What is Projectile Motion?
Projectile motion is a form of motion where an object moves in a bilaterally symmetrical, parabolic path. The path that the object follows is called its trajectory. Projectile motion only occurs when there is one force applied at the beginning on the trajectory, after which the only interference is from gravity. In this atom we are going to discuss what the various components of an object in projectile motion are, we will discuss the basic equations that go along with them in another atom, "Basic Equations and Parabolic Path"
Key Components of Projectile Motion:
Time of Flight, T:
The time of flight of a projectile motion is exactly what it sounds like. It is the time from when the object is projected to the time it reaches the surface. The time of flight depends on the initial velocity of the object and the angle of the projection,
Symmetry:
All projectile motion happens in a bilaterally symmetrical path, as long as the point of projection and return occur along the same horizontal surface. Bilateral symmetry means that the motion is symmetrical in the vertical plane. If you were to draw a straight vertical line from the maximum height of the trajectory, it would mirror itself along this line.
Maximum Height, H:
The maximum height of a object in a projectile trajectory occurs when the vertical component of velocity,
Range of the Projectile, R:
The range of the projectile is the displacement in the horizontal direction. There is no acceleration in this direction since gravity only acts vertically. shows the line of range. Like time of flight and maximum height, the range of the projectile is a function of initial speed.
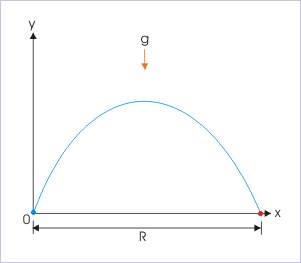
Range
The range of a projectile motion, as seen in this image, is independent of the forces of gravity.