Concept
Version 13
Created by Boundless
The Role of the Basal Ganglia in Movement
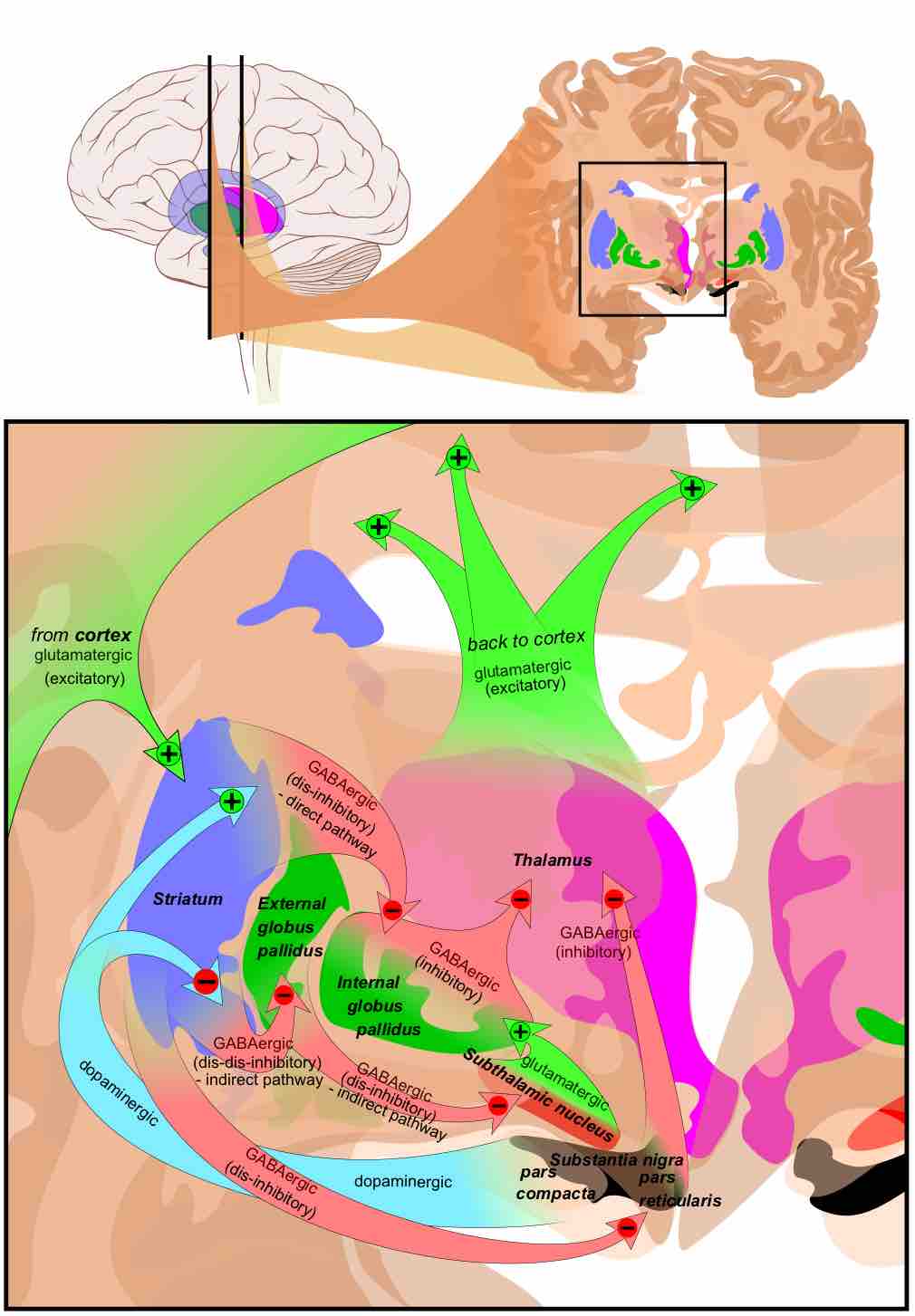
Main circuits of the basal ganglia
This diagram shows the main circuits of the basal ganglia. Two coronal slices have been superimposed to include the involved basal ganglia structures. The + and - signs at the point of the arrows indicate whether the pathway is excitatory or inhibitory, respectively, in effect. Green arrows refer to excitatory glutamatergic pathways, red arrows refer to inhibitory GABAergic pathways and turquoise arrows refer to dopaminergic pathways that are excitatory on the direct pathway and inhibitory on the indirect pathway.
This diagram shows the main circuits of the basal ganglia. Two coronal slices have been superimposed to include the involved basal ganglia structures. The + and - signs at the point of the arrows indicate whether the pathway is excitatory or inhibitory, respectively, in effect. Green arrows refer to excitatory glutamatergic pathways, red arrows refer to inhibitory GABAergic pathways and turquoise arrows refer to dopaminergic pathways that are excitatory on the direct pathway and inhibitory on the indirect pathway.
Source
Boundless vets and curates high-quality, openly licensed content from around the Internet. This particular resource used the following sources:
"Basal ganglia circuits."
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Basal_ganglia_circuits.svg
Wikipedia
CC BY-SA 3.0.