Carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) is an entrapment median neuropathy, causing paresthesia, pain, numbness, and other symptoms in the distribution of the median nerve due to its compression at the wrist in the carpal tunnel. The pathophysiology is not completely understood but can be attributed to the compression of the median nerve traveling through the carpal tunnel.
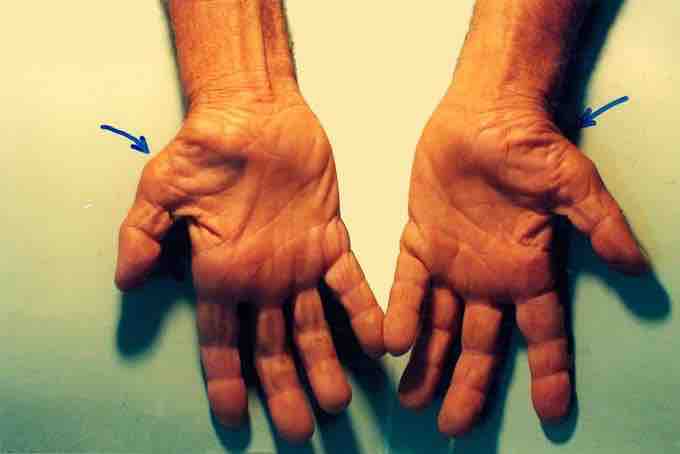
Untreated Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
Patients with CTS experience numbness, tingling, or burning sensations in the thumb and fingers, in particular the index, middle fingers, and radial half of the ring fingers, which are innervated by the median nerve. Less-specific symptoms may include pain in the wrists or hands and loss of grip strength.
Symptoms of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
Patients with CTS experience numbness, tingling, or burning sensations in the thumb and fingers, in particular the index, middle fingers, and radial half of the ring fingers, which are innervated by the median nerve. Less-specific symptoms may include pain in the wrists or hands and loss of grip strength. The numbness often occurs at night, with the hypothesis that the wrists are held flexed during sleep. It can be relieved by wearing a wrist splint that prevents flexion. Long-standing CTS leads to permanent nerve damage with constant numbness, atrophy of some of the muscles of the thenar eminence, and weakness of palmar abduction. Pain in carpal tunnel syndrome is primarily numbness that is so intense that it wakes one from sleep. Pain in electrophysiologically verified CTS is associated with misinterpretation of nociception and depression. Palliative treatments for CTS include use of night splints and corticosteroid injection. The only scientifically established disease modifying treatment is surgery to cut the transverse carpal ligament.
Causes of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
Most cases of CTS are of unknown causes, or idiopathic. Carpal tunnel syndrome can be associated with any condition that causes pressure on the median nerve at the wrist. A variety of patient factors can lead to CTS, including heredity, size of the carpal tunnel, associated local and systematic diseases, and certain habits. Some common conditions that can lead to CTS include obesity, oral contraceptives, hypothyroidism, arthritis, diabetes, and trauma. Carpal tunnel syndrome is also associated with repetitive activities of the hand and wrist, in particular with a combination of forceful and repetitive activities. Non-traumatic causes generally happen over a period of time, and are not triggered by one certain event. Many of these factors are manifestations of physiologic aging.
Treatments of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
Treatments of CTS include immobilization of the wrist, steroid injection, activity modification, physical therapy, massage, medication, or surgery to release the transverse carpal ligament.