribution with two parameters, traditionally indicated by
Named after Jacob Bernoulli, who studied them extensively in the 1600s, a well known example of such an experiment is the repeated tossing of a coin and counting the number of times "heads" comes up.
In a sequence of Bernoulli trials, we are often interested in the total number of successes and not in the order of their occurrence. If we let the random variable
Since the trials are independent and since the probabilities of success and failure on each trial are, respectively,
These probabilities are called binomial probabilities, and the random variable
Wind pollination
These male (a) and female (b) catkins from the goat willow tree (Salix caprea) have structures that are light and feathery to better disperse and catch the wind-blown pollen.
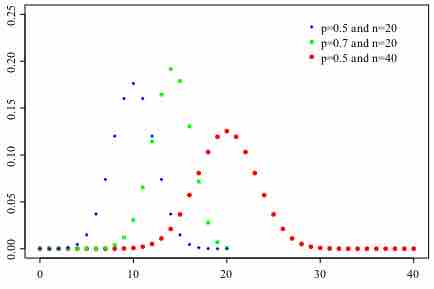
Probability Mass Function
A graph of binomial probability distributions that vary according to their corresponding values for