Contact Force on an Incline
The incline plane has two contact or interface surfaces. One is the incline surface, where the block is placed and the other is the base of the incline, which is in contact with the surface underneath. The motion of the block, therefore, may depend on the motion of the incline itself.
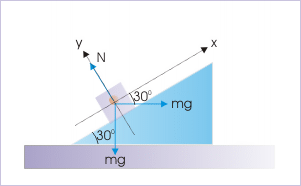
Block and incline system
Forces on the block
When on an incline, calculating the force of friction is different than when the object is on a level surface. Recall that the force of friction depends on both the coefficient of friction and the normal force.
As always, the frictional force resists motion. If the block is being pushed up the incline the friction force points down the incline. If the block is being pulled down the incline, the friction force will hold the block up.
Equilibrium of Forces on an Incline
When not acted on by any other forces, only by gravity and friction, the frictional force will resist the tendency of the block to slide down the incline. If the frictional force is equal to the gravitational force the block will not slide down the incline. The block is said to be in equilibrium since the sum of the forces on it is 0.
Gravitational force down an incline is given by
Where