The hand contains 27 bones. Each one belongs to one of three regions: the carpals, (wrist), the metacarpals, (the palm), and the phalanges (the digits).
Carpals
The eight, irregularly shaped carpals are the most proximal bones of the hand. The carpals are often split into two rows, the proximal row containing the scaphoid, lunate, triquetrum, and pisiform, moving lateral to medial.
The scaphoid and lunate articulate with the radius, and the lunate and triquetrum articulate with the articular disk of the wrist. The pisiform carpal is a sesamoid bone, located within a tendon and is not involved in movement at the wrist.
The distal row contains the trapezium, trapezoid, capitate, and hamate, moving lateral to medial. The trapezium articulates with the scaphoid proximally and the first, thumb, and second metacarpal distally. The trapezoid articulates with the scaphoid proximally and the second metacarpal distally. The capitate articulates with the scaphoid and lunate proximally and the third and fourth metacarpal. Finally, the hamate articulates with the lunate and triquetral proximally and the fourth and fifth, little finger, metacarpals distally.
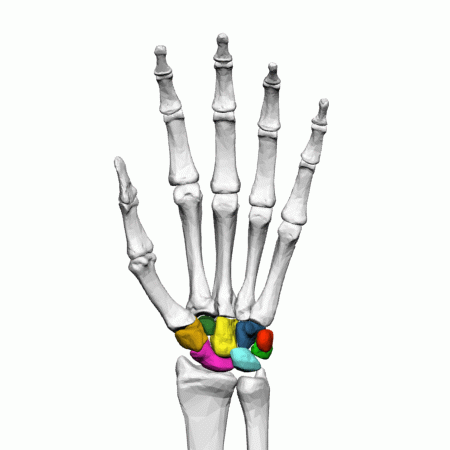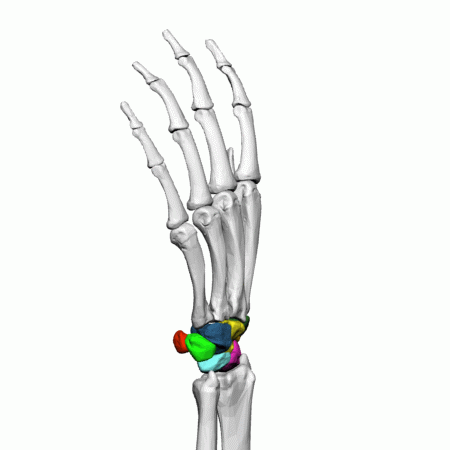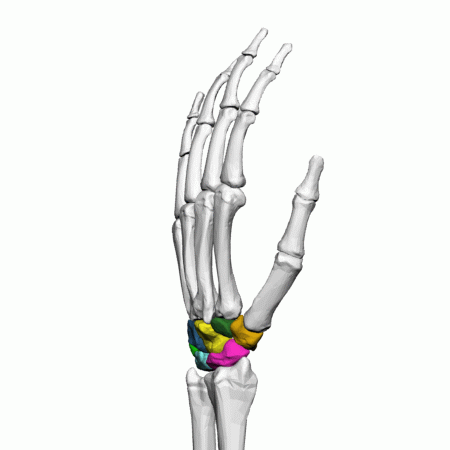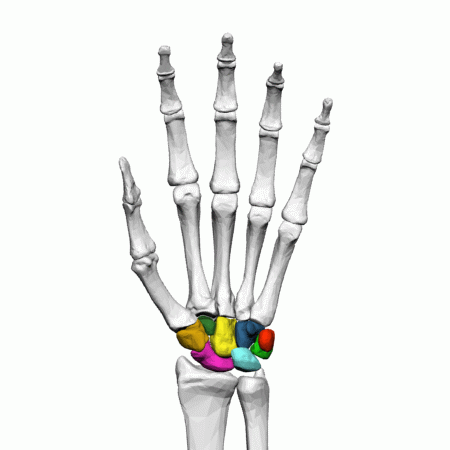
Carpals of the left hand
There are eight carpal bones in each wrist: scaphoid, lunate, triquetral, pisiform, trapezium, trapezoid, capitate, and hamate.
Metacarpals
The hand contains five metacarpal bones that articulate proximally with the carpals and distally with the proximal phalanges. They are numbered moving lateral to medial, and start with the thumb, which is metacarpal I, and end with metacarpal V, the little finger.
Each metacarpal consists of a base, shaft, and head, with the concave lateral and medial borders of the shaft allowing attachment of the interossei muscles.
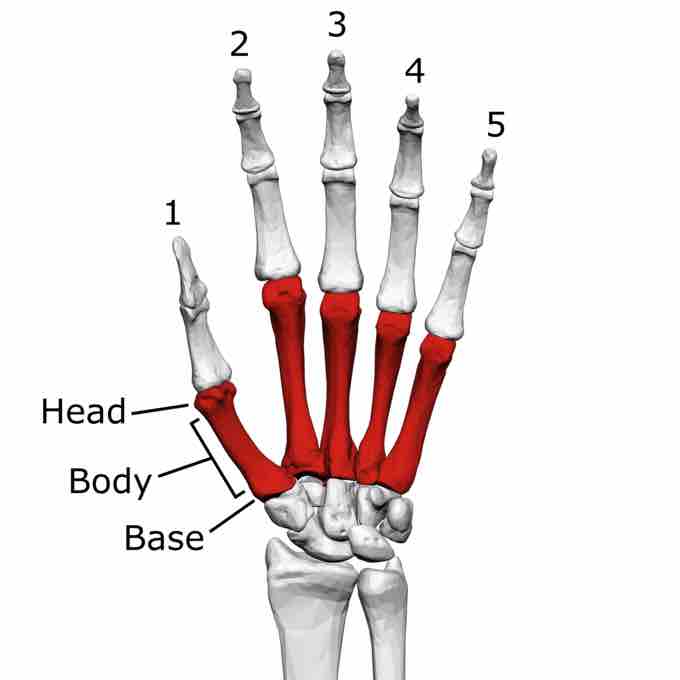
Metacarpal bones of the left hand
The metacarpals connect the carpal bones of the wrist with the phalanges (finger bones).
Phalanges
The digits are named in a similar fashion to the metacarpals, moving lateral to medial, and starting at the thumb. With the exception of the thumb, each digit contains a proximal, intermediate, and distal phalange; the thumb lacks an intermediate phalange. The length of the phalanges decreases distally.
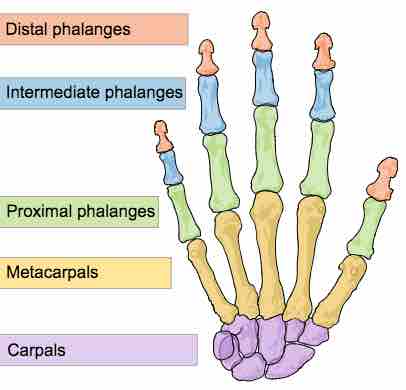
Human hand bones
Fingers are made up of proximal, intermediate, and distal phalanges. The thumb lacks an intermediate phalange.