The decibel, dB, is commonly used to quantify sound levels, although it is not a unit of sound, but a unit of pressure. The decibel is a logarithmic unit that indicates the ratio if a physical quantity to a reference level. It is one tenth of a Bel, which was named after the inventor of the telephone, Alexander Graham Bell. The word decibell comes from the prefix, deci, that is 1/10 of the word it precedes For more information on how to convert units, refer to the unit conversion atom. Although the decibel can be used to talk about a number of different subjects, in this atom we are going to cover its use in acoustics and sound level.
In acoustics, the decibel is quantified relative to a reference which has been set at a sound pressure level of 20 micropascals, and is called a 0 dB. This reference level is a typical threshold of human hearing perception. The following equation is used to calculate the sound pressure level, or amplitude:
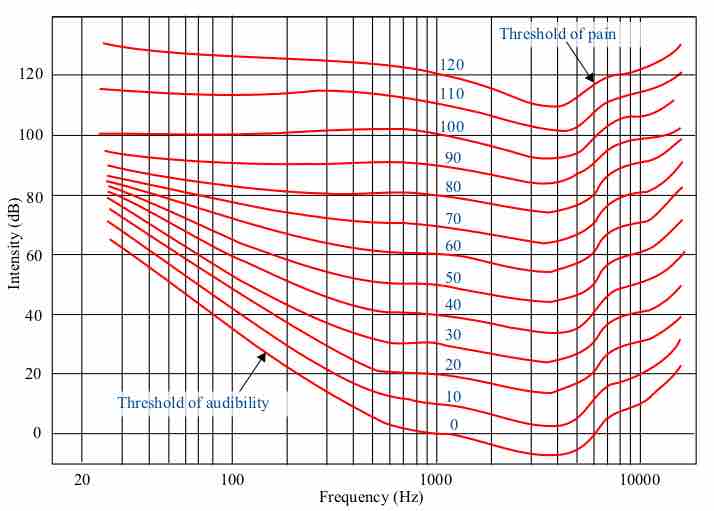
The Fletcher Munson Chart
The Fletcher-Munson equal-loudness contours. Phons are labelled in blue