A burn is a type of injury to flesh caused by heat, electricity, chemicals, light, radiation, or friction. Most burns affect only the first two layers of the skin, the epidermis and dermis. Burns are classified by severity, surface area involvement, and depth of injury. In the latter system, burns are classified as first, second, third, or fourth degree burns based on the depth of injury to the dermis. Burns are also classified as major or minor depending on a combination of factors including age, thickness of burns, surface area of the body involved, and the presence of inhalation injury.
Types of Burns
First degree burns are limited to the epidermis. Second degree burns extend into the superficial papillary dermis. Third degree burns extend through the entire dermis. Fourth degree burns involve all the skin layers as well as the underlying muscle and bone.
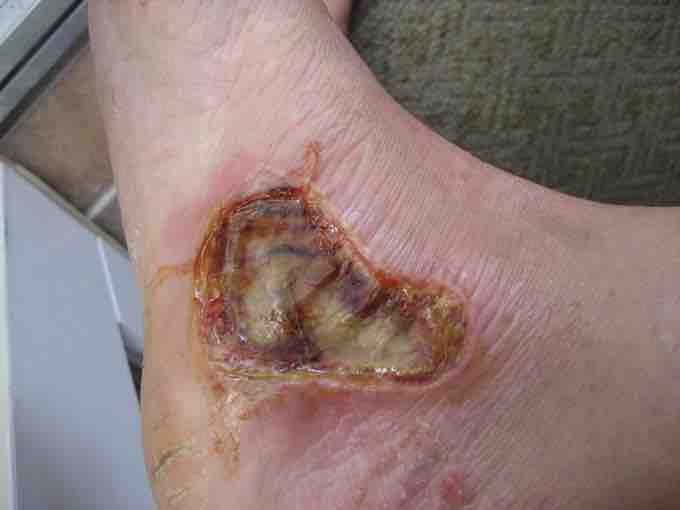
Fourth Degree Burn
Eight day old fourth degree burn on arch of foot caused by motorcycle muffler.
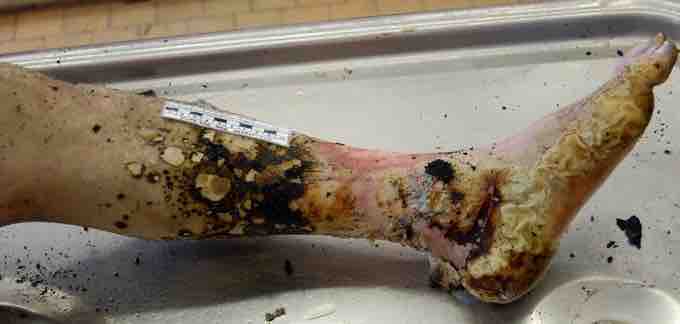
Third Degree Burn
Third degree burns to the lower leg with partial tissue charring.
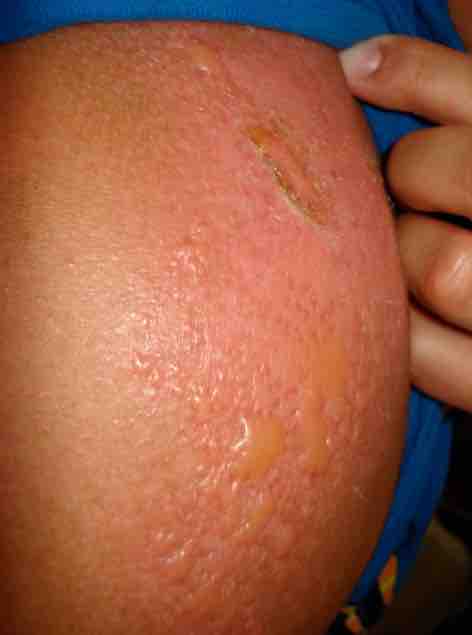
Second Degree Burn
Serious sunburn is an example of a second degree burn.
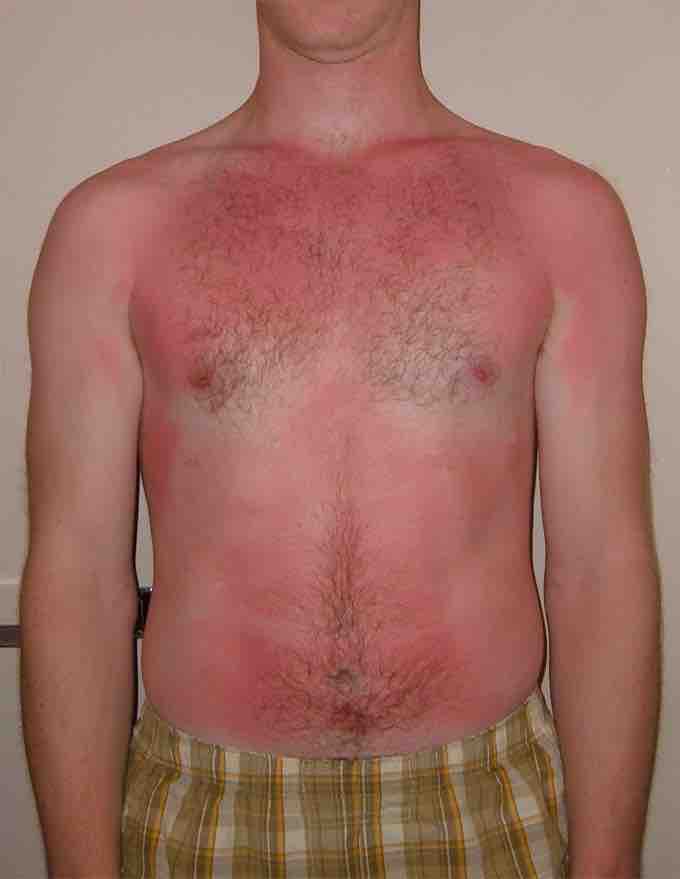
First Degree Burn
Mild sunburn is an example of a first degree burn.
Consequences of Burns
While large burns can be fatal, modern treatments developed in the last 60 years have significantly improved the prognosis of such burns, especially in children and young adults. In the United States, approximately four out of every 100 people to suffer burns will die from their injuries. The majority of these fatalities occur either at the scene or on the way to hospital.
Infection is a major complication of burns. Infection is likely caused by impaired resistance from disruption of the skin's mechanical integrity by the burn and generalized immune suppression. As a deep burn starts to heal, the skin barrier is replaced by eschar. This moist, protein-rich avascular environment encourages microbial growth. Migration of immune cells is hampered by destruction of the vasculature (blood vessels), and there is a release of inflammatory intermediaries that impede the immune response. Eschar also restricts distribution of systemically administered antibiotics because of its avascularity.