The flow rate of a fluid is the volume of fluid which passes through a surface in a given unit of time . It is usually represented by the symbol Q.
Flow Rate
Volumetric flow rate is defined as
where Q is the flow rate, v is the velocity of the fluid, and a is the area of the cross section of the space the fluid is moving through. Volumetric flow rate can also be found with
where Q is the flow rate, V is the Volume of fluid, and t is elapsed time.
Continuity
The equation of continuity works under the assumption that the flow in will equal the flow out. This can be useful to solve for many properties of the fluid and its motion :
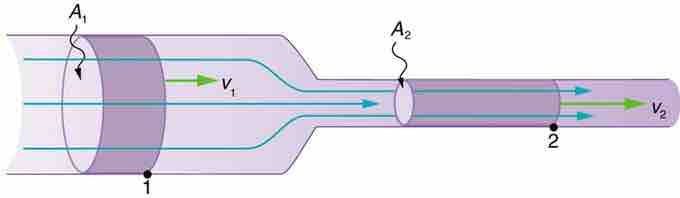
Flow in = Flow out
Using the known properties of a fluid in one condition, we can use the continuity equation to solve for the properties of the same fluid under other conditions.
This can be expressed in many ways, for example:
Applying the Continuity Equation
You can observe the continuity equation's effect in a garden hose. The water flows through the hose and when it reaches the narrower nozzle, the velocity of the water increases. Speed increases when cross-sectional area decreases, and speed decreases when cross-sectional area increases. This is a consequence of the continuity equation. If the flow Q is held constant, when the area A decreases, the velocity v must increase proportionally. For example, if the nozzle of the hose is half the area of the hose, the velocity must double to maintain the continuous flow.