Section 1
The Skull
By Boundless
The human skull is the part of the skeleton that supports the structures of the face and forms a cavity for the brain.
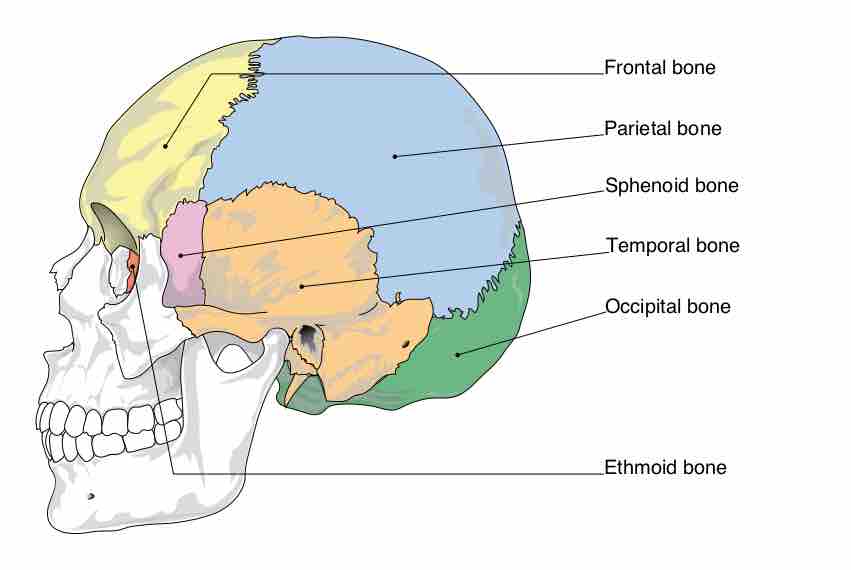
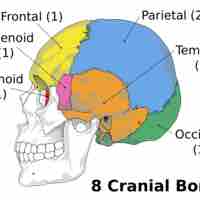
The neurocranium is comprised of eight bones: occipital, two temporal bones, two parietal bones, sphenoid, ethmoid, and the frontal bone.
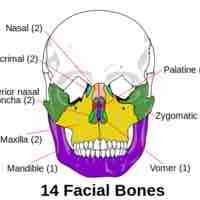
The viscerocranium (face) includes these bones: vomer, 2 inferior nasal conchae, 2 nasals, maxilla, mandible, palatine, 2 zygomatics, and 2 lacrimals.
The orbit is the cavity or socket of the skull in which the eye and its appendages are situated.
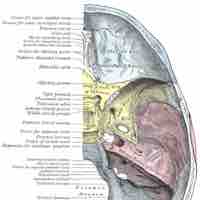
The human skull has numerous holes known as foramina through which cranial nerves, arteries, veins, and other structures pass.
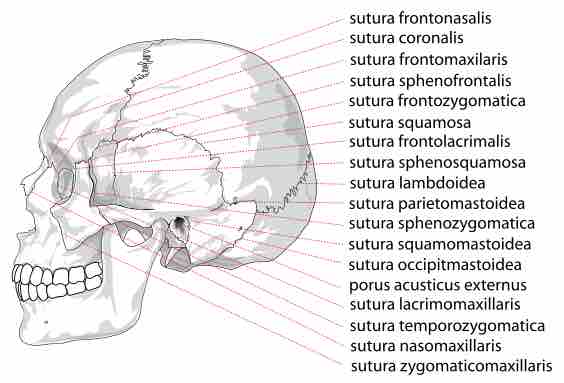
A suture is a type of fibrous joint (or synarthrosis) that only occurs in the skull (or cranium).
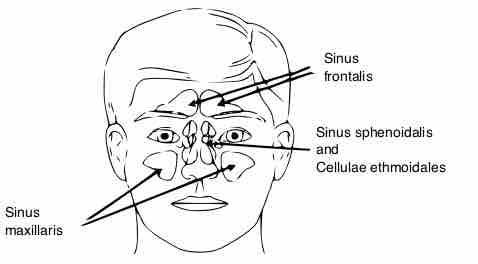
The paranasal sinuses (four, paired, air-filled spaces) surround the nasal cavity, and are located above and between the eyes, and behind the ethmoids.
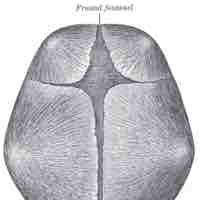
A fontanelle (or fontanel) is an anatomical feature on an infant's skull.