Phase Angle
Impedance is an AC (alternating current) analogue to resistance in a DC circuit. As we studied in a previously Atom ("Impedance"), current, voltage and impedance in an RC circuit are related by an AC version of Ohm's law:
In a series RC circuit connected to an AC voltage source as shown in , conservation of charge requires current be the same in each part of the circuit at all times. Therefore we can say: the currents in the resistor and capacitor are equal and in phase. (We will represent instantaneous current as i(t). )
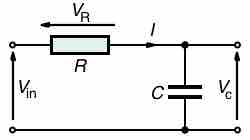
Series RC Circuit
Series RC circuit.
On the other hand, because the total voltage should be equal to the sum of voltages on the resistor and capacitor, so we have:
where
we notice that voltage
For R=0,
Power Factor
Because voltage and current are out of phase, power dissipated by the circuit is not equal to: (peak voltage) times (peak current). The fact that source voltage and current are out of phase affects the power delivered to the circuit. It can be shown that the average power is IrmsVrmscosϕ, where Irms and Vrms are the root mean square (rms) averages of the current and voltage, respectively. For this reason, cosϕ is called the power factor, which can range from 0 to 1.