Relativistic Addition of Velocities
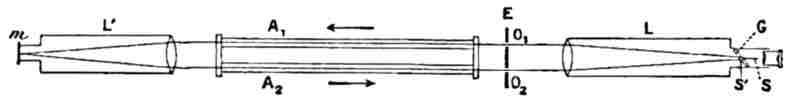
Setup of the Fizeau Experiment
A light ray emanating from the source S' is reflected by a beam splitter G and is collimated into a parallel beam by lens L. After passing the slits O1 and O2, two rays of light travel through the tubes A1 and A2, through which water is streaming back and forth as shown by the arrows. The rays reflect off a mirror m at the focus of lens L', so that one ray always propagates in the same direction as the water stream, and the other ray opposite to the direction of the water stream. After passing back and forth through the tubes, both rays unite at S, where they produce interference fringes that can be visualized through the illustrated eyepiece. The interference pattern can be analyzed to determine the speed of light traveling along each leg of the tube.
Source
Boundless vets and curates high-quality, openly licensed content from around the Internet. This particular resource used the following sources: