Concept
Version 7
Created by Boundless
Gyroscopes
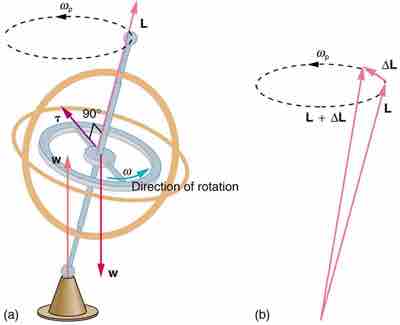
Gyroscopes
As seen in figure (a), the forces on a spinning gyroscope are its weight and the supporting force from the stand. These forces create a horizontal torque on the gyroscope, which create a change in angular momentum ΔL that is also horizontal. In figure (b), ΔL and L add to produce a new angular momentum with the same magnitude, but different direction, so that the gyroscope precesses in the direction shown instead of falling over.
Source
Boundless vets and curates high-quality, openly licensed content from around the Internet. This particular resource used the following sources:
"OpenStax College, College Physics. November 17, 2012."
http://cnx.org/content/m42184/latest/?collection=col11406/1.7
OpenStax CNX
CC BY 3.0.