Structure and Distribution
The lumbar plexus is a nerve plexus in the lumbar region of the body that forms part of the lumbosacral plexus. It is formed by the ventral divisions of the first four lumbar nerves (L1–L4) and from contributions of the subcostal nerve (T12), which is the last thoracic nerve.
This plexus lies within the psoas major muscle. Nerves of the lumbar plexus serve the skin and the muscles of the lower abdominal wall, the thigh, and external genitals. The largest nerve of the plexus is the femoral nerve and it supplies the anterior muscles of the thigh and a part of skin distal to the inguinal ligament.
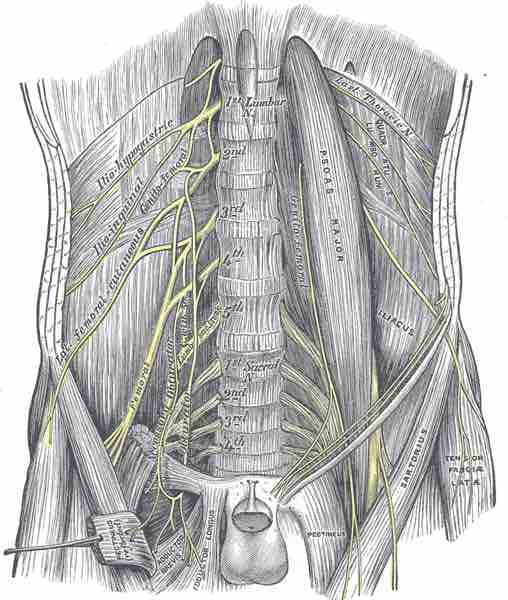
Lumbar plexus
An image of the lumbar plexus with its nerves highlighted in yellow.
Branches of the Lumbar Plexus
- Iliohypogastric nerve: Runs anterior to the psoas major on its proximal lateral border to run laterally and obliquely on the anterior side of the quadratus lumborum. Lateral to this muscle, it pierces the transversus abdominis to run above the iliac crest between that muscle and the abdominal internal oblique. It gives off several motor branches to these muscles and a sensory branch to the skin of the lateral hip. Its terminal branch then runs parallel to the inguinal ligament to exit the aponeurosis of the abdominal external oblique above the external inguinal ring, where it supplies the skin above the inguinal ligament (i.e., the hypogastric region) with the anterior cutaneous branch.
- Ilioinguinal nerve: This nerve closely follows the iliohypogastric nerve on the quadratus lumborum but then passes below it to run at the level of the iliac crest. It pierces the lateral abdominal wall and runs medially at the level of the inguinal ligament where it supplies motor branches to both the transversus abdominis and sensory branches through the external inguinal ring to the skin over the pubic symphysis and the lateral aspect of the labia majora in females, and in males, the scrotum.
- Genitofemoral nerve: Pierces the psoas major anteriorly, below the former two nerves to immediately split into two branches that run downward on the anterior side of the muscle. The lateral femoral branch is purely sensory and pierces the vascular lacuna near the saphenous hiatus and supplies the skin below the inguinal ligament. In males, the genital branch runs in the spermatic cord then sends sensory branches to the scrotal skin and supplies motor innervations to the cremaster muscle. In females, it runs in the inguinal canal together with the teres uteri ligament. It then sends sensory branches to the labia majora in females.
- Lateral cutaneous femoral nerve: Pierces the psoas major on its lateral side and runs obliquely downward below the iliac fascia. Medial to the anterior superior iliac spine, it leaves the pelvic area through the lateral muscular lacuna and enters the thigh by passing behind the lateral end of the inguinal ligament. In the thigh, it briefly passes under the fascia lata before it breaches the fascia and supplies the skin of the anterior thigh.
- Obturator nerve: Leaves the lumbar plexus and descends behind the psoas major on its medial side, follows the linea terminalis into the lesser pelvis, then finally leaves the pelvic area through the obturator canal. In the thigh, it sends motor branches to obturator externus before dividing into an anterior and a posterior branch, both of which continue distally. These branches are separated by the adductor brevis and supply all thigh adductors with motor innervations. The anterior branch contributes a terminal, sensory branch that passes along the anterior border of gracilis and supplies the skin on the medial, distal part of the thigh.
- Femoral nerve: This is the largest and longest of the plexus' nerves. It gives motor innervation to iliopsoas, pectineus, sartorius, and quadriceps femoris, and sensory innervation to the anterior thigh, posterior lower leg, and hindfoot. In the pelvic area, it runs in a groove between the psoas major and iliacus muscles and gives branches to both. It exits the pelvis through the medial aspect of the muscular lacuna. In the thigh, it divides into numerous sensory and muscular branches and the saphenous nerve, its long sensory terminal branch that continues down to the foot.
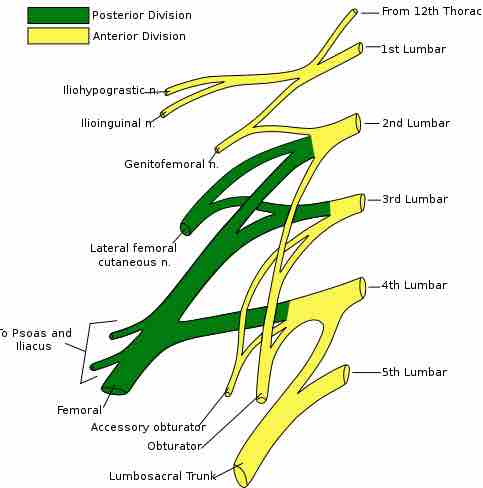
Lumbar plexus
Schematic of the lumbar plexus.