Section 3
Inorganic Compounds
Book
Version 29
By Boundless
By Boundless
Boundless Anatomy and Physiology
Physiology
by Boundless
5 concepts
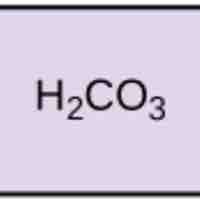
pH, Buffers, Acids, and Bases
Acids dissociate into H+ and lower pH, while bases dissociate into OH- and raise pH; buffers can absorb these excess ions to maintain pH.

Water’s Cohesive and Adhesive Properties
Cohesion allows substances to withstand rupture when placed under stress while adhesion is the attraction between water and other molecules.
Water’s High Heat Capacity
Water is able to absorb a high amount of heat before increasing in temperature, allowing humans to maintain body temperature.
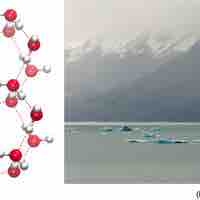
Water’s States: Gas, Liquid, and Solid
The orientation of hydrogen bonds as water changes states dictates the properties of water in its gaseous, liquid, and solid forms.
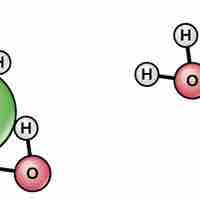
Water’s Solvent Properties
Water's polarity makes it an excellent solvent for other polar molecules and ions.