Newton's laws of motion describe the relationship between the forces acting on a body and its motion due to those forces. For example, if your car breaks down and you need to push it, you must exert a force with your hands on the car in order for it to move. The laws of motion will tell you how quickly the car will move from your pushing. There are three laws of motion:
First law: If an object experiences no net force, then its velocity is constant: the object is either at rest (if its velocity is zero), or it moves in a straight line with constant speed (if its velocity is nonzero). For example, if you don't push the car (no force), then it doesn't move.
Second law: The acceleration
For example, if you push the car with a greater force it will accelerate more. But, if the car is more massive
Third law: When a first body exerts a force
In the figure below there are some practical examples illustrating the concept of force:
- Strain: by using a machine known as pulley you can easily raise or lower a massive body
- Gravitational Force: a massive body is attracted downward by the gravitational force practiced by the Earth
- Magnetic Force: two magnets repel each other when the same poles get closer
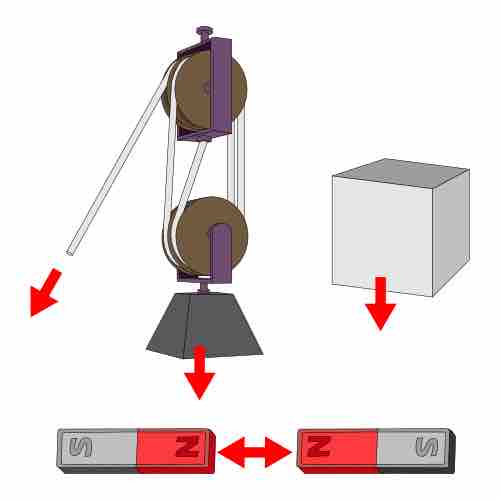
Examples of Force
Some situations in which forces are at play.