In physics, acceleration is the rate at which the velocity of a body changes with time. It is a vector quantity with both magnitude and direction. Acceleration is accompanied by a force, as described by Newton's Second Law; the force, as a vector, is the product of the mass of the object being accelerated and the acceleration (vector), or
Acceleration is a vector that points in the same direction as the change in velocity, though it may not always be in the direction of motion. For example, when an object slows down, or decelerating, its acceleration is in the opposite direction of its motion.
The motion of an object can be depicted graphically by plotting the position of an object over time. This distance-time graph can be used to create another graph that shows changes in velocity over time. Because acceleration is velocity in
is a graph of an object's position over time. This graph is similar to the motion of a car. In the beginning, the object's position changes slowly as it gains speed. In the middle, the speed is constant and the position changes at a constant rate. As it slows down toward the end, the position changes more slowly. From this graph, we can derive a velocity vs time graph.
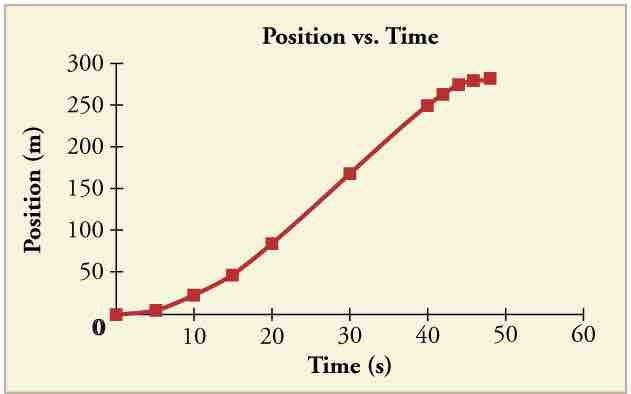
Position vs Time Graph
Notice that the object's position changes slowly at the beginning of the journey, then more and more quickly as it picks up speed. Its position then changes more slowly as it slows down at the end of the journey. In the middle of the journey, while the velocity remains constant, the position changes at a constant rate.
This shows the velocity of the object over time. The object's velocity increases in the beginning as it accelerates at the beginning, then remains constant in the middle before it slows down toward the end. Notice that this graph is a representation of the slope of the previous position vs time graph. From this graph, we can further derive an acceleration vs time graph.
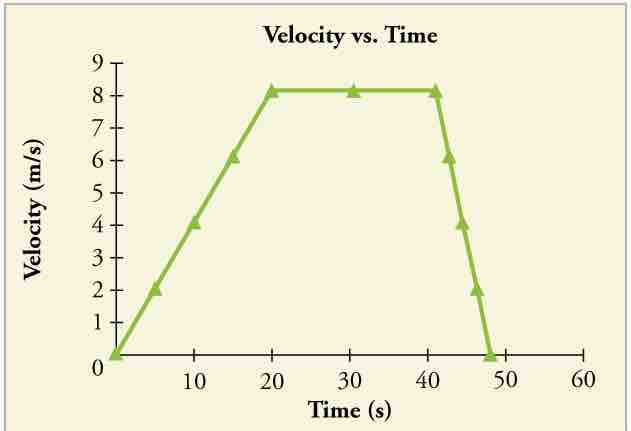
Velocity vs Time
The object's velocity increases as it accelerates at the beginning of the journey. It remains the same in the middle of the journey (where there is no acceleration). It decreases as the object decelerates at the end of the journey.
To do this, we would also plot the slope of the velocity vs time graph. In this graph, the acceleration is constant in the three different stages of motion. As we noted earlier, the object is increasing speed and changing positions slowly in the beginning. The acceleration graph shows that the object was increasing at a positive constant acceleration during this time. In the middle, when the object was changing position at a constant velocity, the acceleration was 0. This is because the object is no longer changing its velocity and is moving at a constant rate. Towards the end of the motion, the object slows down. This is depicted as a negative value on the acceleration graph. Note that in this example, the motion of the object is still forward (positive), but since it is decelerating, the acceleration is negative.
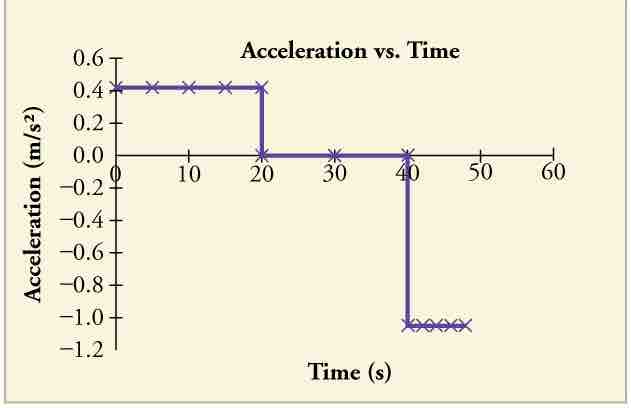
Acceleration vs Time Graph
The object has positive acceleration as it speeds up at the beginning of the journey. It has no acceleration as it travels at constant velocity in the middle of the journey. Its acceleration is negative as it slows down at the end of the journey.