Government and Healthcare
Publicly funded health care is a form of healthcare financing designed to meet the cost of all or most healthcare needs from a publicly managed fund. The fund may be a not-for-profit trust, which pays out for health care according to common rules established by the members or by some other democratic form. In some countries, the fund is controlled directly by the government or by an agency of the government for the benefit of the entire population. This distinguishes it from other forms of private medical insurance. In the private model, the rights of access are subject to contractual obligations between an insurer and an insurance company. The latter seeks to make a profit by managing the flow of funds between funders and providers of health care services.
Publicly funded healthcare systems are usually financed in one of two ways: through taxation or via compulsory national health insurance. In compulsory insurance models, healthcare is financed from some combination of employees' salary deductions, employers' contributions, and possibly additional state funds. Insurance may cover other benefits as well as health. When taxation is the primary means of financing healthcare, all eligible people receive the same level of cover regardless of their financial circumstances or risk factors.
Most developed countries, with the exception of the United States, have partially or fully publicly funded health systems. Most western industrial countries have a system of social insurance based on the principle of social solidarity covers eligible people from bearing the direct burden of most healthcare expenditure, funded by taxation during their working life. Many OECD countries have implemented reforms to achieve policy goals of ensuring access to healthcare, improving the quality of healthcare and health outcomes, allocating an appropriate level of public sector other resources to healthcare, while at the same time ensuring that services are provided in a cost-efficient and cost-effective manner (microeconomic efficiency). A range of measures, such as better payment methods, has improved the microeconomic incentives facing providers. However, introducing improved incentives through a more competitive environment among providers and insurers has proved difficult.
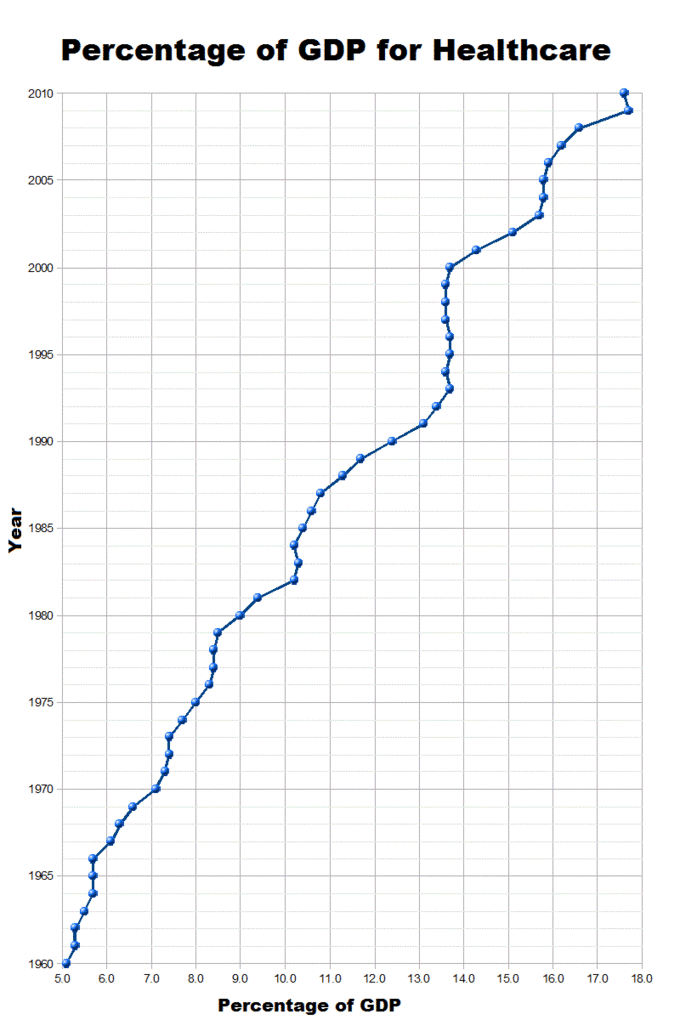
Health Costs USA GDP
Total U.S. healthcare spending from 1960 to 2007 by percent of GDP (gross domestic product)