Concept
Version 8
Created by Boundless
Molecular Transport Phenomena
Diffusion
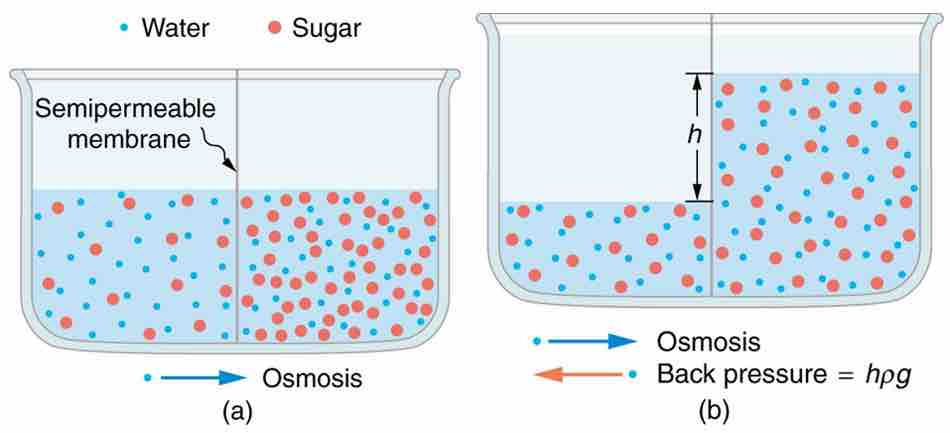
(a) Two sugar-water solutions of different concentrations, separated by a semipermeable membrane that passes water but not sugar. Osmosis will be to the right, since water is less concentrated there. (b) The fluid level rises until the back pressure ρgh equals the relative osmotic pressure; then, the net transfer of water is zero.
Source
Boundless vets and curates high-quality, openly licensed content from around the Internet. This particular resource used the following sources:
"OpenStax College, Molecular Transport Phenomena: Diffusion, Osmosis, and Related Processes. February 16, 2013."
http://cnx.org/content/m42212/latest/
OpenStax CNX
CC BY 3.0.